Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
2. An ideal gas undergoes the reversible process A B shown below. The initial temperature of the gas is TA = 300K. Assume that
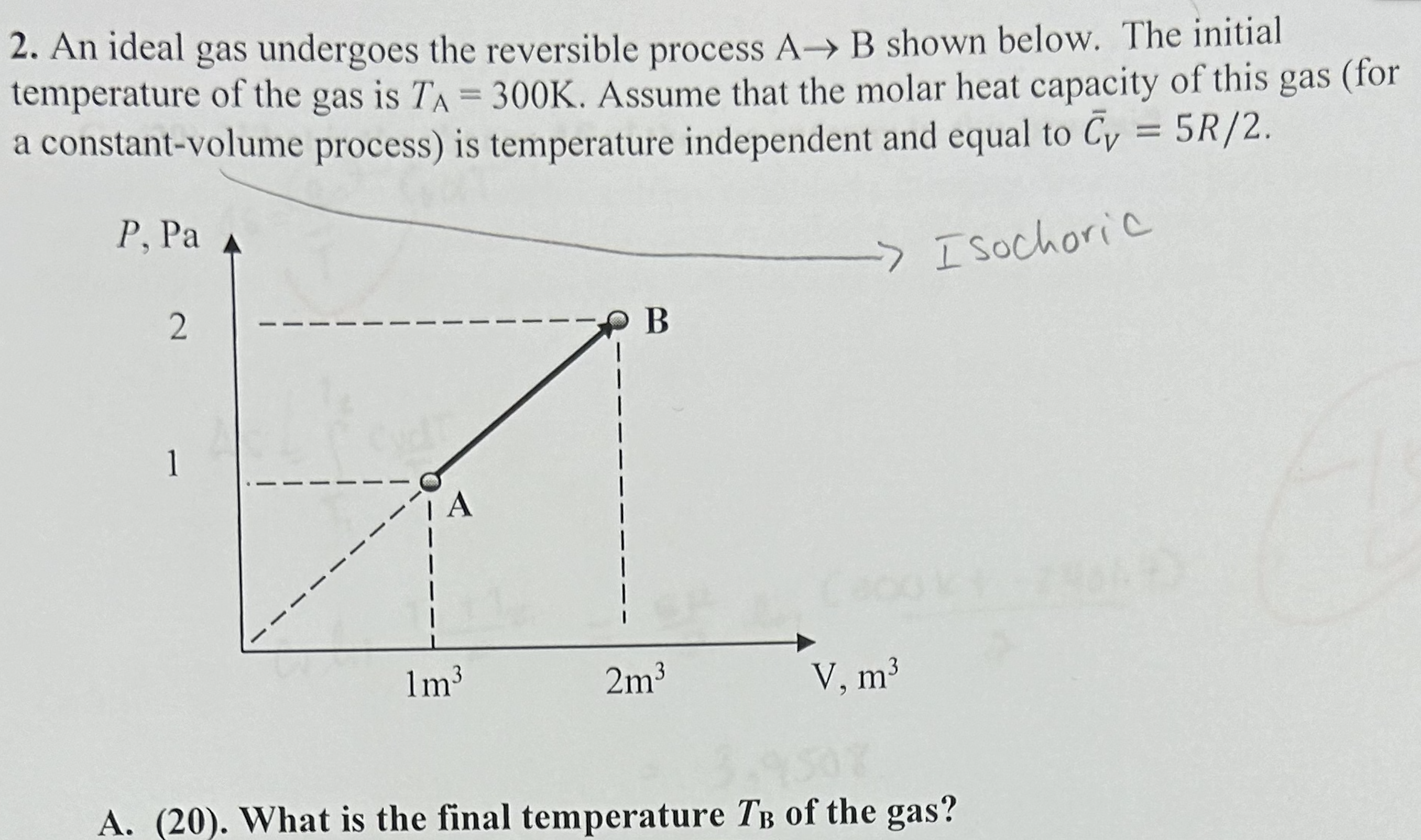



2. An ideal gas undergoes the reversible process A B shown below. The initial temperature of the gas is TA = 300K. Assume that the molar heat capacity of this gas (for a constant-volume process) is temperature independent and equal to Cy = 5R/2. P, Pa 2 -> Isochoric B 1 1m 2m V, m 9507 A. (20). What is the final temperature TB of the gas? 4. A vessel contains n moles of an ideal gas 1 and 2 moles of ideal gas 2 separated by a wall. Both gases are at the same pressure P and temperature T equal to the temperature of the surroundings. The vessel is not thermally insulated from the surroundings. T n2 P, T P, T A. (35) Calculate the change AS of the entropy of the gases after the wall is removed and the gases are mixed. 3(50). A cup of hot coffee at T = 360K is brought to the classroom, whose temperature is T = 300K. The heat capacity of the coffee in the cup is Cp = 400J/K, and the heat capacity of the cup itself is negligible. Estimate the change of the entropy of the Universe resulting from the coffee getting cold and attaining the room temperature. For the purpose of this problem the Universe = coffee + surroundings, where you can think of the surroundings as a giant body (of infinitely large heat capacity) at T = T. 2. 5* (70 extra credit points). A balloon filled with hot air at 7=400K and P = 1 atm is released at sea level and rises until it stops h meters above sea level. The balloon is made from a weightless, rigid material that does not conduct heat such that the volume of the balloon remains constant, and there is no the heat exchange between the balloon and the surroundings. The atmosphere is an ideal gas whose temperature is constant and equal to T = 300K at all elevations. Also assume that the atmospheric pressure changes with the elevation h above sea level according to the barometric formula (derived in the class): P=P exp(-Mgh/RT), where Po= 1 atm and the average molar mass of air is M = 29 g/mol. (Yes, this is the balloon from HW1). Estimate the change of the entropy of the surroundings (i.e., the atmosphere) as a result of this process (i.e. after the balloon stops rising).
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


