Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
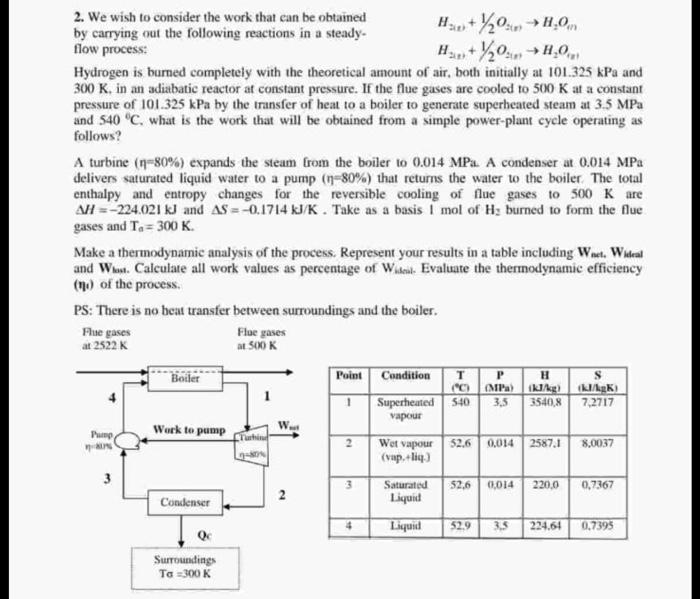
2. We wish to consider the work that can be obtained by carrying out the following reactions in a steady- [ egin{array}{l} mathrm{H}_{2(n)}+1 / 2
2. We wish to consider the work that can be obtained by carrying out the following reactions in a steady- [ egin{array}{l} mathrm{H}_{2(n)}+1 / 2 mathrm{O}_{2(n)} ightarrow mathrm{H}_{2} mathrm{O}_{m} \ mathrm{H}_{2(n)}+1 / 2 mathrm{O}_{2(n)} ightarrow mathrm{H}_{2} mathrm{O}_{i n} end{array} ] flow process: [ mathrm{H}_{2(n)}+1 / 2 mathrm{O}_{-(n)} ightarrow mathrm{H}_{2} mathrm{O}_{(n)} ] Hydrogen is burned completely with the theoretical amount of air, both initially at ( 101.325 mathrm{kPa} ) and ( 300 mathrm{~K} ), in an adiabatic reactor at constant pressure. If the flue gases are cooled to ( 500 mathrm{~K} ) at a constant pressure of ( 101.325 mathrm{kPa} ) by the transfer of heat to a boiler to generate superheated steam at ( 3.5 mathrm{MPa} ) and ( 540^{circ} mathrm{C} ), what is the work that will be obtained from a simple power-plant cycle operating as follows? A turbine ( (eta=80 %) ) expands the steam from the boiler to ( 0.014 mathrm{MPa} ). A condenser at ( 0.014 mathrm{MPa} ) delivers saturated liquid water to a pump ( (eta=80 %) ) that returns the water to the boiler. The total enthalpy and entropy changes for the reversible cooling of flue gases to ( 500 mathrm{~K} ) are ( Delta H=-224.021 mathrm{~kJ} ) and ( Delta S=-0.1714 mathrm{~kJ} / mathrm{K} ). Take as a basis ( 1 mathrm{~mol} ) of ( mathrm{H}_{2} ) burned to form the flue gases and ( mathrm{T}_{a}=300 mathrm{~K} ). Make a thermodynamic analysis of the process. Represent your results in a table including ( mathbf{W}_{ ext {net. }} mathbf{W}_{ ext {ideal }} ) and ( mathbf{W}_{ ext {lost. }} ) Calculate all work values as percentage of ( W_{ ext {iseal. }} ). Evaluate the thermodynamic efficiency (II) of the process. PS: There is no beat transfer between surroundings and the boiler.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


