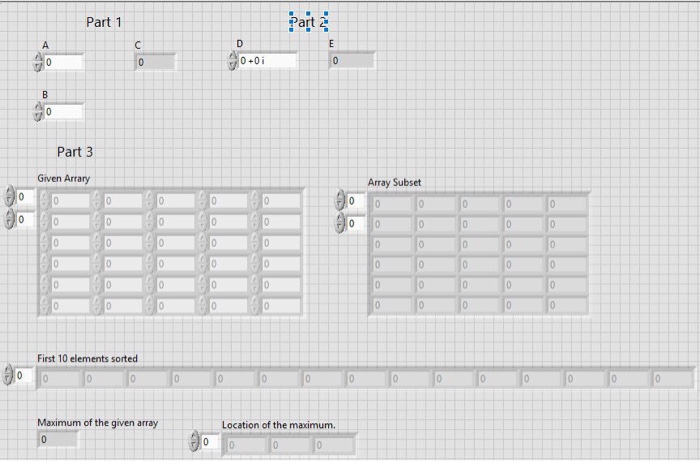
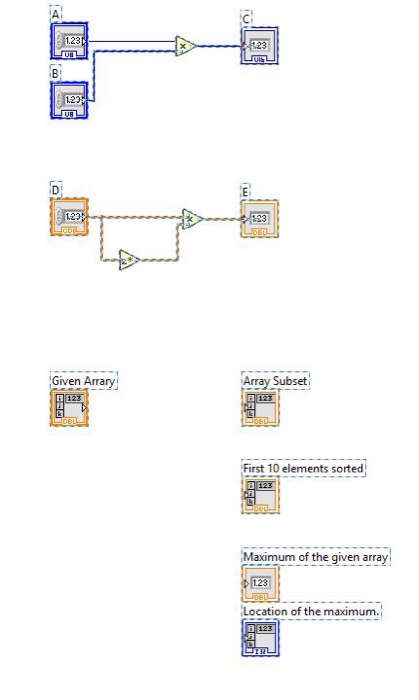
2. (10 points) In part 2, the code takes an input variable D and is computing E DI;ist will always be a real number. The coder implemented this calculation as D2 DD. Knowing the output would be real on the output. Changing the ontput type to a complex double resolves the coercion dot, but, leaves the output complex instead of real. (a) Change the output type from double to complex double and see that the coercion dot is removed. (b) Add two additional indicators to the front panel and implement two alternate calculations that result in the output being a real double precision number 3. (10 pts) In part 3, you will practice some array manipulations. The starter code provides you with an input array and several results indicators. When you are done coding the block diagram, initialize the array with the values provided in figure 4. You will find the function nodes you need on the block diagram's array pallet Part 3 Amay Subue it 10 elenents serted Figure 4: Input array and computed results (a) Add an array subset function node to the block diagram and use four constants to specify the location and range of the array subset to be extracted from the input array. Use the context help to learn how to select the constants. (b) Add a reshape array function node to the block diagram and use it to select the first ten elements from the input array. Use a sort 1-D array function node to sort the result. (c) Use the array max & min function node to determine the input array's maximum value and the indices of its location in the array. Note, when checking your answer, remember that LabVIEW uses zero indexed array dimensions! 2. (10 points) In part 2, the code takes an input variable D and is computing E DI;ist will always be a real number. The coder implemented this calculation as D2 DD. Knowing the output would be real on the output. Changing the ontput type to a complex double resolves the coercion dot, but, leaves the output complex instead of real. (a) Change the output type from double to complex double and see that the coercion dot is removed. (b) Add two additional indicators to the front panel and implement two alternate calculations that result in the output being a real double precision number 3. (10 pts) In part 3, you will practice some array manipulations. The starter code provides you with an input array and several results indicators. When you are done coding the block diagram, initialize the array with the values provided in figure 4. You will find the function nodes you need on the block diagram's array pallet Part 3 Amay Subue it 10 elenents serted Figure 4: Input array and computed results (a) Add an array subset function node to the block diagram and use four constants to specify the location and range of the array subset to be extracted from the input array. Use the context help to learn how to select the constants. (b) Add a reshape array function node to the block diagram and use it to select the first ten elements from the input array. Use a sort 1-D array function node to sort the result. (c) Use the array max & min function node to determine the input array's maximum value and the indices of its location in the array. Note, when checking your answer, remember that LabVIEW uses zero indexed array dimensions