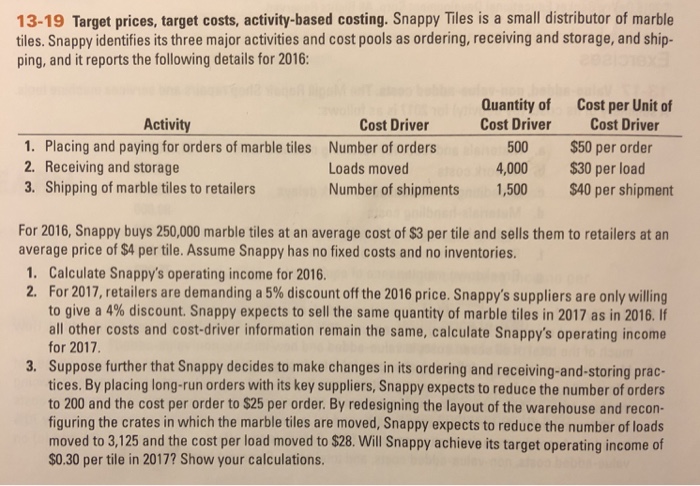
13-19 Target prices, target costs, activity-based costing. Snappy Tiles is a small distributor of marble tiles. Snappy identifies its three major activities and cost pools as ordering, receiving and storage, and ship- ping, and it reports the following details for 2016 Quantity of Cost Driver 500 4,000 1,500 Cost per Unit of Activity Cost Driver Cost Driver 1. Placing and paying for orders of marble tiles 2. Receiving and storage 3. Shipping of marble tiles to retailers Number of orders Loads moved Number of shipments $50 per order $30 per load $40 per shipment For 2016, Snappy buys 250,000 marble tiles at an average cost of $3 per tile and sells them to retailers at an average price of $4 per tile. Assume Snappy has no fixed costs and no inventories 1. Calculate Snappy's operating income for 2016. 2. For 2017,retailers are demanding a 5% discount off the 2016 price. Snappy's suppliers are only willing to give a 4% discount. Snappy expects to sell the same quantity of marble tiles in 2017 as in 2016, if all other costs and cost-driver information remain the same, calculate Snappy's operating income for 2017 3. Suppose further that Snappy decides to make changes in its ordering and receiving-and-storing prac- tices. By placing long-run orders with its key suppliers, Snappy expects to reduce the number of orders to 200 and the cost per order to $25 per order. By redesigning the layout of the warehouse and recon- figuring the crates in which the marble tiles are moved, Snappy expects to reduce the number of loads moved to 3,125 and the cost per load moved to $28. Will Snappy achieve its target operating income of $0.30 per tile in 2017? Show your calculations 13-19 Target prices, target costs, activity-based costing. Snappy Tiles is a small distributor of marble tiles. Snappy identifies its three major activities and cost pools as ordering, receiving and storage, and ship- ping, and it reports the following details for 2016 Quantity of Cost Driver 500 4,000 1,500 Cost per Unit of Activity Cost Driver Cost Driver 1. Placing and paying for orders of marble tiles 2. Receiving and storage 3. Shipping of marble tiles to retailers Number of orders Loads moved Number of shipments $50 per order $30 per load $40 per shipment For 2016, Snappy buys 250,000 marble tiles at an average cost of $3 per tile and sells them to retailers at an average price of $4 per tile. Assume Snappy has no fixed costs and no inventories 1. Calculate Snappy's operating income for 2016. 2. For 2017,retailers are demanding a 5% discount off the 2016 price. Snappy's suppliers are only willing to give a 4% discount. Snappy expects to sell the same quantity of marble tiles in 2017 as in 2016, if all other costs and cost-driver information remain the same, calculate Snappy's operating income for 2017 3. Suppose further that Snappy decides to make changes in its ordering and receiving-and-storing prac- tices. By placing long-run orders with its key suppliers, Snappy expects to reduce the number of orders to 200 and the cost per order to $25 per order. By redesigning the layout of the warehouse and recon- figuring the crates in which the marble tiles are moved, Snappy expects to reduce the number of loads moved to 3,125 and the cost per load moved to $28. Will Snappy achieve its target operating income of $0.30 per tile in 2017? Show your calculations