13.4 VPA Project: Olympus Tours
help me out please I will rate high!
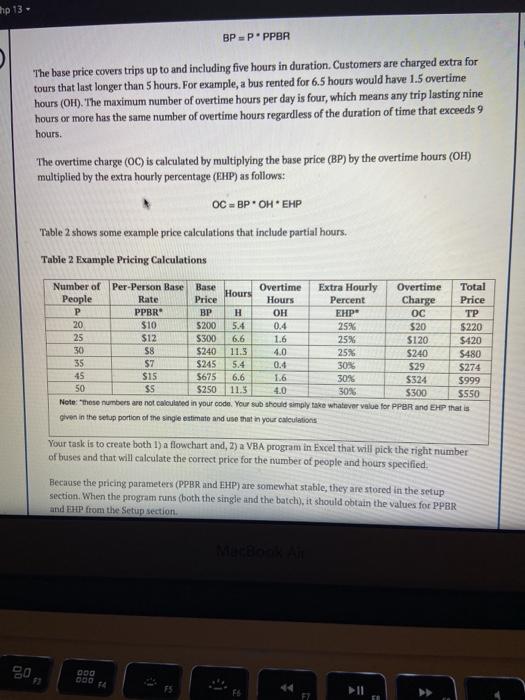
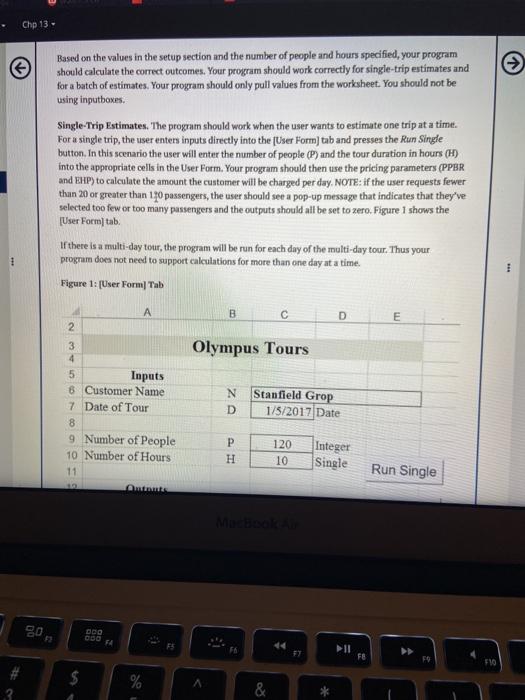
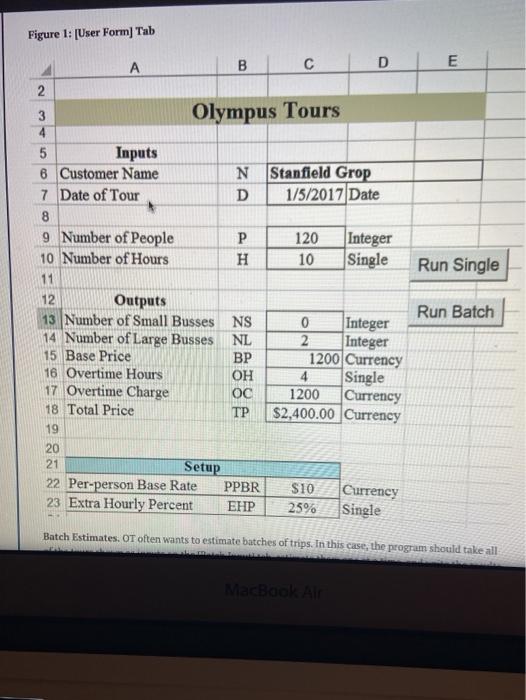
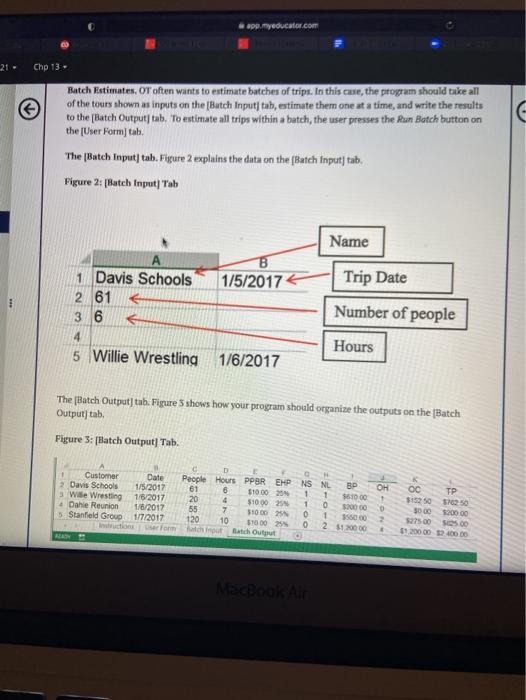
Chp 13 - 13.4 VBA Project: Olympus Tours Assume you have just been hired by Olympus Tours (OT), a bus-rental company located in Orem, Utah. OT provides buses for groups such as schools, family reunions, travel clubs, etc. The smallest group OT will bus is 20 people and the largest group is 120 people. Two types of buses are available for use: small buses (25 maximum riders per bus) and large buses (60 maximum riders per bus). Assume that OT has access to all of the small and large buses it needs. Table 1. Bus Combinations w of Buses Option Riders Small Big Min 20 1 1 0 Max 25 Min 26 2 2 O Max 50 Min 51 3 0 1 Max 60 Min 61 4 1 1 Max 85 Min 86 5 0 2 Max.120 4 OT's pricing structure is as follows. The base price (BP) is calculated by multiplying the number of people (P) included in the trip by a per-person base rate (PPBR). BP-PPPBR The base price covers trips up to and including five hours in duration Customers are charged extra for tours that last longer than 5 hours. For example, a bus rented for 6.5 hours would have 1.5 overtime hours (OH). The maximum number of overtime hours per day is four, which means any trip lasting nine MacBook hp 13 - BPPPPBR The base price covers trips up to and including five hours in duration Customers are charged extra for tours that last longer than 5 hours. For example, a bus rented for 6.5 hours would have 1.5 overtime hours (OH). The maximum number of overtime hours per day is four, which means any trip lasting nine hours or more has the same number of overtime hours regardless of the duration of time that exceeds 9 hours. The overtime charge (OC) is calculated by multiplying the base price (BP) by the overtime hours (OH) multiplied by the extra hourly percentage (EHP) as follows: OC - BP.OH EHP Table 2 shows some example price calculations that include partial hours. Table 2 Example Pricing Calculations Number of Per-Person Base Base Overtime Overtime Extra Hourly Total Hours People Rate Price Hours Percent Charge Price PPBR BP OH EHP OC 20 $10 5200 5.4 0.4 25%6 $20 $220 25 $12 $300 6.6 1.6 25% $120 $420 50 S8 $240 11.3 4.0 25% $240 $480 35 $7 $245 5.4 0.4 30% 529 $274 45 $15 5675 6.6 1.6 30% $324 $999 50 $S $250 11.5 4.0 30% $300 $550 Note: these numbers are not called in your code. Your sub should simply take whatever value for PPBR and EHP that is given in the setup portion of the single estimate and use that in your calculations Your task is to create both 1) a flowchart and, 2) a VBA program in Excel that will pick the right number of buses and that will calculate the correct price for the number of people and hours specified. Because the pricing parameters (PPBR and EHP) ate somewhat stable, they are stored in the setup section. When the program runs (both the single and the batch), it should obtain the values for PPBR and EHP from the Setup section 09 Chp 13 > Based on the values in the setup section and the number of people and hours specified, your program should calculate the correct outcomes. Your program should work correctly for single-trip estimates and for a batch of estimates. Your program should only pull values from the worksheet. You should not be using inputboxes Single-Trip Estimates. The program should work when the user wants to estimate one trip at a time. For a single trip, the user enters inputs directly into the [User Form) tab and presses the Run Single button. In this scenario the user will enter the number of people (P) and the tour duration in hours (H) into the appropriate cells in the User Form. Your program should then use the pricing parameters (PPER and EHP) to calculate the amount the customer will be charged per day. NOTE: If the user requests fewer than 20 or greater than 120 passengers, the user should see a pop-up message that indicates that they've selected too few or too many passengers and the outputs should all be set to zero. Figure 1 shows the [User Form tab If there is a multi-day tour, the program will be run for each day of the multi-day tour. Thus your program does not need to support calculations for more than one day at a time. Figure 1: (User Form] Tab B D E Olympus Tours N D 3 4 5 Inputs 8 Customer Name 7 Date of Tour 8 9 Number of People 10 Number of Hours 11 mm Stanfield Grop 1/5/2017 Date P H 120 10 Integer Single Run Single MENA gos II FE $ % & Figure 1: [User Form) Tab B C D E 2. Run Single 2 3 Olympus Tours 4 5 Inputs 6 Customer Name N Stanfield Grop 7 Date of Tour D 1/5/2017 Date 8 9 Number of People P 120 Integer 10 Number of Hours H 10 Single 11 12 Outputs 13 Number of Small Busses NS Integer 14 Number of Large Busses NL Integer 15 Base Price BP 1200 Currency 16 Overtime Hours OH 4 Single 17 Overtime Charge OC 1200 Currency 18 Total Price $2,400.00 Currency 19 20 21 Setup 22 Per-person Base Rate PPBR $10 Currency 23 Extra Hourly Percent EHP 25% Single Run Batch ON Batch Estimates. OT often wants to estimate batches of trips. In this case, the program should take all MacBook Air penyeducator.com Chp 13 Batch Estimates, OT often wants to estimate batches of trips. In this case, the program should take all of the tours shown as inputs on the Butch Inputs tab, estimate them one at a time, and write the results to the Batch Output/ tab. "To estimate all trips within a batch, the user presses the Run Batch button on the [User Form tab The (Batch Input| tab. Figure 2 explains the data on the (Batch Input) tab. Figure 2: Batch Input Tab Name 1 Davis Schools 2 61 3 6 1/5/2017 Trip Date Number of people 4 Hours 5 Willie Wrestling 1/6/2017 The Patch Output| tab. Figure 5 shows how your program should organize the outputs on the (Batch Output) tab, Figure 3: (Batch Output Tab. 1 Customer Date 2 Davis Schools 1/5/2017 3 Wille Wrestling 1/6/2017 Dahle Reunion 1/6/2017 5. Stanfield Group 1/7/2017 conform OH + TP D People Hours PPBR EHPNS NL BP 61 6 $10.00 20 1 1 $51000 20 4 $10.00 25 0 $200.00 55 7 5100025 0 1 155000 120 10 5100025 0 2 S120000 co Batch Out 00 315250 3000 520000 2 1 200 00 00 00 MacBook Air Summary of the Project Assignments and Details: 1. Create a flowchart for the process of completing an estimate for a single-tour. You are not required to create a flowchart for the Run Batch process. Upload this flowchart separately from your completed workbook in the file upload box below (to facilitate grading) 2. Download the Olympus Tours Programming Project Worksheet below. Do not make your own workbook. Add VBA code to complete the project. 3. Your VBA code should work with the cells that are already positioned on the (User Form) tab of the workbook. Do not change the cell locations or layout on the (User Form] tab within the workbook. In addition, do NOT add or delete any columns or rows. 4. Use VBA to do all of the calculations. Do not use spreadsheet functions. 5. Add your VBA code to the two existing sub routines that have been started in Modulei already within the workbook. Add your code to the sub routine named EstSingle that will run when the user presses the Run Single Button. Add your code to the sub routine named EstBatch that will run when the user presses the Run Batch Button. Connect the appropriate subroutine to the respective buttons, so that the correct sub routine will run when the button is pushed. 6. In your code, use the Option Explicit setting for both subroutines. (This should already be set.) Verify this by ensuring that the first line of code says "Option Explicit." 7. Use Dim statements to declare all variables that you use in your code. Declare the variables as the data types shown on Column of the [User Form) tab. 8. Test your program with a variety of inputs to ensure it works properly before you turn in your assignment 9. You do not need to calculate PPBR or EHP. Rather, your sub should take whatever values of PPBR and EHP are provided by the user in the setup variables section in the single estimate user form. 10. Upload your completed Excel workbook in the appropriate upload box below. 11. Do not forget to handle user inputs that are invalid (.e Based on the values in the setup section and the number of people and hours specified, your program should calculate the correct outcomes. Your program should work correctly for single-trip estimates and for a batch of estimates. Your program should only pull values from the worksheet. You should not be using inputboxes Single-Trip Estimates. The program should work when the user wants to estimate one trip at a time. For a single trip, the user enters inputs directly into the [User Form) tab and presses the Run Single button. In this scenario the user will enter the number of people (P) and the tour duration in hours (H) into the appropriate cells in the User Form. Your program should then use the pricing parameters (PPER and EHP) to calculate the amount the customer will be charged per day. NOTE: If the user requests fewer than 20 or greater than 120 passengers, the user should see a pop-up message that indicates that they've selected too few or too many passengers and the outputs should all be set to zero. Figure 1 shows the [User Form tab If there is a multi-day tour, the program will be run for each day of the multi-day tour. Thus your program does not need to support calculations for more than one day at a time. Figure 1: (User Form] Tab B D E Olympus Tours N D 3 4 5 Inputs 8 Customer Name 7 Date of Tour 8 9 Number of People 10 Number of Hours 11 mm Stanfield Grop 1/5/2017 Date P H 120 10 Integer Single Run Single MENA gos II FE $ % & Figure 1: [User Form) Tab B C D E 2. Run Single 2 3 Olympus Tours 4 5 Inputs 6 Customer Name N Stanfield Grop 7 Date of Tour D 1/5/2017 Date 8 9 Number of People P 120 Integer 10 Number of Hours H 10 Single 11 12 Outputs 13 Number of Small Busses NS Integer 14 Number of Large Busses NL Integer 15 Base Price BP 1200 Currency 16 Overtime Hours OH 4 Single 17 Overtime Charge OC 1200 Currency 18 Total Price $2,400.00 Currency 19 20 21 Setup 22 Per-person Base Rate PPBR $10 Currency 23 Extra Hourly Percent EHP 25% Single Run Batch ON Batch Estimates. OT often wants to estimate batches of trips. In this case, the program should take all MacBook Air penyeducator.com Chp 13 Batch Estimates, OT often wants to estimate batches of trips. In this case, the program should take all of the tours shown as inputs on the Butch Inputs tab, estimate them one at a time, and write the results to the Batch Output/ tab. "To estimate all trips within a batch, the user presses the Run Batch button on the [User Form tab The (Batch Input| tab. Figure 2 explains the data on the (Batch Input) tab. Figure 2: Batch Input Tab Name 1 Davis Schools 2 61 3 6 1/5/2017 Trip Date Number of people 4 Hours 5 Willie Wrestling 1/6/2017 The Patch Output| tab. Figure 5 shows how your program should organize the outputs on the (Batch Output) tab, Figure 3: (Batch Output Tab. 1 Customer Date 2 Davis Schools 1/5/2017 3 Wille Wrestling 1/6/2017 Dahle Reunion 1/6/2017 5. Stanfield Group 1/7/2017 conform OH + TP D People Hours PPBR EHPNS NL BP 61 6 $10.00 20 1 1 $51000 20 4 $10.00 25 0 $200.00 55 7 5100025 0 1 155000 120 10 5100025 0 2 S120000 co Batch Out 00 315250 3000 520000 2 1 200 00 00 00 MacBook Air Summary of the Project Assignments and Details: 1. Create a flowchart for the process of completing an estimate for a single-tour. You are not required to create a flowchart for the Run Batch process. Upload this flowchart separately from your completed workbook in the file upload box below (to facilitate grading) 2. Download the Olympus Tours Programming Project Worksheet below. Do not make your own workbook. Add VBA code to complete the project. 3. Your VBA code should work with the cells that are already positioned on the (User Form) tab of the workbook. Do not change the cell locations or layout on the (User Form] tab within the workbook. In addition, do NOT add or delete any columns or rows. 4. Use VBA to do all of the calculations. Do not use spreadsheet functions. 5. Add your VBA code to the two existing sub routines that have been started in Modulei already within the workbook. Add your code to the sub routine named EstSingle that will run when the user presses the Run Single Button. Add your code to the sub routine named EstBatch that will run when the user presses the Run Batch Button. Connect the appropriate subroutine to the respective buttons, so that the correct sub routine will run when the button is pushed. 6. In your code, use the Option Explicit setting for both subroutines. (This should already be set.) Verify this by ensuring that the first line of code says "Option Explicit." 7. Use Dim statements to declare all variables that you use in your code. Declare the variables as the data types shown on Column of the [User Form) tab. 8. Test your program with a variety of inputs to ensure it works properly before you turn in your assignment 9. You do not need to calculate PPBR or EHP. Rather, your sub should take whatever values of PPBR and EHP are provided by the user in the setup variables section in the single estimate user form. 10. Upload your completed Excel workbook in the appropriate upload box below. 11. Do not forget to handle user inputs that are invalid (.e