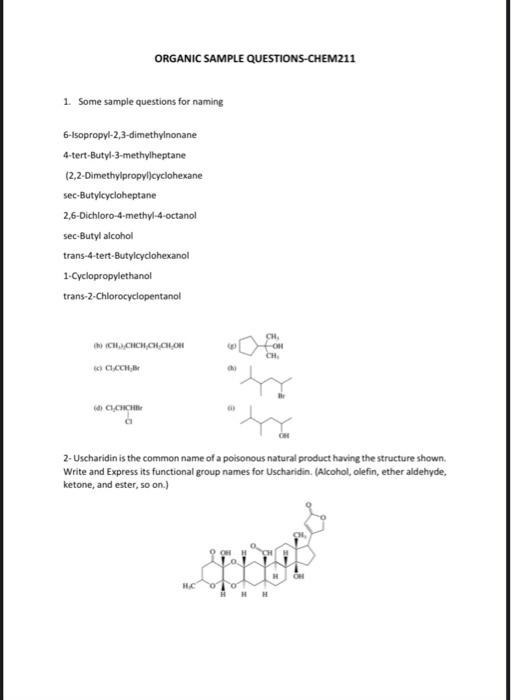
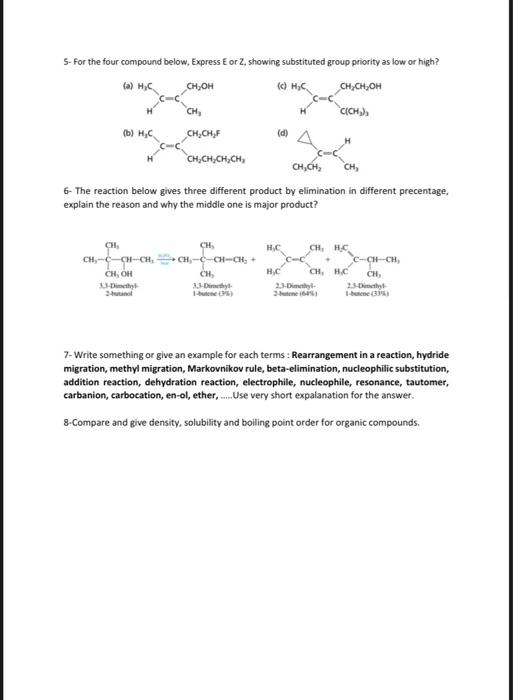
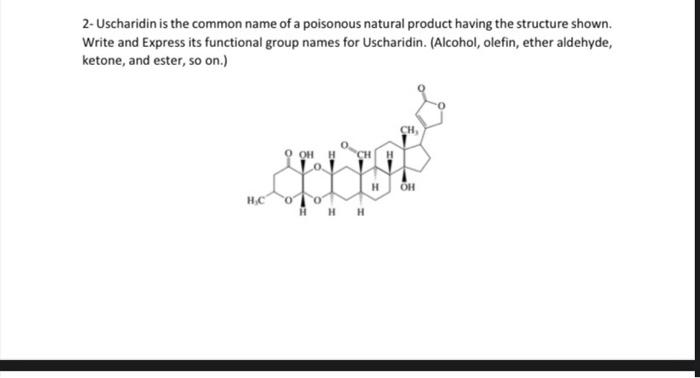
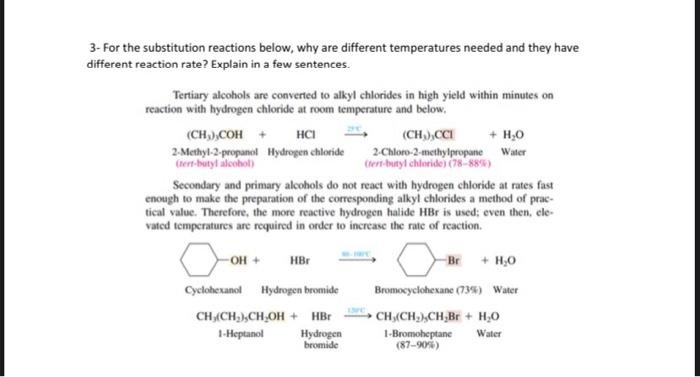
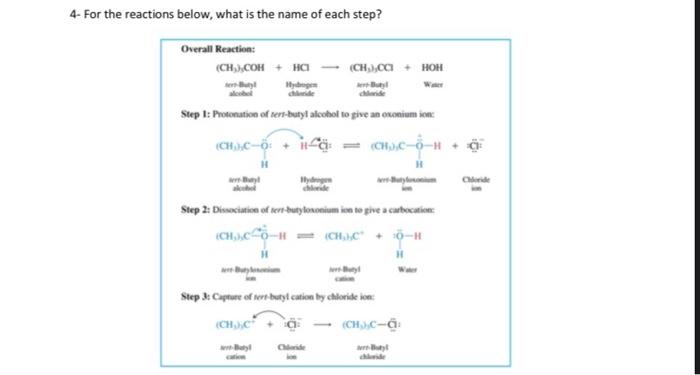
2- Uscharidin is the common name of a poisonous natural product having the structure shown. Write and Express its functional group names for Uscharidin. (Alcohol, olefin, ether aldehyde, ketone, and ester, so on.) 3. For the substitution reactions below, why are different temperatures needed and they have different reaction rate? Explain in a few sentences. Tertiary alcobols are canvened to alkyl chlorides in Myh yicld within minutes ce reaction with hydrogen chloride at foom inmperaturt and briow. Secondary and grimary alcobols do ave react with bydrogen dllorile at nates fast cocogh to make the porparation of the coeresponding alkyl dikides a methad of practical valoe. Therefore, the more reactive hydrogen halide Mill is wed; even then. elevaled temperaheres art requirol in onder bo increase the rats of ncactice. 4. For the reactions below, what is the name of each step? 5- For the four compound below, Express E or Z, showing substituted group priority as low or high? (a) ( (b) (d) 6- The reaction below gives three different product by elimination in different precentage, explain the reason and why the middle one is major product? 7- Write something or give an example for each terms: Rearrangement in a reaction, hydride migration, methyl migration, Markovnikov rule, beta-elimination, nucleophilic substitution, addition reaction, dehydration reaction, electrophile, nucleophile, resonance, tautomer, carbanion, carbocation, en-ol, ether, Use very short expalanation for the answer. 8-Compare and give density, solubility and boiling point order for organic compounds. 2- Uscharidin is the common name of a poisonous natural product having the structure shown. Write and Express its functional group names for Uscharidin. (Alcohol, olefin, ether aldehyde, ketone, and ester, so on.) 3- For the substitution reactions below, why are different temperatures needed and they have different reaction rate? Explain in a few sentences. Tertiary alcohols are converted to alkyl chlorides in high yield within minutes on reaction with hydrogen chloride at room temperature and below. Secondary and primary alcohols do not react with hydrogen chloride at rates fast enough to make the preparation of the corresponding alkyl chlorides a method of practical value. Therefore, the more reactive hydrogen halide HBr is used; even then, elevated temperatures are required in order to increase the rate of reaction. 4- For the reactions below, what is the name of each step? Overall Reaction: (CH3)3COH+HC(CH3)3CCO+HOHtersAlafyl Step I: Photonation of tert-buryl alcohol to give an exonium inne Step 2: Diswociation of terthutylosonium in te give a carbocation: Step 3: Captare of Nert-buty cation by claloride ion