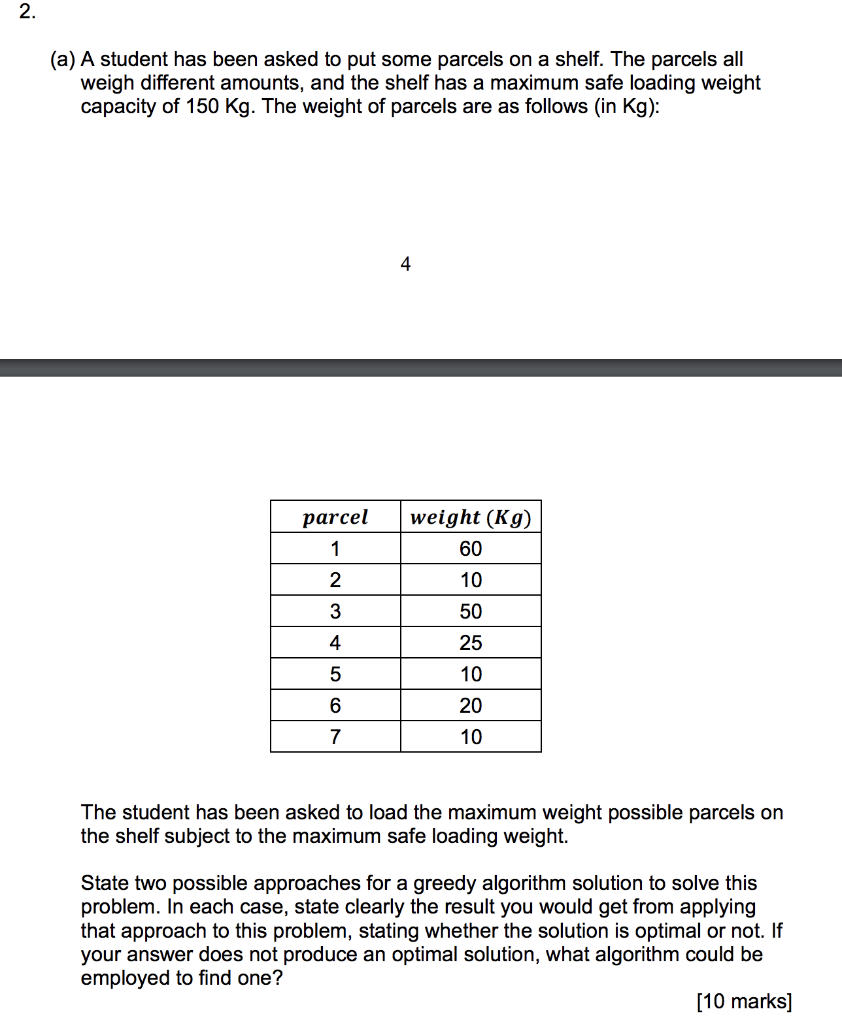


2. (a) A student has been asked to put some parcels on a shelf. The parcels all weigh different amounts, and the shelf has a maximum safe loading weight capacity of 150 Kg. The weight of parcels are as follows (in kg): 4 parcel 1 weight (Kg) 60 2 10 3 50 4 25 5 10 6 20 7 10 The student has been asked to load the maximum weight possible parcels on the shelf subject to the maximum safe loading weight. State two possible approaches for a greedy algorithm solution to solve this problem. In each case, state clearly the result you would get from applying that approach to this problem, stating whether the solution is optimal or not. If your answer does not produce an optimal solution, what algorithm could be employed to find one? [10 marks] (b) Explain, using diagrams as appropriate, why Dijkstra's algorithm for finding the lowest cost path through a weighted graph is an example of a greedy algorithm. Your answer should include the key concept of an invariant. [5 marks] (c) A balanced binary heap is to be constructed using the following data elements: 95 56 34 86 41 17 29 32 58 3 4 11 60 77 82 using a bottom up heap construction method. (1) Explain how the bottom up construction method can be shown to have running time complexity O(n) where n is the number of elements in the binary heap. You may find it helpful to recall that: h=00 h 2 2h h=0 l.e. that 20 + + + ...+ h +2 as h 00 [10 marks] 5 (ii) Show the heap that results from the bottom up construction. Fill the heap levels starting from the lowest first, and working from the right hand side to the left hand side. [5 marks] = (d) A recursive algorithm is applied to some data A (a1, ... , am) where m > 2. The running time T is characterised using the following recurrence equations: T(2) = c when the size of A is 2 T(m) = T(m 1) + 2c otherwise Determine the running time complexity of this algorithm. [10 marks] (e) Another recursive algorithm is applied to some data A = (a1, ... , am) where m = 2* (i.e. 2, 4, 8,16 ...) where x is an integer > 1. The running time T is characterised using the following recurrence equations: T(1) T(m) = 27 (m) c when the size of A is 1 + c otherwise Determine the running time complexity of this algorithm. [10 marks]









