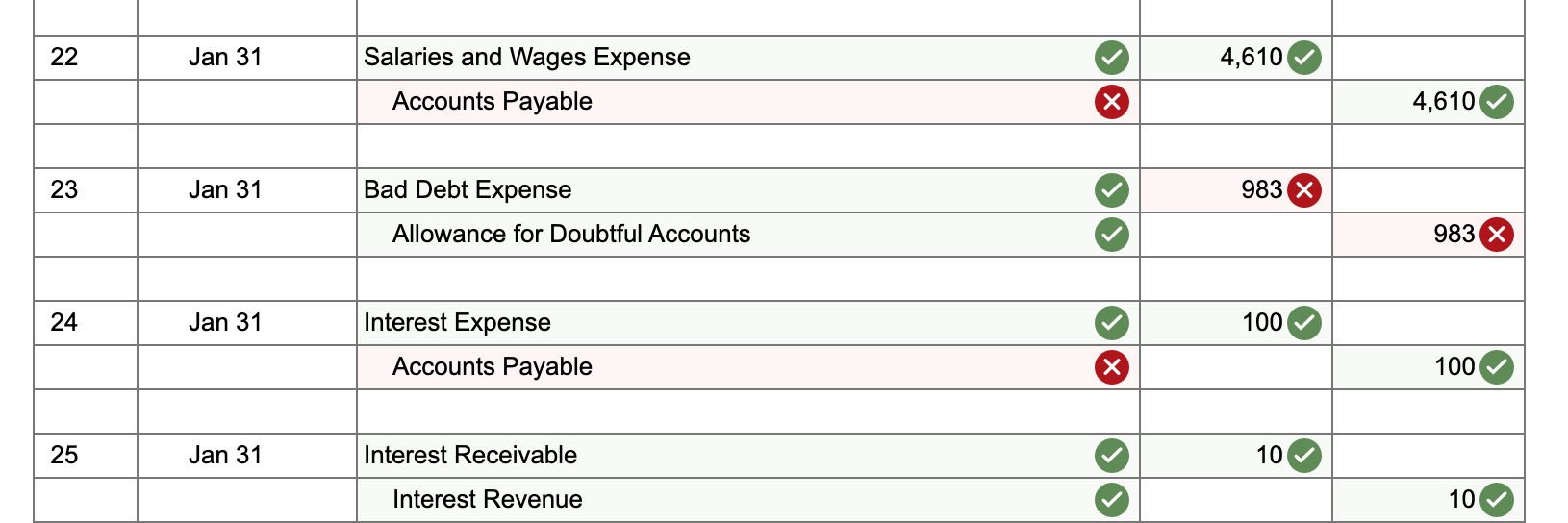

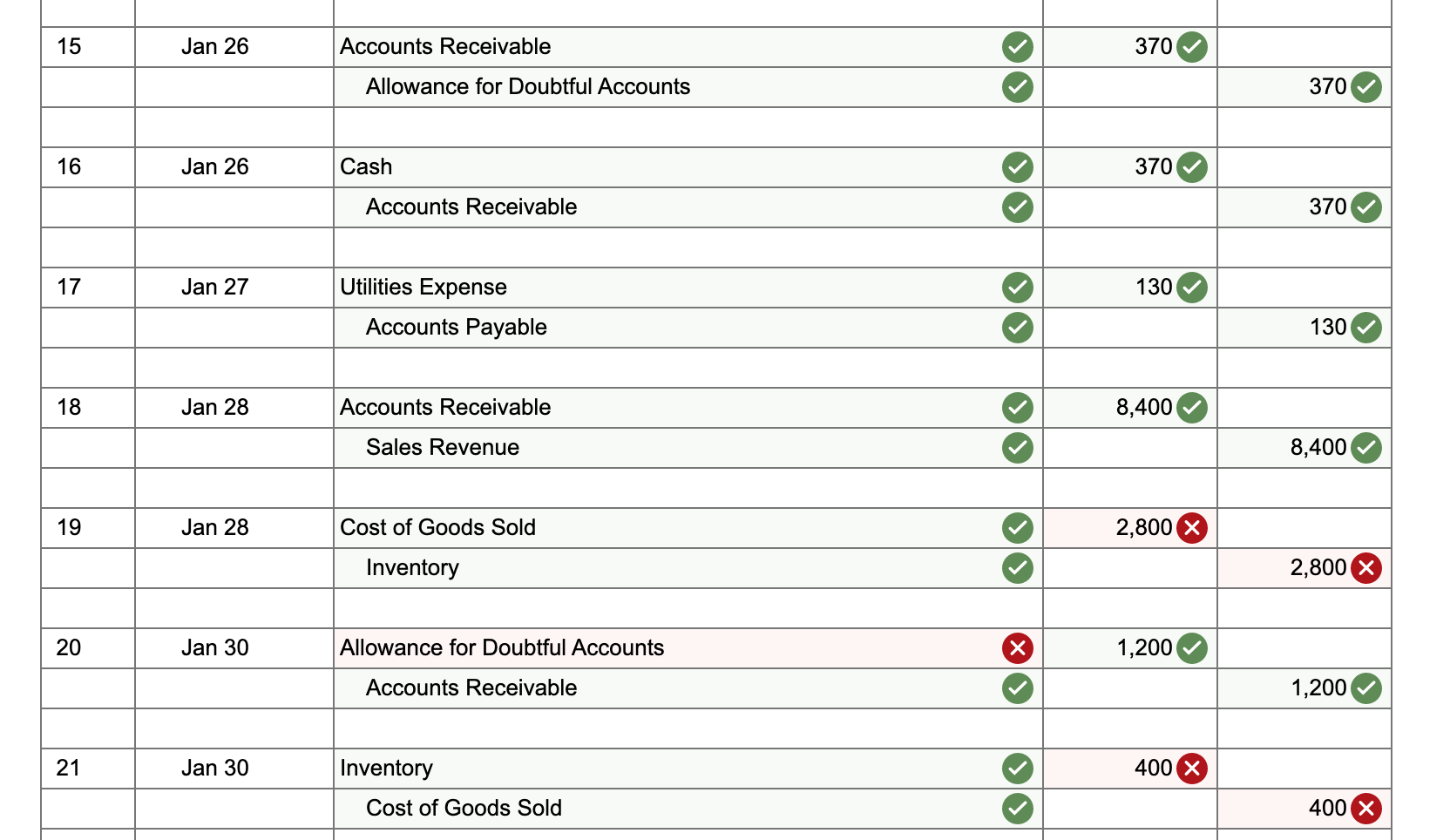

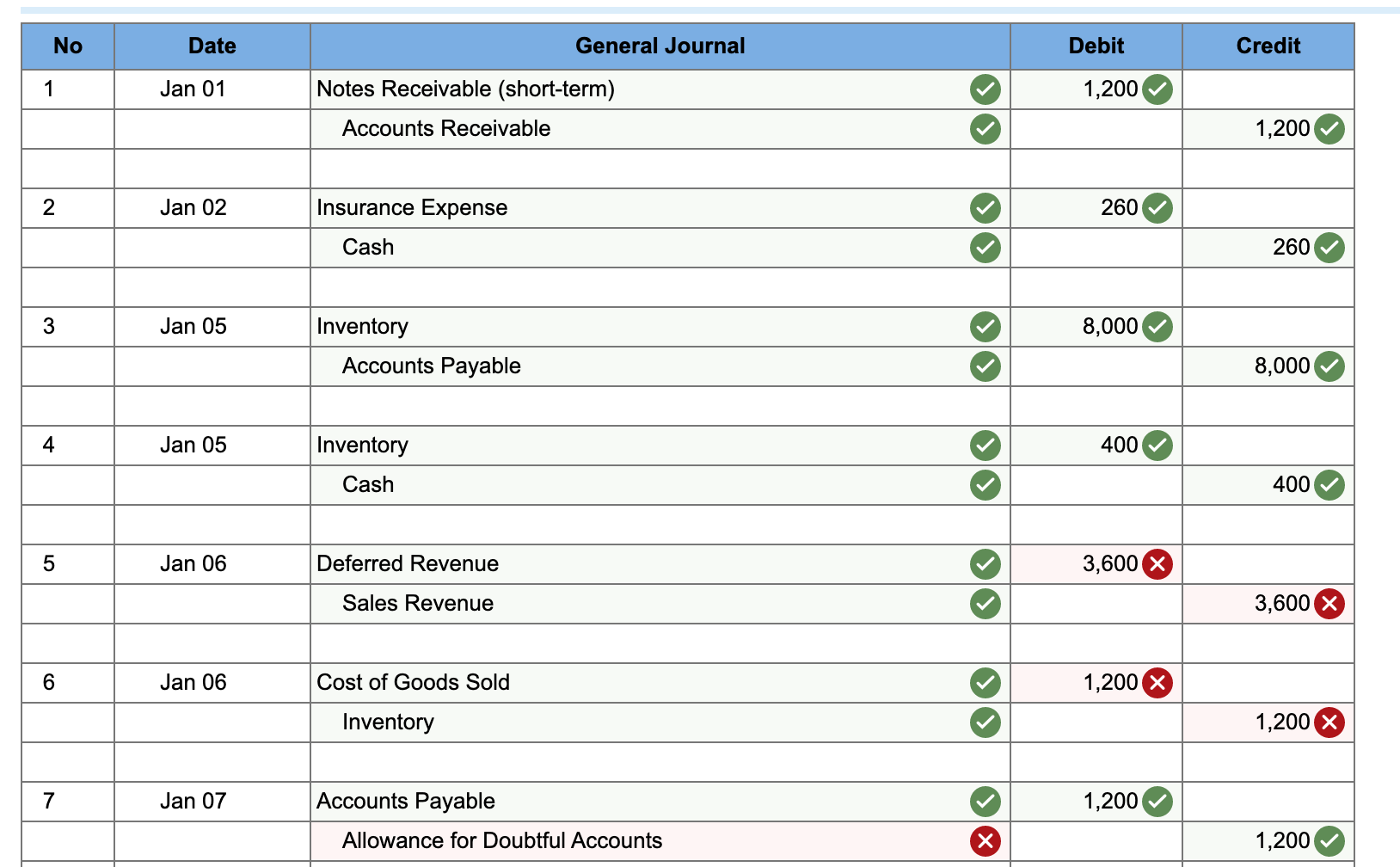
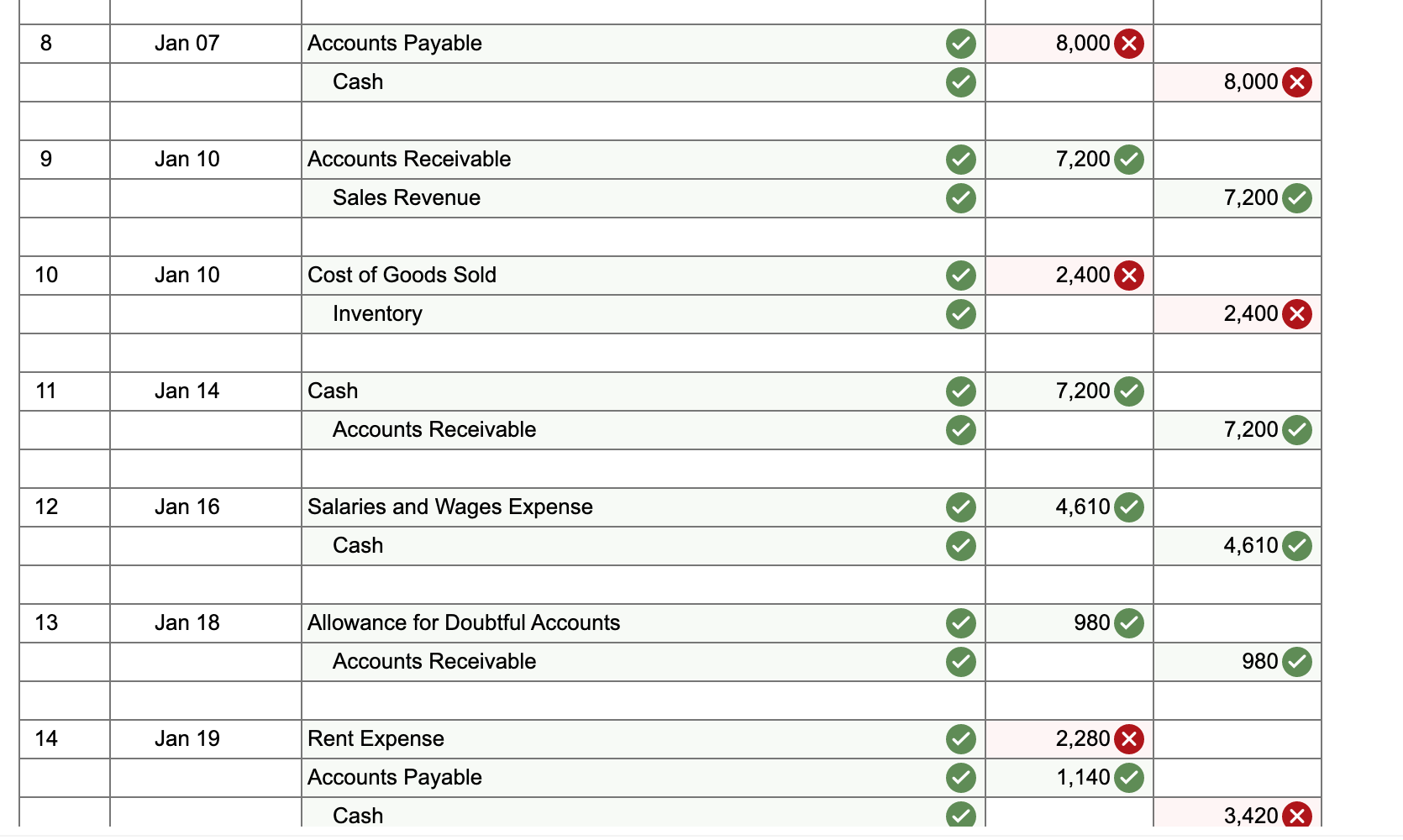
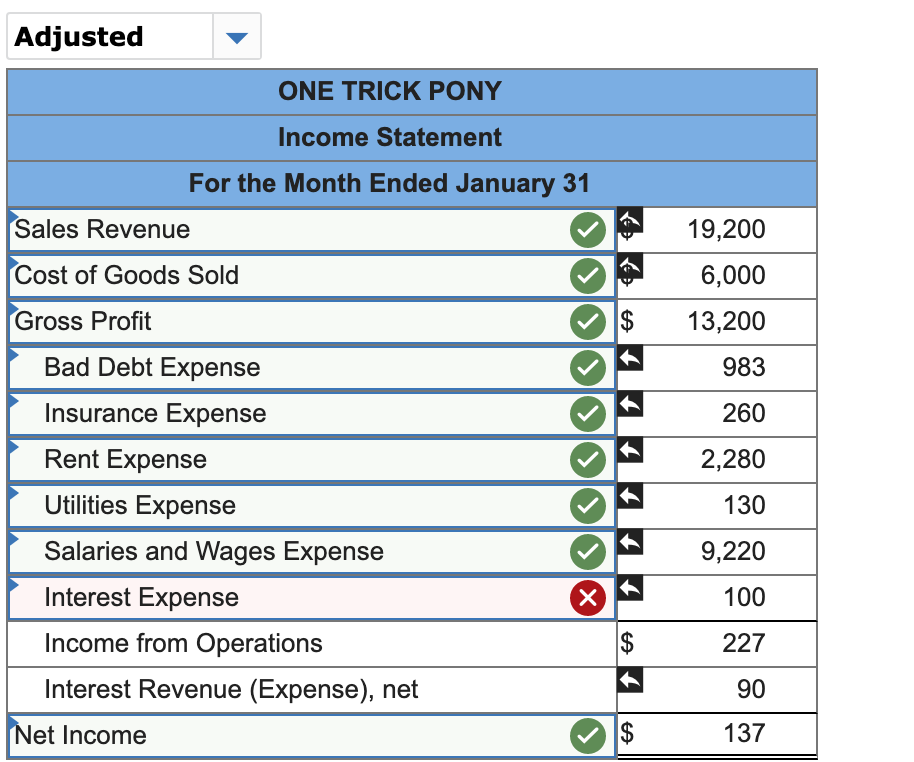
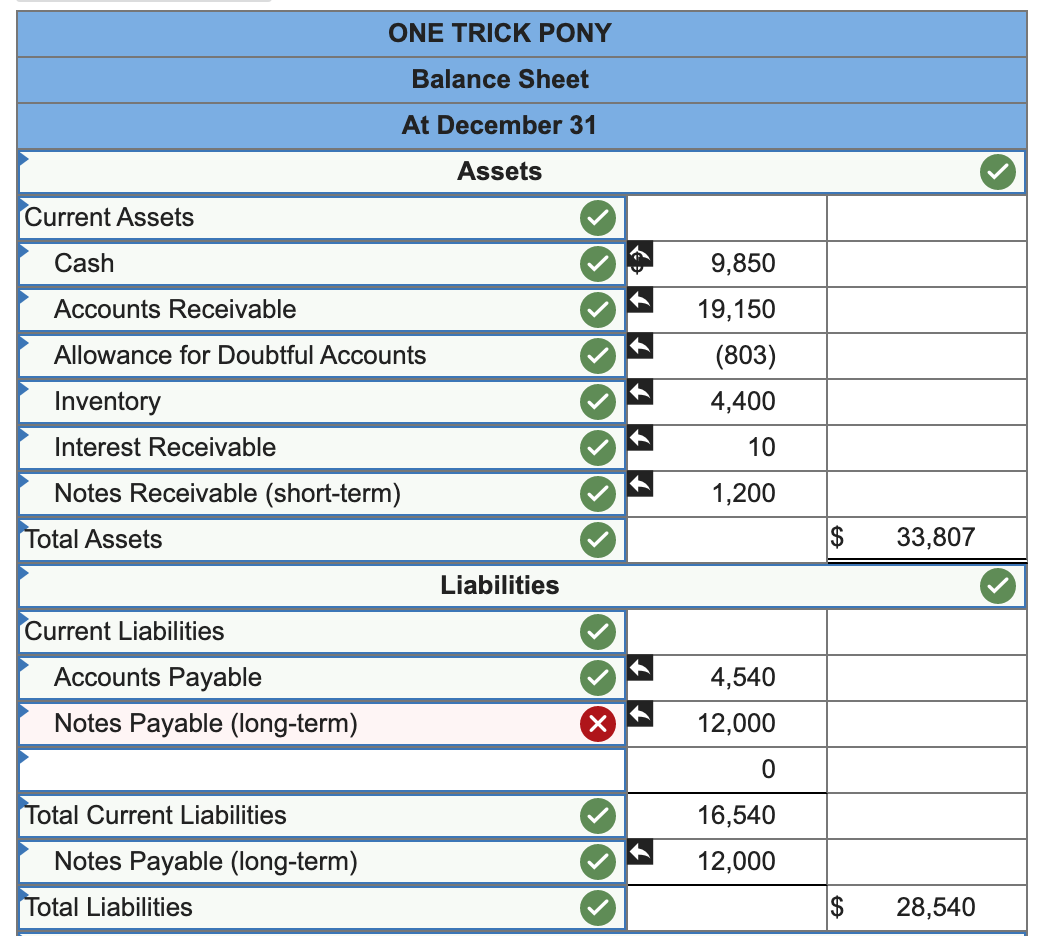
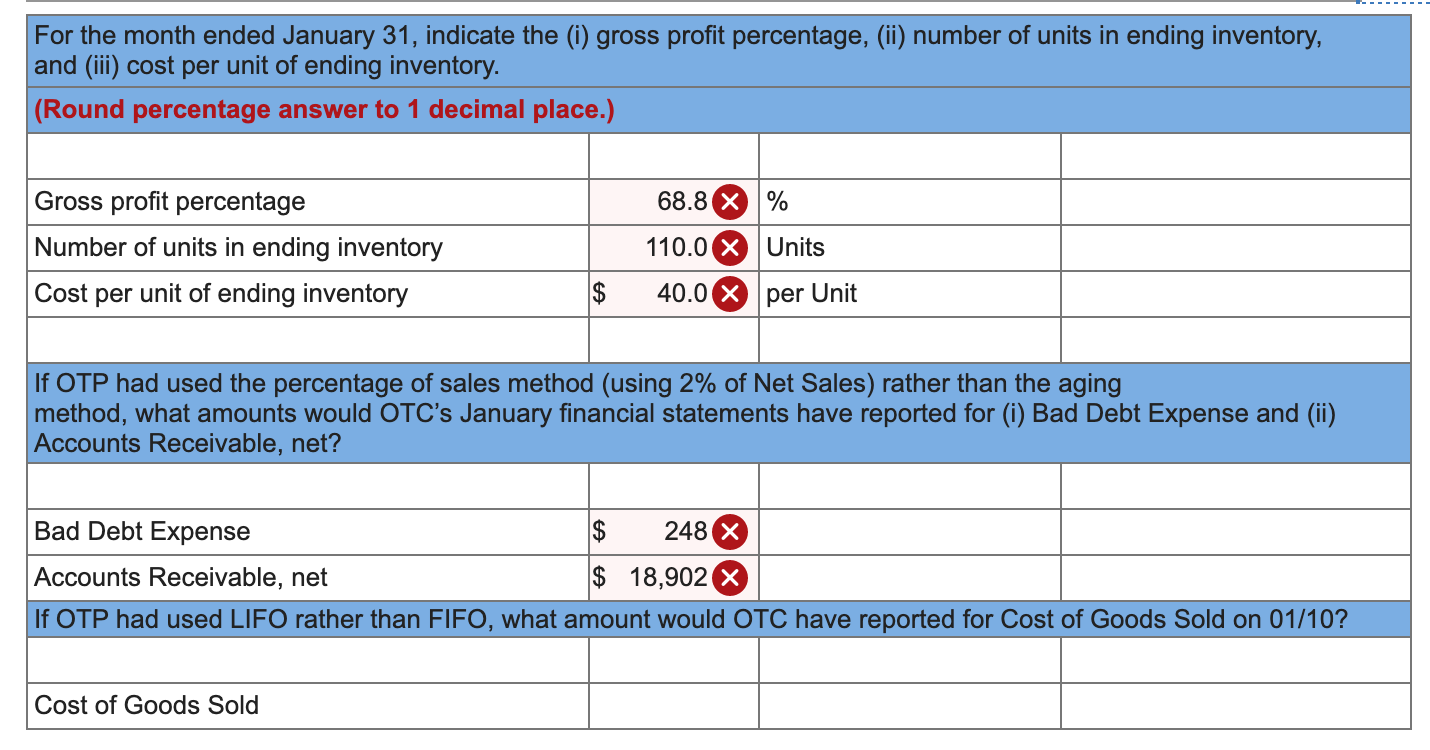
22 Jan 31 4,610 Salaries and Wages Expense Accounts Payable 4,610 23 Jan 31 983 Bad Debt Expense Allowance for Doubtful Accounts 983 x 24 Jan 31 100 Interest Expense Accounts Payable 100 25 Jan 31 Interest Receivable 10 Interest Revenue 10 One Trick Pony (OTP) incorporated and began operations near the end of the year, resulting in the following post-closing balances at December 31: Cash Accounts Receivable Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Inventories Deferred Revenue (40 units) Accounts Payable Note Payable (long-term) Common Stock Retained Earnings $ 18,970 14,130 430* 2,000 4,800 2,040 12,000 10,900 4,930 * credit balance. The following information is relevant to the first month of operations in the following year: OTP will sell inventory at $120 per unit. OTP's January 1 inventory balance consists of 50 units at a total cost of $2,000. OTP's policy is to use the FIFO method, recorded using a perpetual inventory system. In December, OTP received a $4,800 payment for 40 units OTP is to deliver in January; this obligation was recorded in Deferred Revenue. Rent of $1,140 was unpaid and recorded in Accounts Payable at December 31. OTP's note payable matures in three years, and accrues interest at a 10% annual rate. 15 Jan 26 Accounts Receivable 370 Allowance for Doubtful Accounts 370 16 Jan 26 Cash 370 Accounts Receivable 370 17 Jan 27 130 Utilities Expense Accounts Payable 130 18 Jan 28 Accounts Receivable 8,400 Sales Revenue 8,400 19 Jan 28 Cost of Goods Sold 2,800 Inventory 2,800 20 Jan 30 Allowance for Doubtful Accounts x 1,200 Accounts Receivable 1,200 21 Jan 30 400 x Inventory Cost of Goods Sold 400 Return to January 11 C11SALLIUIIS a. Included in OTP's January 1 Accounts Receivable balance is a $1,200 balance due from Jeff Letrotski. Jeff is having cash flow problems and cannot pay the $1,200 balance at this time. On 01/01, OTP arranges with Jeff to convert the $1,200 balance to a six- month note, at 10% annual interest. Jeff signs the promissory note, which indicates the principal and all interest will be due and payable to OTP on July 1 of this year. b. OTP paid a $260 insurance premium on 01/02, covering the month of January; the payment is recorded directly as an expense. C. OTP purchased an additional 200 units of inventory from a supplier on account on 01/05 at a total cost of $8,000, with terms n/30. d. OTP paid a courier $400 cash on 01/05 for same-day delivery of the 200 units of inventory. e. The 40 units that OTP's customer paid for in advance in December are delivered to the customer on 01/06. f. On 01/07, OTP received a purchase allowance of $1,200 on account, and then paid the amount necessary to settle the balance owed to the supplier for the 1/05 purchase of inventory (in c). g. Sales of 60 units of inventory occurring during the period of 01/0701/10 are recorded on 01/10. The sales terms are n/30. h. Collected payments on 01/14 from sales to customers recorded on 01/10. i. OTP paid the first 2 weeks' wages to the employees on 01/16. The total paid is $4,610. j. Wrote off a $980 customer's account balance on 01/18. OTP uses the allowance method, not the direct write-off method. k. Paid $2,280 on 01/19 for December and January rent. See the earlier bullets regarding the December portion. The January portion will expire soon, so it is charged directly to expense. 1. OTP recovered $370 cash on 01/26 from the customer whose account had previously been written off on 01/18. m. An unrecorded $130 utility bill for January arrived on 01/27. It is due on 02/15 and will be paid then. n. Sales of 70 units of inventory during the period of 01/10-01/28, with terms n/30, are recorded on 01/28. o. Of the sales recorded on 01/28, 10 units are returned to OTP on 01/30. The inventory is not damaged and can be resold. OTP charges sales returns directly against Sales Revenue. p. On 01/31, OTP records the $4,610 employee salary that is owed but will be paid February 1. q. OTP uses the aging method to estimate and adjust for uncollectible accounts on 01/31. All of OTP's accounts receivable fall into a single aging category, for which 10% is estimated to be uncollectible. (Update the balances of both relevant accounts prior to determining the appropriate adjustment.) r. Accrue interest for January on the note payable on 01/31. s. Accrue interest for January on Jeff Letrotski's note on 01/31 (see a). No Date General Journal Debit Credit 1 Jan 01 Notes Receivable (short-term) 1,200 Accounts Receivable 1,200 2 Jan 02 Insurance Expense 260 Cash 260 3 Jan 05 8,000 Inventory Accounts Payable 8,000 Jan 05 Inventory 400 Cash 400 5 Jan 06 Deferred Revenue 3,600 Sales Revenue 3,600 6 Jan 06 Cost of Goods Sold 1,200 Inventory 1,200 X 7 Jan 07 Accounts Payable 1,200 Allowance for Doubtful Accounts 1,200 8 Jan 07 Accounts Payable 8,000 Cash 8,000 9 Jan 10 Accounts Receivable 7,200 Sales Revenue 7,200 10 Jan 10 Cost of Goods Sold 2,400 Inventory 2,400 X 11 Jan 14 Cash 7,200 Accounts Receivable 7,200 12 Jan 16 Salaries and Wages Expense 4,610 Cash 4,610 13 Jan 18 Allowance for Doubtful Accounts 980 Accounts Receivable 980 14 Jan 19 Rent Expense Accounts Payable 2,280 1,140 Cash 3,420 X Adjusted ONE TRICK PONY Income Statement For the Month Ended January 31 Sales Revenue 19,200 Cost of Goods Sold 6,000 Gross Profit $ 13,200 983 260 2,280 Bad Debt Expense Insurance Expense Rent Expense Utilities Expense Salaries and Wages Expense Interest Expense Income from Operations Interest Revenue (Expense), net corror 130 9,220 >IX 100 $ 227 90 Net Income $ 137 ONE TRICK PONY Balance Sheet At December 31 Assets Current Assets Cash Accounts Receivable 9,850 19,150 (803) 4,400 Allowance for Doubtful Accounts T t t T 17 Inventory Interest Receivable 10 Notes Receivable (short-term) 1,200 Total Assets $ 33,807 Liabilities Current Liabilities Accounts Payable Notes Payable (long-term) 4,540 12,000 0 Total Current Liabilities 16,540 Notes Payable (long-term) 12,000 Total Liabilities $ 28,540 For the month ended January 31, indicate the (i) gross profit percentage, (ii) number of units in ending inventory, and (iii) cost per unit of ending inventory. (Round percentage answer to 1 decimal place.) 68.8 X % Gross profit percentage Number of units in ending inventory Cost per unit of ending inventory 110.0 X Units $ 40.0 X per Unit If OTP had used the percentage of sales method (using 2% of Net Sales) rather than the aging method, what amounts would OTC's January financial statements have reported for (i) Bad Debt Expense and (ii) Accounts Receivable, net? Bad Debt Expense $ 248 X Accounts Receivable, net $ 18,902 X If OTP had used LIFO rather than FIFO, what amount would OTC have reported for Cost of Goods Sold on 01/10? Cost of Goods Sold















