
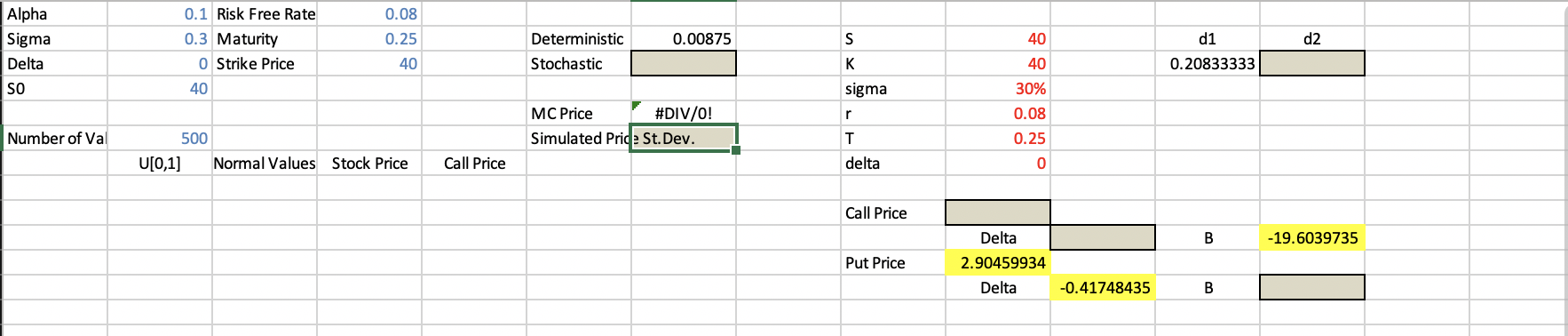
19.4. MC Valuation of a European Call Option Method. Use risk neutral pricing: Given S. = 40, o = 0.30, r = 0.08, 8 = 0, T = .25, K = 40 1. Choose a random number u in U[0,1]. 2. Determine z~N(0,1), z = N-1(u) 3. Calculate value for St from its distribution, 1 r Sy = Soe(r-8-202)T+OVT:2 = 4. Calculate the value of the option, Vi = max [S} K, 0], where i = trial #. 5. Discount the option value back to time 0, e-TT V 6. Repeat 1-5 many times, i = 1, ..., n. 1 i=1 n Note that 1 in n = 7. Take the average - =1 e-PTV; 22-1 e-rTV; approximates E[e=r7 max( St K,)). For the parameters listed above, the B-S price is $2.78 and the standard deviation of the call price as approximated by the sample distribution is $4.05. Accuracy: Let oc be the standard deviation of a single draw for a call price. on = van OC For our example with 500 draws, 0500 = 4.05 = .181 , which is 6.5% of the price V500 0.08 0.1 Risk Free Rate 0.3 Maturity O Strike Price 0.25 0.00875 S 40 d1 Alpha Sigma Delta SO d2 Deterministic Stochastic 40 K 40 0.20833333 40 sigma 30% 0.08 r MC Price #DIV/0! Simulated Pride St.Dev. Number of Val T 0.25 500 U[0,1] Normal Values Stock Price Call Price delta 0 Call Price Delta B -19.6039735 Put Price 2.90459934 Delta -0.41748435 B 19.4. MC Valuation of a European Call Option Method. Use risk neutral pricing: Given S. = 40, o = 0.30, r = 0.08, 8 = 0, T = .25, K = 40 1. Choose a random number u in U[0,1]. 2. Determine z~N(0,1), z = N-1(u) 3. Calculate value for St from its distribution, 1 r Sy = Soe(r-8-202)T+OVT:2 = 4. Calculate the value of the option, Vi = max [S} K, 0], where i = trial #. 5. Discount the option value back to time 0, e-TT V 6. Repeat 1-5 many times, i = 1, ..., n. 1 i=1 n Note that 1 in n = 7. Take the average - =1 e-PTV; 22-1 e-rTV; approximates E[e=r7 max( St K,)). For the parameters listed above, the B-S price is $2.78 and the standard deviation of the call price as approximated by the sample distribution is $4.05. Accuracy: Let oc be the standard deviation of a single draw for a call price. on = van OC For our example with 500 draws, 0500 = 4.05 = .181 , which is 6.5% of the price V500 0.08 0.1 Risk Free Rate 0.3 Maturity O Strike Price 0.25 0.00875 S 40 d1 Alpha Sigma Delta SO d2 Deterministic Stochastic 40 K 40 0.20833333 40 sigma 30% 0.08 r MC Price #DIV/0! Simulated Pride St.Dev. Number of Val T 0.25 500 U[0,1] Normal Values Stock Price Call Price delta 0 Call Price Delta B -19.6039735 Put Price 2.90459934 Delta -0.41748435 B








