
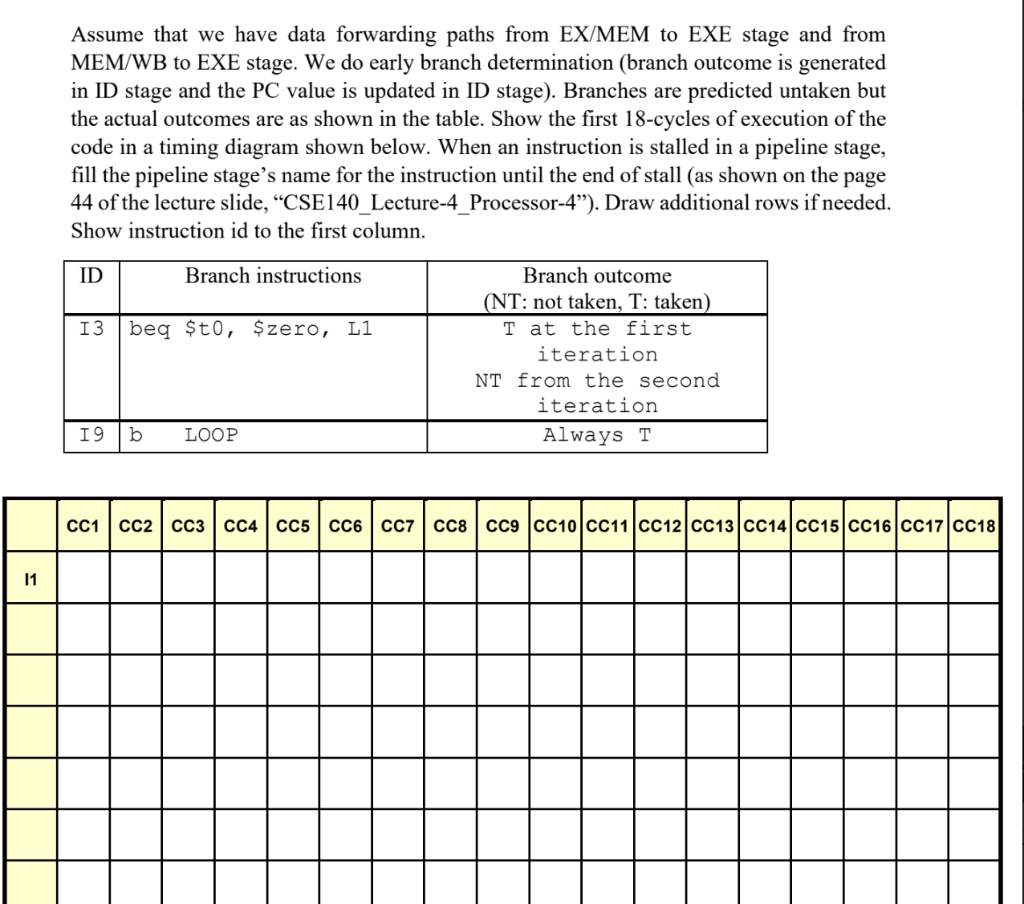
2. Consider the following code. LOOP: 11: 12: 13: 14: 15: 16: 17: 18: 19: 110: lw $a0, 0 ($sp) slti $t0, $a0, 1 beg $t0, $zero, L1 addi $v0, $zero, 1 addi $sp, $sp, 8 lw $ra, 4 ($sp) addi $t4, $ra, 8 SW $t4, 0($t1) b LOOP add $t4, $t4, $t3 L1: Assume that we have data forwarding paths from EX/MEM to EXE stage and from MEM/WB to EXE stage. We do early branch determination (branch outcome is generated in ID stage and the PC value is updated in ID stage). Branches are predicted untaken but the actual outcomes are as shown in the table. Show the first 18-cycles of execution of the code in a timing diagram shown below. When an instruction is stalled in a pipeline stage, fill the pipeline stage's name for the instruction until the end of stall (as shown on the page 44 of the lecture slide, CSE140_Lecture-4_Processor-4). Draw additional rows if needed. Show instruction id to the first column. ID Branch instructions 13 beg $t0, $zero, L1 Branch outcome (NT: not taken, T: taken) T at the first iteration NT from the second iteration Always T 19 b LOOP CC1 CC2 C3 CC4 CC5CC6C07 CC8CC9 CC10 CC11 CC12 CC13 CC14 CC15 CC16 CC17CC18 11 2. Consider the following code. LOOP: 11: 12: 13: 14: 15: 16: 17: 18: 19: 110: lw $a0, 0 ($sp) slti $t0, $a0, 1 beg $t0, $zero, L1 addi $v0, $zero, 1 addi $sp, $sp, 8 lw $ra, 4 ($sp) addi $t4, $ra, 8 SW $t4, 0($t1) b LOOP add $t4, $t4, $t3 L1: Assume that we have data forwarding paths from EX/MEM to EXE stage and from MEM/WB to EXE stage. We do early branch determination (branch outcome is generated in ID stage and the PC value is updated in ID stage). Branches are predicted untaken but the actual outcomes are as shown in the table. Show the first 18-cycles of execution of the code in a timing diagram shown below. When an instruction is stalled in a pipeline stage, fill the pipeline stage's name for the instruction until the end of stall (as shown on the page 44 of the lecture slide, CSE140_Lecture-4_Processor-4). Draw additional rows if needed. Show instruction id to the first column. ID Branch instructions 13 beg $t0, $zero, L1 Branch outcome (NT: not taken, T: taken) T at the first iteration NT from the second iteration Always T 19 b LOOP CC1 CC2 C3 CC4 CC5CC6C07 CC8CC9 CC10 CC11 CC12 CC13 CC14 CC15 CC16 CC17CC18 11








