Question
18.8 LAB: Natural merge sort (IN PYTHON PLEASE) The merge sort algorithm recursively divides the list in half until a list with one element is
18.8 LAB: Natural merge sort (IN PYTHON PLEASE)
The merge sort algorithm recursively divides the list in half until a list with one element is reached. A variant of merge sort, called natural merge sort, instead finds already-sorted runs of elements and merges the runs together.
Ex: The unsorted list below has five sorted runs.
Natural merge sort starts at index 0 and finds sorted runs A and B. Runs A and B are merged, using the same merging algorithm as merge sort, to make run F.
Next, the algorithm starts after the merged part F, again looking for two sequential, sorted runs. Runs C and D are found and merged to make run G.
The algorithm then starts after the merged portion G. Only one run exists, run E, until the end of the list is reached. So the algorithm starts back at index 0, finds runs F and G, and merges to make run H.
Again a single run is found after the just-merged part, so the search starts back at index 0. Runs H and E are found and merged.
One last search for a sorted run occurs, finding a sorted run length equal to the list's length. So the list is sorted and the algorithm terminates.
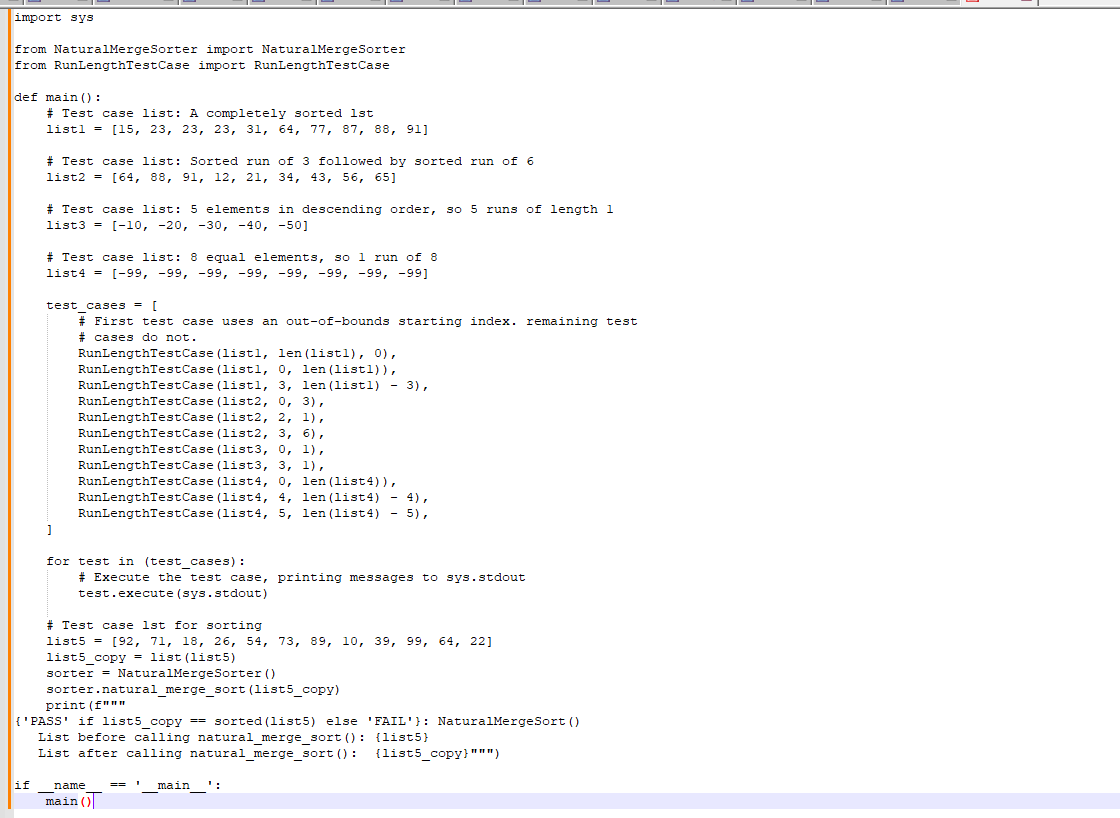
Step 1: Implement the get_sorted_run_length() method
Implement the get_sorted_run_length() method in NaturalMergeSorter.py. Access NaturalMergeSorter.py by clicking on the orange arrow next to main.py at the top of the coding window.
get_sorted_run_length() has two parameters:
integer_list: a list of integers and
start_index: an integer for the run's starting index.
The method returns the number of list elements sorted in ascending order, starting at start_index and ending either at the end of the sorted run, or the end of the list, whichever comes first. The method returns 0 if start_index is out of bounds.
File main.py has several test cases for get_sorted_run_length() that can be run by clicking the "Run program" button. One test case also exists for natural_merge_sort(), but that can be ignored until step two is completed.
The program's output does not affect grading.
Submit for grading to ensure that the get_sorted_run_length() unit tests pass before proceeding.
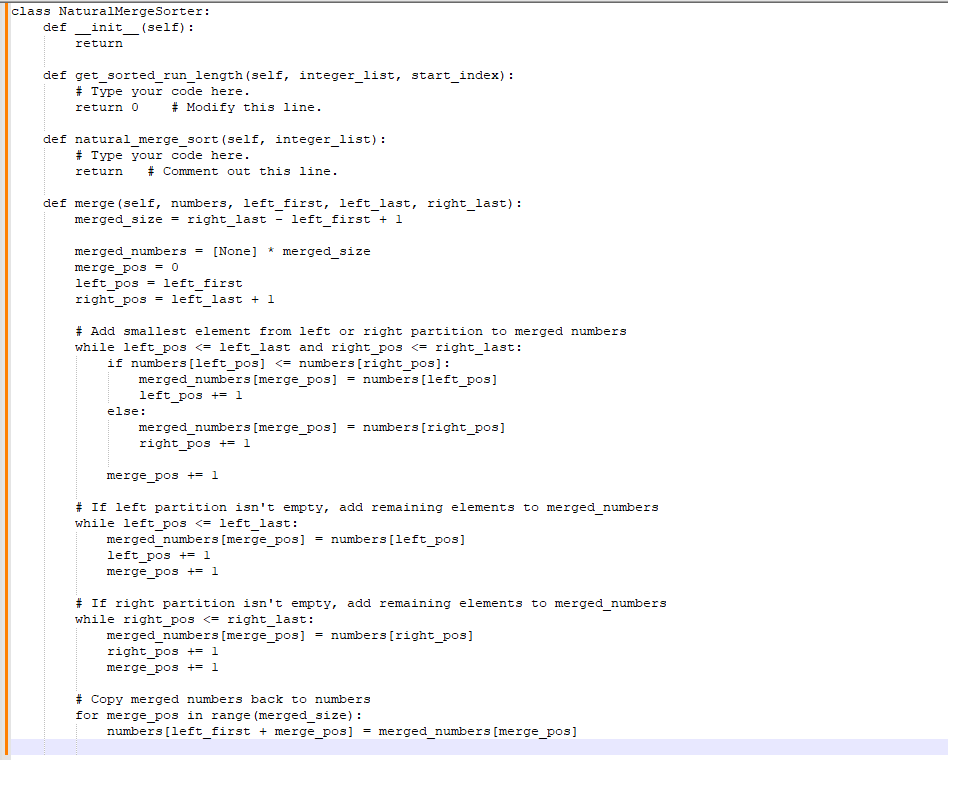
Step 2: Implement the natural_merge_sort() method
Implement the natural_merge_sort() method in NaturalMergeSorter.py. natural_merge_sort() must:
Start at index i=0
Get the length of the first sorted run, starting at i
Return if the first run's length equals the list's length
If the first run ends at the list's end, reassign i=0 and repeat step 2
Get the length of the second sorted run, starting immediately after the first
Merge the two runs with the provided merge() method
Reassign i with the first index after the second run, or 0 if the second run ends at the list's end
Go to step 2
Main.py
RunLenghtTestCase.py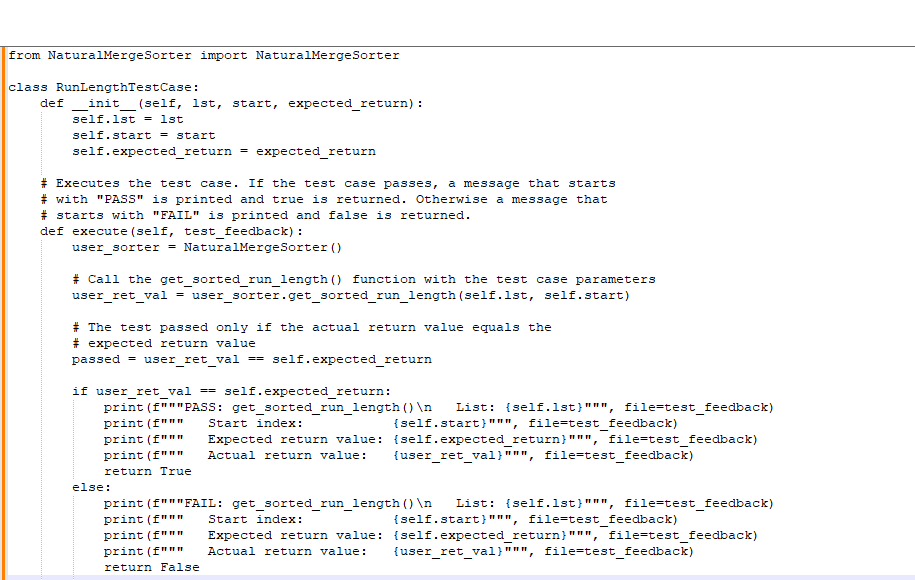
NaturalMergeSorter.py
 (
(
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


