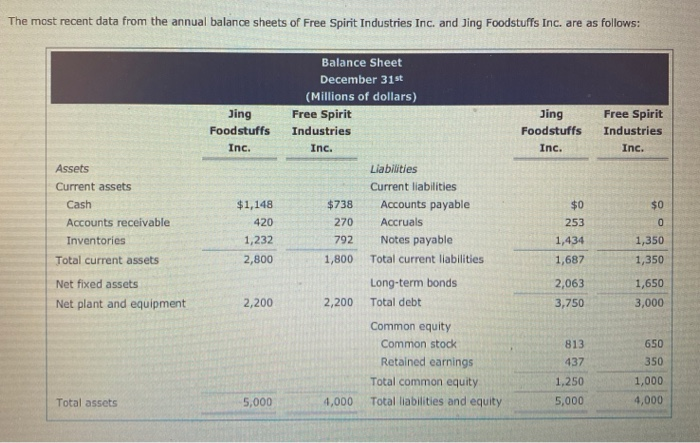
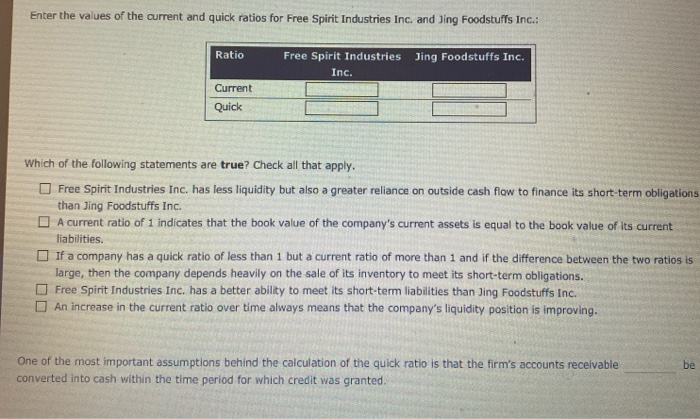
2. Liquidity ratios A liquid asset can be converted quickly to cash with little sacrifice in its value. Which of the following asset classes is generally considered to be the least liquid? O Accounts receivable Inventories Cash O The most recent data from the annual balance sheets of Free Spirit Industries Inc. and Jing Foodstuffs Inc. are as follows: Jing Foodstuffs Inc. Jing Foodstuffs Inc. Free Spirit Industries Inc. Balance Sheet December 31st (Millions of dollars) Free Spirit Industries Inc. Liabilities Current liabilities $738 Accounts payable 270 Accruals 792 Notes payable 1,800 Total current liabilities Long-term bonds 2,200 Total debt $0 $0 Assets Current assets Cash Accounts receivable Inventories Total current assets Net fixed assets Net plant and equipment 253 $1,148 420 1,232 2,800 1,434 1,350 1,350 1,687 2,200 2,063 3,750 1,650 3,000 Common equity Common stock Retained earnings Total common equity Total liabilities and equity 813 437 1,250 5,000 650 350 1,000 4,000 Total assets 5,000 4,000 Enter the values of the current and quick ratios for Free Spirit Industries Inc. and Jing Foodstuffs Inc. Ratio Free Spirit Industries Jing Foodstuffs Inc. Inc. Current Quick Which of the following statements are true? Check all that apply. Free Spirit Industries Inc. has less liquidity but also a greater reliance on outside cash flow to finance its short-term obligations than Jing Foodstuffs Inc. A current ratio of 1 indicates that the book value of the company's current assets is equal to the book value of its current liabilities. If a company has a quick ratio of less than 1 but a current ratio of more than 1 and if the difference between the two ratios is large, then the company depends heavily on the sale of its inventory to meet its short-term obligations. Free Spirit Industries Inc. has a better ability to meet its short-term liabilities than Jing Foodstuffs Inc. An increase in the current ratio over time always means that the company's liquidity position is improving. One of the most important assumptions behind the calculation of the quick ratio is that the firm's accounts receivable converted into cash within the time period for which credit was granted