Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
13-1 excel Preparing Common-Size Statements and Financial Ratios for Creditors [LO1 - CC1; LO2-CC3, 4] CHECK FIGURES (1e) Inventory turnover this year: 5.0 times (1g)
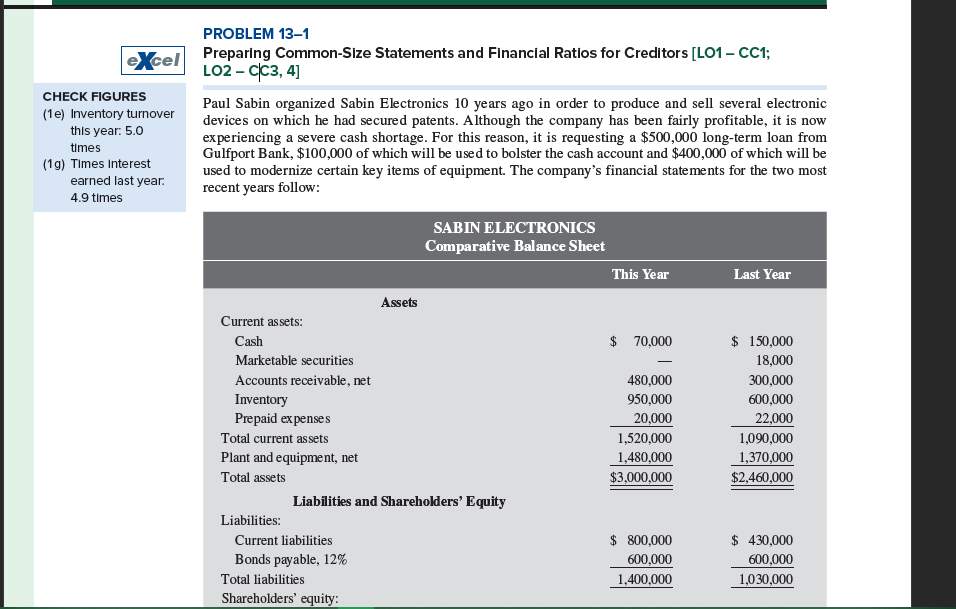
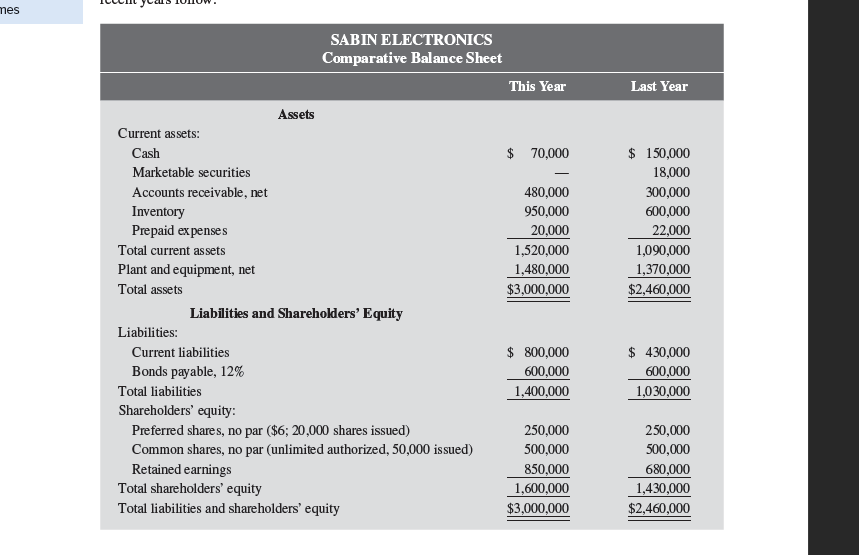
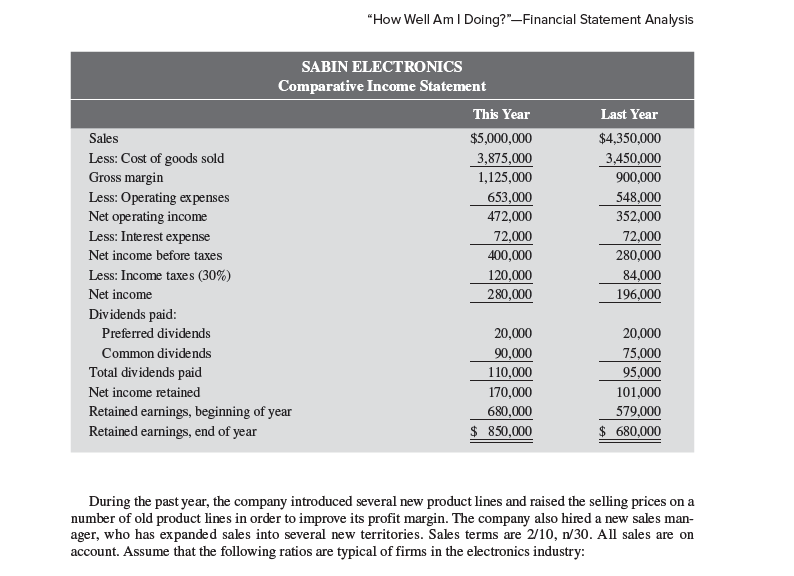

 13-1 excel Preparing Common-Size Statements and Financial Ratios for Creditors [LO1 - CC1; LO2-CC3, 4] CHECK FIGURES (1e) Inventory turnover this year: 5.0 times (1g) Times Interest earned last year: 4.9 times Paul Sabin organized Sabin Electronics 10 years ago in order to produce and sell several electronic devices on which he had secured patents. Although the company has been fairly profitable, it is now experiencing a severe cash shortage. For this reason, it is requesting a $500,000 long-term loan from Gulfport Bank, $100,000 of which will be used to bolster the cash account and $400,000 of which will be used to modernize certain key items of equipment. The company's financial statements for the two most recent years follow: Current assets: Assets SABIN ELECTRONICS Comparative Balance Sheet This Year Last Year Cash Marketable securities Accounts receivable, net Inventory Prepaid expenses Total current assets Plant and equipment, net Total assets Liabilities and Shareholders' Equity Liabilities: Current liabilities Bonds payable, 12% Total liabilities Shareholders' equity: $ 70,000 $ 150,000 - 18,000 480,000 300,000 950,000 600,000 20,000 22,000 1,520,000 1,090,000 1,480,000 $3,000,000 1,370,000 $2,460,000 $ 800,000 600,000 1,400,000 $ 430,000 600,000 1,030,000 mes Assets SABIN ELECTRONICS Comparative Balance Sheet Current assets: Cash Marketable securities Accounts receivable, net Inventory Prepaid expenses Total current assets Plant and equipment, net Liabilities and Shareholders' Equity This Year Last Year $ 70,000 $ 150,000 18,000 480,000 300,000 950,000 600,000 20,000 22,000 1,520,000 1,090,000 1,480,000 1,370,000 $3,000,000 $2,460,000 Total assets Liabilities: Current liabilities $ 800,000 Bonds payable, 12% 600,000 $ 430,000 600,000 Total liabilities 1,400,000 1,030,000 Shareholders' equity: Preferred shares, no par ($6; 20,000 shares issued) 250,000 250,000 Common shares, no par (unlimited authorized, 50,000 issued) 500,000 500,000 Retained earnings 850,000 680,000 Total shareholders' equity 1,600,000 1,430,000 Total liabilities and shareholders' equity $3,000,000 $2,460,000 "How Well Am I Doing?"-Financial Statement Analysis SABIN ELECTRONICS Comparative Income Statement This Year Last Year Sales Less: Cost of goods sold Gross margin Less: Operating expenses Net operating income $5,000,000 $4,350,000 3,875,000 3,450,000 1,125,000 900,000 653,000 548,000 472,000 352,000 Less: Interest expense 72,000 72,000 Net income before taxes 400,000 280,000 Less: Income taxes (30%) 120,000 84,000 Net income 280,000 196,000 Dividends paid: Preferred dividends 20,000 20,000 Common dividends 90,000 75,000 Total dividends paid 110,000 95,000 Net income retained 170,000 101,000 Retained earnings, beginning of year 680,000 579,000 Retained earnings, end of year $ 850,000 $ 680,000 During the past year, the company introduced several new product lines and raised the selling prices on a number of old product lines in order to improve its profit margin. The company also hired a new sales man- ager, who has expanded sales into several new territories. Sales terms are 2/10, n/30. All sales are on account. Assume that the following ratios are typical of firms in the electronics industry: During the past year, the company introduced several new product lines and raised the selling prices on a number of old product lines in order to improve its profit margin. The company also hired a new sales man- ager, who has expanded sales into several new territories. Sales terms are 2/10, n/30. All sales are on account. Assume that the following ratios are typical of firms in the electronics industry: Current ratio Acid-test (quick) ratio Average age of receivables Inventory turnover in days Debt-to-equity ratio Times interest earned Return on total assets Price-earnings ratio 2.5 to 1 1.3 to 1 18 days 60 days 0.90 to 1 6.0 times 13% 12 PROBLEM 13-2 Computing Financial Ratios for Common Shareholders [LO2 - CC2] Refer to the financial statements and other data in Problem 13-1. Assume that you are an account executive for a large brokerage house and that one of your clients has asked for a recommendation about the possible purchase of Sabin Electronics' shares. You are not acquainted with the company and for this reason wish to do certain analytical work before making a recommendation. Required: 1. You decide first to assess the well-being of the common shareholders. For both this year and last year, compute the following: a. The earnings per share. There has been no change in preferred or common shares over the last two years. b. The dividend yield ratio for common shares. The company's shares are currently selling for $40 per share; last year, they sold for $36 per share. c. The dividend payout ratio for common shares. d. The price-earnings ratio. How do investors regard Sabin Electronics as compared with other firms in the industry? Explain. e. The book value per share of common shares. Does the difference between market value and book value suggest that the shares are overpriced? Explain. 2. You decide next to assess the company's rate of return. Compute the following for both this year and last year: a. The return on total assets. (Total assets at the beginning of last year were $2,300,000.) b. The return on common equity. (Shareholders' equity at the beginning of last year was $1,329,000.) c. The financial leverage. Is it positive or negative? Explain. 3. Would you recommend that your client purchase Sabin Electronics shares? Explain
13-1 excel Preparing Common-Size Statements and Financial Ratios for Creditors [LO1 - CC1; LO2-CC3, 4] CHECK FIGURES (1e) Inventory turnover this year: 5.0 times (1g) Times Interest earned last year: 4.9 times Paul Sabin organized Sabin Electronics 10 years ago in order to produce and sell several electronic devices on which he had secured patents. Although the company has been fairly profitable, it is now experiencing a severe cash shortage. For this reason, it is requesting a $500,000 long-term loan from Gulfport Bank, $100,000 of which will be used to bolster the cash account and $400,000 of which will be used to modernize certain key items of equipment. The company's financial statements for the two most recent years follow: Current assets: Assets SABIN ELECTRONICS Comparative Balance Sheet This Year Last Year Cash Marketable securities Accounts receivable, net Inventory Prepaid expenses Total current assets Plant and equipment, net Total assets Liabilities and Shareholders' Equity Liabilities: Current liabilities Bonds payable, 12% Total liabilities Shareholders' equity: $ 70,000 $ 150,000 - 18,000 480,000 300,000 950,000 600,000 20,000 22,000 1,520,000 1,090,000 1,480,000 $3,000,000 1,370,000 $2,460,000 $ 800,000 600,000 1,400,000 $ 430,000 600,000 1,030,000 mes Assets SABIN ELECTRONICS Comparative Balance Sheet Current assets: Cash Marketable securities Accounts receivable, net Inventory Prepaid expenses Total current assets Plant and equipment, net Liabilities and Shareholders' Equity This Year Last Year $ 70,000 $ 150,000 18,000 480,000 300,000 950,000 600,000 20,000 22,000 1,520,000 1,090,000 1,480,000 1,370,000 $3,000,000 $2,460,000 Total assets Liabilities: Current liabilities $ 800,000 Bonds payable, 12% 600,000 $ 430,000 600,000 Total liabilities 1,400,000 1,030,000 Shareholders' equity: Preferred shares, no par ($6; 20,000 shares issued) 250,000 250,000 Common shares, no par (unlimited authorized, 50,000 issued) 500,000 500,000 Retained earnings 850,000 680,000 Total shareholders' equity 1,600,000 1,430,000 Total liabilities and shareholders' equity $3,000,000 $2,460,000 "How Well Am I Doing?"-Financial Statement Analysis SABIN ELECTRONICS Comparative Income Statement This Year Last Year Sales Less: Cost of goods sold Gross margin Less: Operating expenses Net operating income $5,000,000 $4,350,000 3,875,000 3,450,000 1,125,000 900,000 653,000 548,000 472,000 352,000 Less: Interest expense 72,000 72,000 Net income before taxes 400,000 280,000 Less: Income taxes (30%) 120,000 84,000 Net income 280,000 196,000 Dividends paid: Preferred dividends 20,000 20,000 Common dividends 90,000 75,000 Total dividends paid 110,000 95,000 Net income retained 170,000 101,000 Retained earnings, beginning of year 680,000 579,000 Retained earnings, end of year $ 850,000 $ 680,000 During the past year, the company introduced several new product lines and raised the selling prices on a number of old product lines in order to improve its profit margin. The company also hired a new sales man- ager, who has expanded sales into several new territories. Sales terms are 2/10, n/30. All sales are on account. Assume that the following ratios are typical of firms in the electronics industry: During the past year, the company introduced several new product lines and raised the selling prices on a number of old product lines in order to improve its profit margin. The company also hired a new sales man- ager, who has expanded sales into several new territories. Sales terms are 2/10, n/30. All sales are on account. Assume that the following ratios are typical of firms in the electronics industry: Current ratio Acid-test (quick) ratio Average age of receivables Inventory turnover in days Debt-to-equity ratio Times interest earned Return on total assets Price-earnings ratio 2.5 to 1 1.3 to 1 18 days 60 days 0.90 to 1 6.0 times 13% 12 PROBLEM 13-2 Computing Financial Ratios for Common Shareholders [LO2 - CC2] Refer to the financial statements and other data in Problem 13-1. Assume that you are an account executive for a large brokerage house and that one of your clients has asked for a recommendation about the possible purchase of Sabin Electronics' shares. You are not acquainted with the company and for this reason wish to do certain analytical work before making a recommendation. Required: 1. You decide first to assess the well-being of the common shareholders. For both this year and last year, compute the following: a. The earnings per share. There has been no change in preferred or common shares over the last two years. b. The dividend yield ratio for common shares. The company's shares are currently selling for $40 per share; last year, they sold for $36 per share. c. The dividend payout ratio for common shares. d. The price-earnings ratio. How do investors regard Sabin Electronics as compared with other firms in the industry? Explain. e. The book value per share of common shares. Does the difference between market value and book value suggest that the shares are overpriced? Explain. 2. You decide next to assess the company's rate of return. Compute the following for both this year and last year: a. The return on total assets. (Total assets at the beginning of last year were $2,300,000.) b. The return on common equity. (Shareholders' equity at the beginning of last year was $1,329,000.) c. The financial leverage. Is it positive or negative? Explain. 3. Would you recommend that your client purchase Sabin Electronics shares? Explain Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


