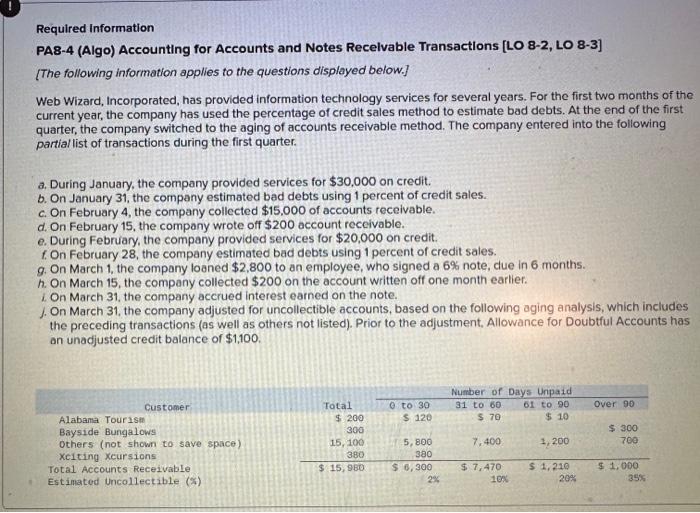
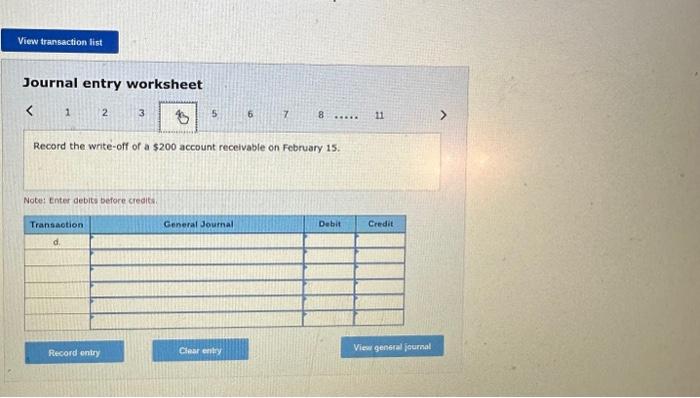
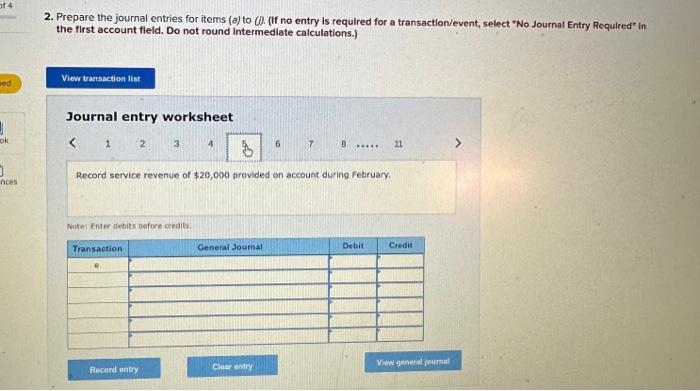
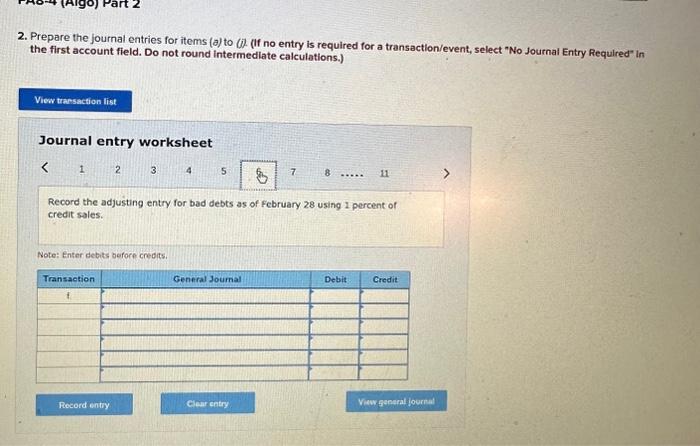
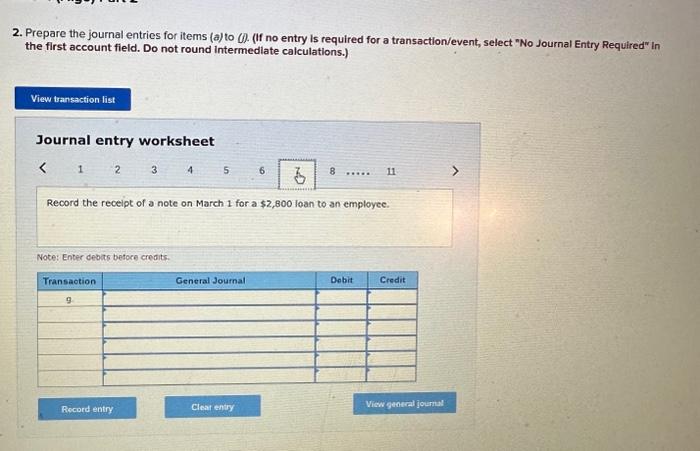
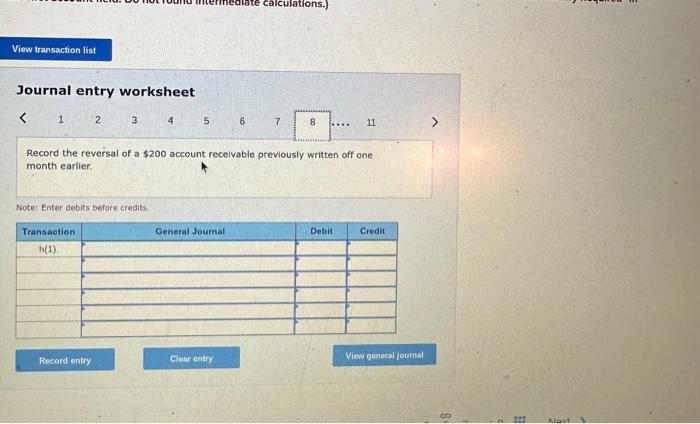
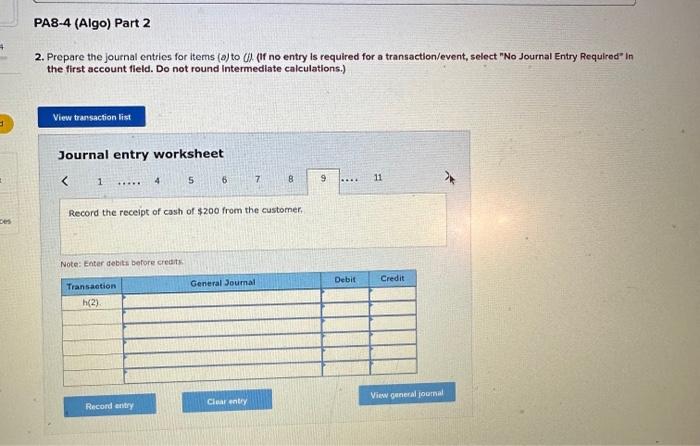
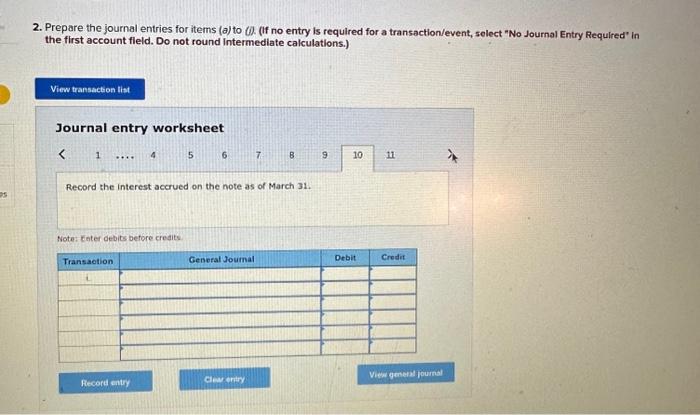
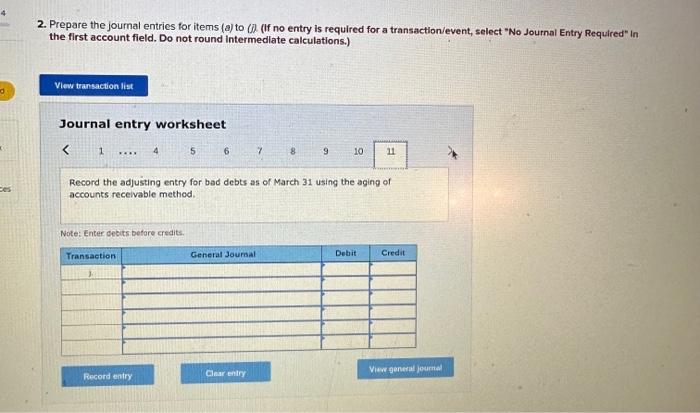
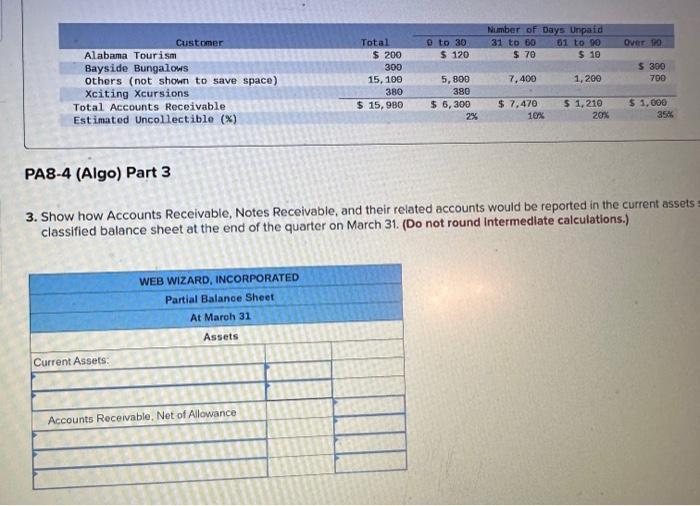
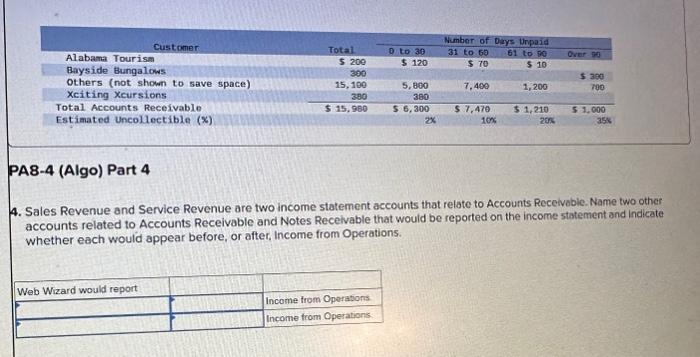
2. Prepare the journal entries for items (a) to (i). (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No Journal Entry Required the first account field. Do not round intermedlate calculations.) Journal entry worksheet Record service revenue of $30,000 sold on account during January. Note: Enter debits before credits. Show how Accounts Receivable, Notes Receivable, and their related accounts would be reported in the current assets classified balance sheet at the end of the quarter on March 31. (Do not round Intermedlate calculations.) Prepare the journal entries for items (a) to (i). (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No Journal Entry Required" in the first account field. Do not round Intermediate calculations.) Journal entry worksheet Note: Enter debits before credits. 2. Prepare the journal entries for items (a) to (j) (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No Journal Entry Required" in the first account field. Do not round Intermedlate calculations.) Note: Enter debits before crearts. Sales Revenue and Service Revenue are two income statement accounts that relate to Accounts Recelvable. Name two other accounts related to Accounts Receivable and Notes Receivable that would be reported on the income statement and indicate whether each would appear before, or after, Income from Operations. 2. Prepare the journal entries for items (a) to (i). (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No Journal Entry Required" In the first account field. Do not round intermedlate calculations.) Journal entry worksheet Note: Enter debits betore credits. Journal entry worksheet 567 8 Record the write-off of a $200 account receivable on February 15 Note: Enter debits before credits. 2. Prepare the journal entries for items (a) to (i). (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No Journal Entry Required" in the first account field. Do not round intermedlate calculations.) Journal entry worksheet Note: Enter debits before credits. 2. Prepare the journal entries for items (a) to (i) (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No Journal Entry Required" in the first account field. Do not round intermediate calculations.) Journal entry worksheet 8 11 Record the adjusting entry for bad debts as of February 28 using 2 percent of credit sales. Note: Enter debits before credits. 2. Prepare the journal entries for items (a) to Q. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No Journal Entry Required" in the first account fleld. Do not round Intermediate calculations.) Journal entry worksheet Note: Fater debits before credits: Journal entry worksheet 1234567 Record the reversal of a $200 account receivable previously written off one month earlier. Note: Enter debits before credits. 2. Prepare the journal entries for items (a) to (il) (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No Journal Entry Required" In the first account field. Do not round intermedlate calculations.) Journal entry worksheet Record the adjusting entry for bad debts as of March 31 using the aging of accounts receivable method. Note: Enter debits betore credits. Required information PA8-4 (Algo) Accounting for Accounts and Notes Recelvable Transactions [LO 8-2, LO 8-3] [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Web Wizard, Incorporated, has provided information technology services for several years. For the first two months of the current year, the company has used the percentage of credit sales method to estimate bad debts. At the end of the first quarter, the company switched to the aging of accounts receivable method. The company entered into the following partial list of transactions during the first quarter. a. During January, the company provided services for $30,000 on credit. b. On January 31, the company estimated bad debts using 1 percent of credit sales. c. On February 4 , the company collected $15.000 of accounts teceivable. d. On February 15 , the company wrote off $200 account receivable. e. During February, the company provided services for $20,000 on credit. f. On February 28 , the company estimated bad debts using 1 percent of credit sales. g. On March 1, the company loaned $2,800 to an employee, who signed a 6% note, due in 6 months. h. On March 15, the company collected $200 on the account written off one month earlier. i. On March 31, the company accrued interest earned on the note. 1. On March 31, the company adjusted for uncollectible accounts, based on the following aging analysis, which includes the preceding transactions (as well as others not listed). Prior to the adjustment. Allowance for Doubtful Accounts has an unadjusted credit balance of $1,100