Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
2. (a) (5 pts) Consider the following family of hash functions H'p,m mapping elements of U = {0, 1, ...p-1} to a hash table with
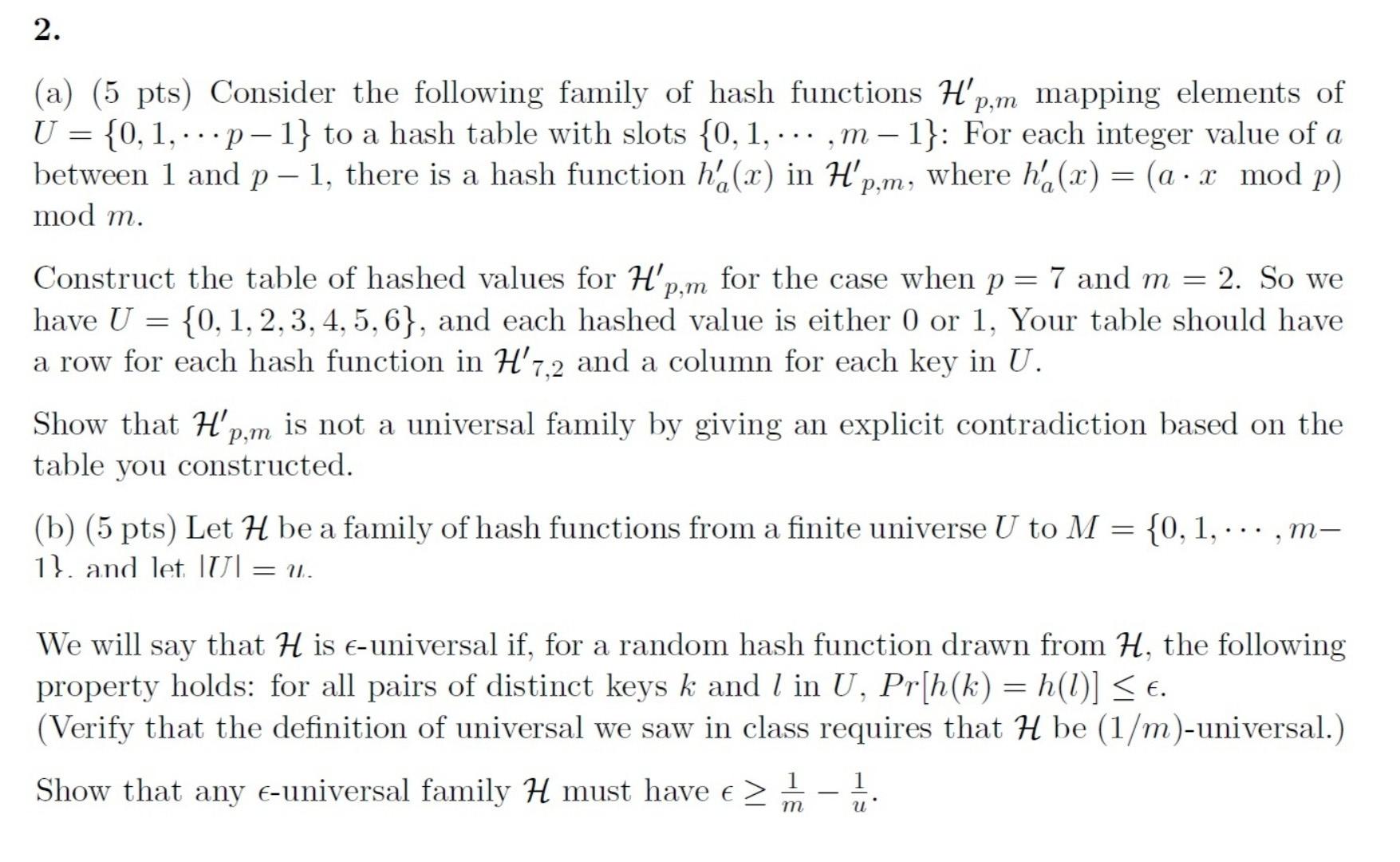
2. (a) (5 pts) Consider the following family of hash functions H'p,m mapping elements of U = {0, 1, ...p-1} to a hash table with slots {0, 1, ... , m 1}: For each integer value of a between 1 and p-1, there is a hash function h'a (2) in H'p,m, where ha (x) = (a x mod p) mod m. = Construct the table of hashed values for H', for the case when p = 7 and m = 2. So we P,m have U {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}, and each hashed value is either 0 or 1, Your table should have a row for each hash function in H' 7,2 and a column for each key in U. Show that H'p,m is not a universal family by giving an explicit contradiction based on the table you constructed. (b) (5 pts) Let H be a family of hash functions from a finite universe U to M {0, 1,...,m- 1). and let IUI = =U. We will say that H is e-universal if, for a random hash function drawn from H, the following property holds: for all pairs of distinct keys k and I in U, Pr[h(k) = h(1)] - 1 u m 2. (a) (5 pts) Consider the following family of hash functions H'p,m mapping elements of U = {0, 1, ...p-1} to a hash table with slots {0, 1, ... , m 1}: For each integer value of a between 1 and p-1, there is a hash function h'a (2) in H'p,m, where ha (x) = (a x mod p) mod m. = Construct the table of hashed values for H', for the case when p = 7 and m = 2. So we P,m have U {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}, and each hashed value is either 0 or 1, Your table should have a row for each hash function in H' 7,2 and a column for each key in U. Show that H'p,m is not a universal family by giving an explicit contradiction based on the table you constructed. (b) (5 pts) Let H be a family of hash functions from a finite universe U to M {0, 1,...,m- 1). and let IUI = =U. We will say that H is e-universal if, for a random hash function drawn from H, the following property holds: for all pairs of distinct keys k and I in U, Pr[h(k) = h(1)] - 1 u m
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


