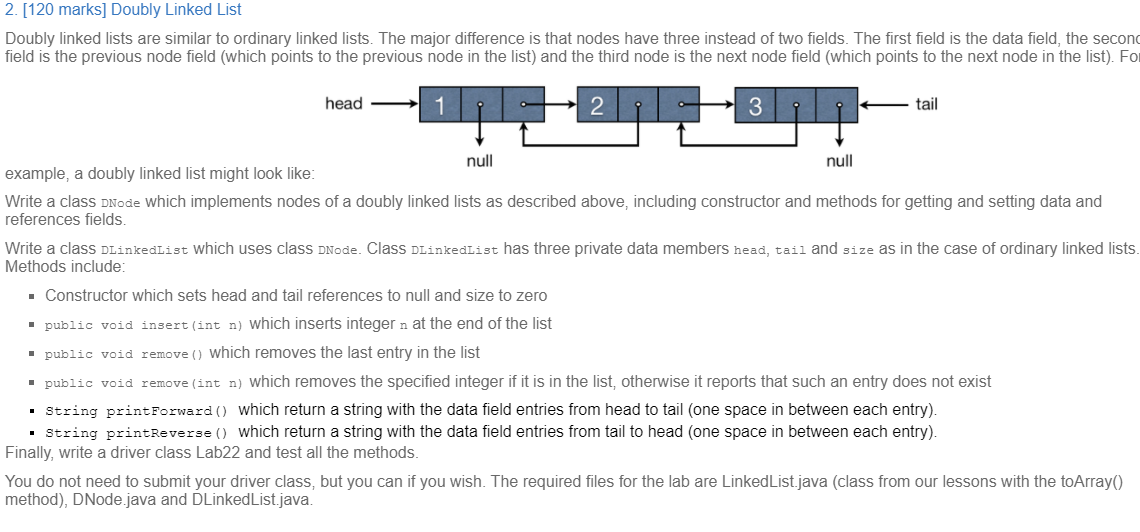
2. [120 marks] Doubly Linked List Doubly linked lists are similar to ordinary linked lists. The major difference is that nodes have three instead of two fields. The first field is the data field, the second field is the previous node field (which points to the previous node in the list) and the third node is the next node field (which points to the next node in the list). Foi head 2 11 3 tail null null example, a doubly linked list might look like: Write a class DNode which implements nodes of a doubly linked lists as described above, including constructor and methods for getting and setting data and references fields Write a class DLinkedlist which uses class DNode. Class DLinkedlist has three private data members head, tail and size as in the case of ordinary linked lists. Methods include: . Constructor which sets head and tail references to null and size to zero public void insert(int n) which inserts integer n at the end of the list public void remove () which removes the last entry in the list public void remove (int n) which removes the specified integer if it is in the list, otherwise it reports that such an entry does not exist String printForward() which return a string with the data field entries from head to tail (one space in between each entry). String printReverse () which return a string with the data field entries from tail to head (one space in between each entry). Finally, write a driver class Lab22 and test all the methods. You do not need to submit your driver class, but you can if you wish. The required files for the lab are Linked List.java (class from our lessons with the toArray method), DNode.java and DLinkedList.java. 2. [120 marks] Doubly Linked List Doubly linked lists are similar to ordinary linked lists. The major difference is that nodes have three instead of two fields. The first field is the data field, the second field is the previous node field (which points to the previous node in the list) and the third node is the next node field (which points to the next node in the list). Foi head 2 11 3 tail null null example, a doubly linked list might look like: Write a class DNode which implements nodes of a doubly linked lists as described above, including constructor and methods for getting and setting data and references fields Write a class DLinkedlist which uses class DNode. Class DLinkedlist has three private data members head, tail and size as in the case of ordinary linked lists. Methods include: . Constructor which sets head and tail references to null and size to zero public void insert(int n) which inserts integer n at the end of the list public void remove () which removes the last entry in the list public void remove (int n) which removes the specified integer if it is in the list, otherwise it reports that such an entry does not exist String printForward() which return a string with the data field entries from head to tail (one space in between each entry). String printReverse () which return a string with the data field entries from tail to head (one space in between each entry). Finally, write a driver class Lab22 and test all the methods. You do not need to submit your driver class, but you can if you wish. The required files for the lab are Linked List.java (class from our lessons with the toArray method), DNode.java and DLinkedList.java







