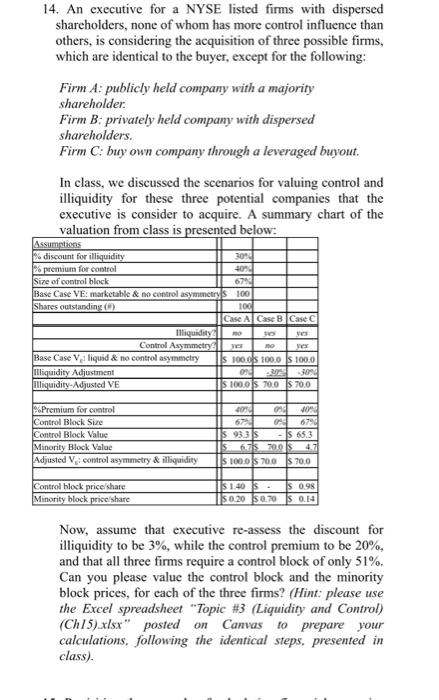
14. An executive for a NYSE listed firms with dispersed shareholders, none of whom has more control influence than others, is considering the acquisition of three possible firms, which are identical to the buyer, except for the following: Firm A: publicly held company with a majority shareholder. Firm B: privately held company with dispersed shareholders. Firm C: buy own company through a leveraged buyout. In class, we discussed the scenarios for valuing control and illiquidity for these three potential companies that the executive is consider to acquire. A summary chart of the valuation from class is presented below: Assumptions % discount for illiquidity % premium for control 30% 40% Size of control block 67% Base Case VE: marketable & no control asymmetrys 100 Shares outstanding (8) 100 Case A Case B Case C yes Illiquidity Control Asymmetry Base Case V: liquid & no control asymmetry Illiquidity Adjustment Illiquidity-Adjusted VE %Premium for control Control Block Size Control Block Value Minority Block Value Adjusted V: control asymmetry & illiquidity Control block price/share Minority block price/share yes no s 100.0s 100.0 $ 100.0 09 -30% -30% $100.0 S 70.0 $70.0 4070 67% $ 93.3 S als: 0% 40% 0% 67% - $65.3 6.75 700$ 4.7 s 100.0s 70.0 $70.0 $ 1.40 S- $ 0.98 $0.20 50.70 S 0.14 Now, assume that executive re-assess the discount for illiquidity to be 3%, while the control premium to be 20%, and that all three firms require a control block of only 51%. Can you please value the control block and the minority block prices, for each of the three firms? (Hint: please use the Excel spreadsheet "Topic #3 (Liquidity and Control) (Ch15).xlsx" posted on Canvas to prepare your calculations, following the identical steps, presented in class). 14. An executive for a NYSE listed firms with dispersed shareholders, none of whom has more control influence than others, is considering the acquisition of three possible firms, which are identical to the buyer, except for the following: Firm A: publicly held company with a majority shareholder. Firm B: privately held company with dispersed shareholders. Firm C: buy own company through a leveraged buyout. In class, we discussed the scenarios for valuing control and illiquidity for these three potential companies that the executive is consider to acquire. A summary chart of the valuation from class is presented below: Assumptions % discount for illiquidity % premium for control 30% 40% Size of control block 67% Base Case VE: marketable & no control asymmetrys 100 Shares outstanding (8) 100 Case A Case B Case C yes Illiquidity Control Asymmetry Base Case V: liquid & no control asymmetry Illiquidity Adjustment Illiquidity-Adjusted VE %Premium for control Control Block Size Control Block Value Minority Block Value Adjusted V: control asymmetry & illiquidity Control block price/share Minority block price/share yes no s 100.0s 100.0 $ 100.0 09 -30% -30% $100.0 S 70.0 $70.0 4070 67% $ 93.3 S als: 0% 40% 0% 67% - $65.3 6.75 700$ 4.7 s 100.0s 70.0 $70.0 $ 1.40 S- $ 0.98 $0.20 50.70 S 0.14 Now, assume that executive re-assess the discount for illiquidity to be 3%, while the control premium to be 20%, and that all three firms require a control block of only 51%. Can you please value the control block and the minority block prices, for each of the three firms? (Hint: please use the Excel spreadsheet "Topic #3 (Liquidity and Control) (Ch15).xlsx" posted on Canvas to prepare your calculations, following the identical steps, presented in class)