Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
3. (30 points) A sample of pure helium gas at 20.0C and a pressure of 6.0 bars is stored in a glass (SiO2) cylindrical

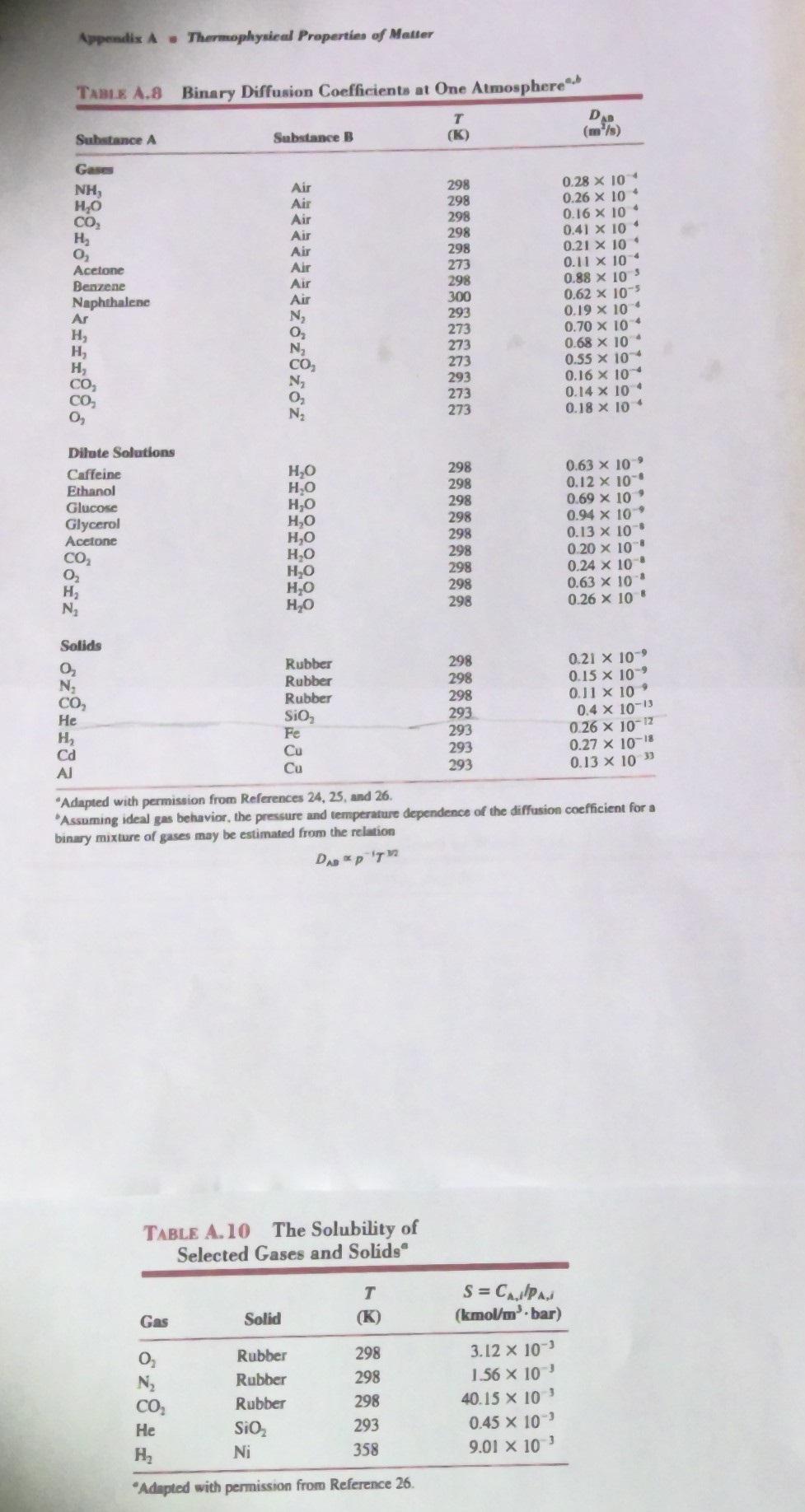
3. (30 points) A sample of pure helium gas at 20.0C and a pressure of 6.0 bars is stored in a glass (SiO2) cylindrical vial with an inner diameter of 25 mm and a wall thickness of 1.00 mm. There is negligible helium at the exterior vial surface. We can assume the helium gas is an ideal gas. Assume diffusion is one-dimensional through the thickness of the vial wall. Analyze the system assuming steady state. There is no generation or consumption of He in the glass. Assume the total molar concentration C is constant and He is dilute in the vial wall. He gas 12 (a) Use Tables A.8 and A. 10 to find the diffusivity and solubility of helium gas in the glass. (b) Using the solubility, determine the helium molar concentration (CA) at the interior surface of the glass (r = r;). What is the helium concentration at the exterior glass surface (r = r)? (e) Starting from the governing Mass Diffusion Equation and using Fick's Law, find the simplified MDE in terms of the helium molar concentration (CA) in the vial glass wall (d) Solve the simplified equation in (e) for the general solution of the concentration profile C(r) in the glass wall of the vial (e) Solve for the symbolic expression of the helium concentration in the vial wall, C^(r) (f) What is the mass transfer rate of helium per unit height (L) of the vial in g/(m/s)? Appendix A Thermophysical Properties of Matter TABLE A.8 Binary Diffusion Coefficients at One Atmosphere T Substance A Substance B (K) DAB (m/s) Gases NH, Air 298 0.28 x 10 HO Air 298 CO Air 298 0.26 x 10 * 0.16 x 10 H Air 298 0.41 x 104 0 Air 298 0.21 x 10' Acetone Air 273 0.11 10 Benzene Air 298 0.88 x 105 Naphthalene Air 300 0.62 x 105 Ar N 293 0.19 10 4 H 0 273 0.70 x 10 H N 273 0.68 x 10 H CO 273 0.55 10 CO N 293 0.16 10 CO 273 0.14 x 104 0 N 273 0.18 10 4 Dilute Solutions Caffeine HO 298 0.63 x 109 Ethanol HO 298 0.12 10 Glucose Glycerol Acetone HO 298 0.69 x 10' HO 298 0.94 x 10' HO 298 0.13 x 10 8612 HO 298 0.20 x 10 HO 298 0.24 x 10 HO 298 0.63 x 10' HO 298 0.26 x 10" Solids 0 Rubber 298 0.21 10 N Rubber 298 0.15 x 109 CO Rubber 298 0.11 x 10' He SiO 293 0.4 10-13 H Cd Al 233 Fe 293 0.26 10-12 Cu 293 0.27 x 10-18 293 0.13 x 10" "Adapted with permission from References 24, 25, and 26. Assuming ideal gas behavior, the pressure and temperature dependence of the diffusion coefficient for a binary mixture of gases may be estimated from the relation DAB PT TABLE A.10 The Solubility of Selected Gases and Solids T Gas Solid (K) S = CAPA (kmol/m bar) 0 Rubber 298 3.12 x 10 N Rubber 298 1.56 x 10 CO Rubber 298 40.15 x 10' He SiO 293 0.45 x 10' H Ni 358 9.01 10 "Adapted with permission from Reference 26.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


