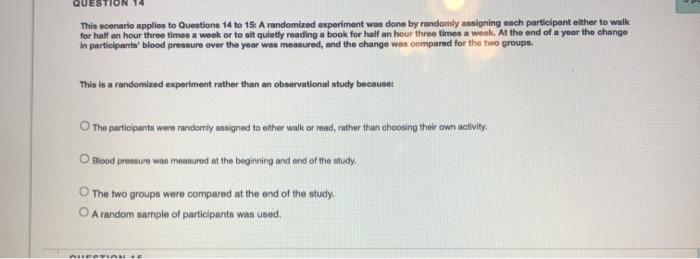
16. A company uses a new supplement in their chicken feed. They perform a randomised experiment on two groups of chicken. One group is given the standard chicken feed for two months, and the other is given the feed with supplement for two months. The company is interested if the average weight of chickens for those that had the feed with supplement is larger than those chickens that had the standard feed after two months. The resulting data from this experiment is an example of: a) Paired samples b) Two independent samples c) One independent sample d) Categorical Data 17. Which of the following statements is TRUE? a) A two-sample t-test is used for testing the equality of means of three or more populations b) A two-sample t-test is used for assessing the difference between the means of two independent populations c) A two-sample t-test is used for assessing the difference between the proportions of two independent populations d) A pooled standard deviation is used in a two-sample t-test when we assume unequal population variances 18. Data collected in a survey of voters in Australia and New Zealand showed that 57/100 Australian voters were satisfied with their Prime Minister, and 72/120 New Zealand voters were satisfied with their Prime Minister. In a test of the difference between the two population proportions, what would the value of the pooled proportion be (to 2 decimal places)? a) 0.57 b) 0.62 c) 0.05 d) 0.59 Questions 19 and 20 use the following information: A sample of students were asked how long they spent studying for an exam ("study"; in hours), and what mark they received for the exam ("mark"; out of 100). A linear regression was fitted to this data, and the fitted model was: mark = 20 + 4.2 x study 19. Which of the following statements is FALSE? a) The model suggests that, on average, a student that does not study could expect to get a mark of 20 b) There is a positive relationship between the variables "mark" and "study" c) For each additional hour of study, a student could expect to increase their mark by 4.2, on average d) The correlation coefficient between mark and study is r = 4.2QUESTION 1 This scenario applies to Questions 14 to 15: A randomized experiment was done by randomly assigning each participant either to walk for half an hour three times a week or to sit quietly reading a book for half an hour three times a weak. At the end of a year the change in participants' blood pressure over the year was measured, and the change was compared for the two groups. This is a randomized experiment rather than an observational study because: The participants were randomly assigned to either walk or read, rather than choosing their own activity. O Blood pressure was measured at the beginning and and of the study. O The two groups were compared at the end of the study. O A random sample of participants was used.Which of the following is not a condition that must be satisfied such that the instrumental variable used in a quasi-experiment is a valid instrument for the treatment actually received? O A. The instrument should influence the receipt of the treatment. B. The data should be available both on the instrument and on the treatment actually received. O C. The instrument should be "as if" randomly assigned. O D. There should be complete compliance with the treatment protocol. Studies that exploit a discontinuity in the probability of receiving treatment at value are called regression discontinuity designs. Which of the following statements are true about regression discontinuity designs? (Check all that apply.) A. In a sharp regression discontinuity design, the slope estimator can be estimated by instrumental variables estimation given that the instrument is valid. B. In a fuzzy regression discontinuity design, crossing the threshold influences receipt of the treatment but is not the sole determinant of whether the treatment will be received. C. In a sharp regression discontinuity design, receipt of treatment is entirely determined by whether the forcing variable exceeds the threshold or not. [)D. In a fuzzy regression discontinuity design, the jump in regressand value at the threshold equals the average treatment effect for the subpopulation.[Questions 1-4] In Ability, Gender, and Performance Standards: Evidence from Academic Probation, Jason M. Lindo, Nicholas J. Sanders, and Philip Oreopoulos find evidence using regression discontinuity methods that being placed on academic probation increases the probability that a student voluntarily leaves the university. Figure I below shows the estimated discontinuity in probation status at the end of the first year, and Figure 2 shows the impact of being placed on academic probation on the decision of male students to permanently leave the university at the end of their first year. Figure 1 Figure 2 Men 0.2 Probation status Left university voluntarily 50.1 -1.50 Fire your GPA minus probation cutoff -1.50 -1.00 -0.50 0.00 0.50 1.00 1.50 First year GPA minus probation cutoff 1) Why doesn't the mean difference between the rates of voluntary leaving for students placed on probation and those not placed on probation provide an unbiased estimate of the effect of being placed on probation? (3 points) 2) Based on Figure 1, which type of RD do you think this study is using, sharp or fuzzy RD? Explain the difference between the two. (2 points) 3) Briefly explain why the regression discontinuity estimates provide an unbiased estimate of the effect of being placed on probation? (3 points) 4) In this study, GPA is used as a running variable. Describe the role of the running variable in a sharp regression discontinuity design. (2 points)