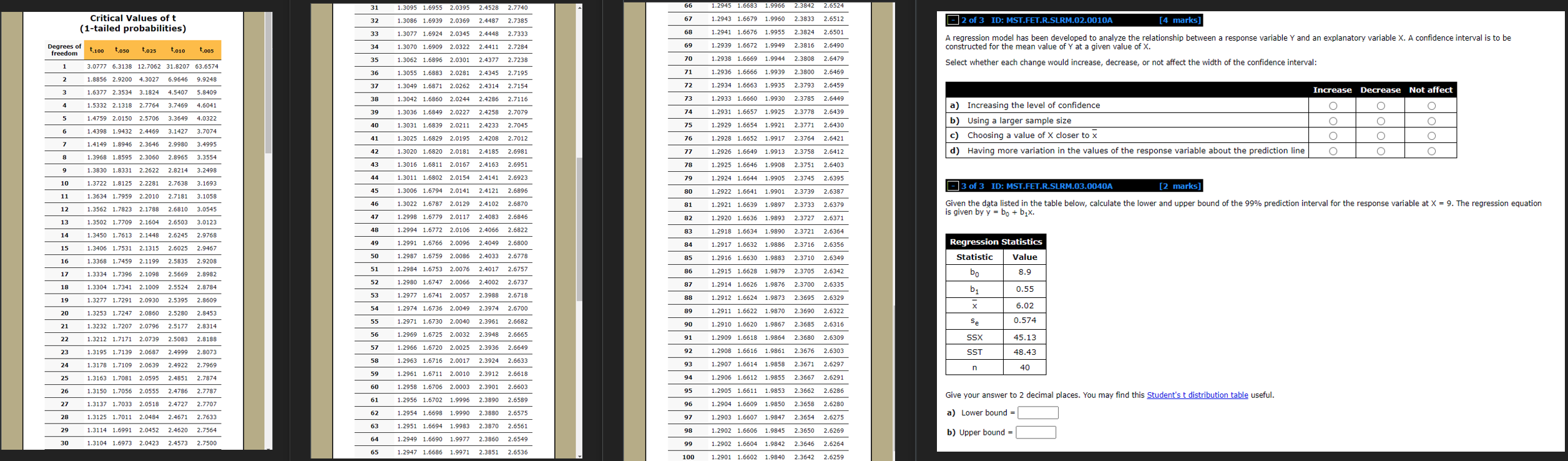
1.3095 1.6955 2.0395 2.4528 2.7740 1.2945 1. 1.9966 Critical Values of t 1.3086 1.6939 2.0369 2.4487 2.7385 67 1.2943 1.6679 1.9960 2.3833 2.6512 1-tailed probabilities) 32 -2 of 3 ID: MST.FET.R.SLRM.02.0010A [4 marks] 33 1.3077 1.6924 2.0345 2.4448 2.7333 68 1.2941 1.6676 1.9955 2.3824 2.6501 A regression model has been developed to analyze the relationship between a response variable Y and an explanatory variable X. A confidence interval is to be freedom t,100 t,oso t.025 t,010 t,o05 34 1.3070 1.6909 2.0322 2.4411 2.7284 69 1.2939 1.6672 1.9949 2.3816 2.6490 constructed for the mean value of Y at a given value of X. 35 70 3.0777 6.3138 12.7062 31.8207 63.6574 1.3062 1.6896 2.0301 2.4377 2.7238 1.2938 1.6669 1.9944 2.3808 2.6479 36 1.8856 2.9200 4.3027 6.9646 9.9248 71 Select whether each change would increase, decrease, or not affect the width of the confidence interval: 1.3055 1.6883 2.0281 2.4345 2.7195 1.2936 1.6666 1.9939 2.3800 2.6469 1.6377 2.3534 3.1824 4.5407 5.8409 1.3049 1.6871 2.0262 2.4314 2.7154 72 1.2934 1.6663 1.9935 2.3793 2.6459 1.5332 2.1318 2.7764 3.7469 4.6041 1.3042 1.6860 2.0244 2.4286 2.7116 73 1.2933 1.6660 1.9930 2.3785 2.6449 Increase Decrease Not affect 39 1.4759 2.0150 2.5706 3.3649 4.0322 1.3036 1.6849 2.0227 2.4258 2.7079 74 1.2931 1.6657 1.9925 2.3778 2.6439 a) Increasing the level of confidence O O O 1.4398 1.9432 2.4469 3.1427 3.7074 40 1.3031 1.6839 2.0211 2.4233 2.7045 75 1.2929 1.6654 1.9921 2.3771 2.6430 b) Using a larger sample size O O O 1.4149 1.8946 2.3646 2.9980 3.4995 41 1.3025 1.6829 2.0195 2.4208 2.7012 76 1.2928 1.6652 1.9917 2.3764 2.6421 c) Choosing a value of X closer to x O 1.3968 1.8595 2.3060 2.8965 3.3554 1.3020 1.6820 2.0181 2.4185 2.6981 77 1.2926 1.6649 1.9913 2.3758 2.6412 d) Having more variation in the values of the response variable about the prediction line O O 1.3830 1.8331 2.2622 2.8214 3.2498 43 1.3016 1.6811 2.0167 2.4163 2.6951 78 1.2925 1.6646 1.9 2.3751 10 1.3722 1.8125 2.2281 2.7638 3.1693 44 1.3011 1.6802 2.0154 2.4141 2.6923 79 1.2924 1.6644 1.9905 2.3745 2.6395 11 1.3634 1.7959 2.2010 2.7181 3.1058 45 1.3006 1.6794 2.0141 2.4121 2.6896 1.2922 1.6641 1.9901 2.3739 2.6387 3 of 3 ID: MST.FET.R.SLRM.03.0040A [2 marks] 1.3562 1.7823 2.1788 2.6810 3.0545 46 1.3022 1.6787 2.0129 2.4102 2.6870 81 1.2921 1.6639 1.9897 2.3733 2.6379 data listed in the table below, calculate the lower and upper bound of the 99% prediction interval for the response variable at X = 9. The regression equation 13 1.3502 1.7709 2.1604 2.6503 3.0123 47 1.2998 1.6779 2.0117 2.4083 2.6846 82 1.2920 1.6636 1.9893 2.3727 2.6371 s given by y = bo + bix. 1.3450 1.7613 2.1448 2.6245 2.9768 48 1.2994 1.6772 2.0106 2.4066 2.6822 83 1.2918 1.6634 1.9890 2.3721 2.6364 15 1.3406 1.7531 2.1315 2.6025 2.9467 1.2991 1.6766 2.0096 2.4049 2.6800 84 1.2917 1.6632 1.9836 2.3716 2.6356 Regression Statistics 16 1.3368 1.7459 2.1199 2.5835 2.9208 SO 1.2987 1.6759 2.0086 2.4033 2.6778 85 1.2916 1.6630 1.9883 2.3710 2.6349 Statistic Value 17 1.3334 1.7396 2.1098 2.5669 2.8982 51 1.2984 1.6753 2.0076 2.4017 2.6757 86 1.2915 1.6628 1.9879 2.3705 2.6342 8.9 18 1.3304 1.7341 2.1009 2.5524 2.8784 52 1.2980 1.6747 2.0066 2.4002 2.6737 87 1.2914 1.6626 1.9876 2.3700 2.6335 b1 0.55 19 1.3277 1.7291 2.0930 2.5395 2.8609 53 1.2977 1.6741 2.0057 2.3988 2.6718 88 1.2912 1.6624 1.9873 2.3695 2.6329 20 1.3253 1.7247 2.0860 2.5280 2.8453 54 1.2974 1.6736 2.0049 2.3974 2.6700 89 1.2911 1.6622 1.9870 2.3690 2.6322 6.02 21 1.3232 1.7207 2.0796 2.5177 2.8314 55 1.2971 1.6730 2.0040 2.3961 2.6682 90 1.2910 1.6620 1.9867 35 2.6316 Se 0.574 22 1.3212 1.7171 2.0739 2.5083 2.8188 56 1.2969 1.6725 2.0032 2.3948 2.6665 91 1.2909 1.6618 1.9864 2.3680 2.6309 SSX 45.13 23 1.3195 1.7139 2.0687 2.4999 2.8073 57 1.2966 1.6720 2.0025 2.3936 2.6649 92 58 1.2908 1.6616 1.9861 2.3676 2.6303 SST 48.43 24 1.3178 1.7109 2.0639 2.4922 2.7969 1.2963 1.6716 2.0017 2.3924 2.6633 93 1.2907 1.6614 1.9858 2.3671 2.6297 n 25 1.2961 1.6711 2.0010 2.3912 2.6618 40 1.3163 1.7081 2.0595 2.4851 2.7874 59 94 1.3150 1.7056 2.0555 2.4786 2.7787 60 1.2906 1.6612 1.9855 2.3667 2.6291 26 1.2958 1.6706 2.0003 2.3901 2.6603 95 1.2905 1.6611 1.9853 2.3662 2.6286 27 1.3137 1.7033 2.0518 2.4727 2.7707 61 1.2956 1.6702 1.9996 2.3890 2.6589 Give your answer to 2 decimal places. You may find this Student's t distribution table useful. 62 96 1.2904 1.6609 1.9850 2.3658 2.6280 28 1.3125 1.7011 2.0484 2.4671 2.7633 1.2954 1.6698 1.9990 2.3880 2.6575 97 1.2903 1.6607 1.9847 2.3654 2.6275 a) Lower bound = 29 1.3114 1.6991 2.0452 2.4620 2.7564 63 1.2951 1.6694 1.9983 2.3870 2.6561 98 30 1.3104 1.6973 2.0423 2.4573 2.7500 64 1.2902 1.6606 1.9845 2.3650 2.6269 1.2949 1.6690 1.9977 2.3860 2.6549 b) Upper bound = 99 65 1.2947 1.6686 1.9971 2. 1.2902 1.6604 1.9842 2.3646 2.6264 1 2.6536