Question
3. Consider an economy with two goods, gizmos and a numeraire commodity. The market for gizmos is perfectly competitive. Each firm in the industry produces
3. Consider an economy with two goods, gizmos and a numeraire commodity. The market for gizmos is perfectly competitive. Each firm in the industry produces gizmos with the same technology and has cost function
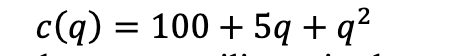
Each consumer has preferences that are quasilinear in the numeraire consumed, with utility function
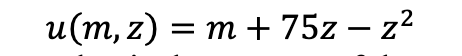 where z is the number of gizmos and m is the amount of the numeraire. a. Assume that there are K consumers in the market. Derive the short-run aggregate demand curve. b. Assume that there are N firms in the market. Derive the short-run aggregate supply curve. c. Derive the short-run market equilibrium price and quantity under the assumption that the market comprises 300 consumers and 30 firms. How much profit does each firm earn? d. What is the long-run equilibrium price and quantity in this market with 300 consumers? How many firms will there be in the market in long-run equilibrium? You should ignore integer problems: a fractional number of firms is permissible. e. Suppose the market comprises 300 consumers and the government wants there to be exactly 70 firms in the industry when it is in long-run equilibrium. In order to implement this policy, the government requires firms to purchase a license for selling gizmos. Once a firm purchases a license, it can sell as many gizmos as it wants, but a firm without a license cannot sell any gizmos. Firms may not share licenses. How much should the government charge for the license?
where z is the number of gizmos and m is the amount of the numeraire. a. Assume that there are K consumers in the market. Derive the short-run aggregate demand curve. b. Assume that there are N firms in the market. Derive the short-run aggregate supply curve. c. Derive the short-run market equilibrium price and quantity under the assumption that the market comprises 300 consumers and 30 firms. How much profit does each firm earn? d. What is the long-run equilibrium price and quantity in this market with 300 consumers? How many firms will there be in the market in long-run equilibrium? You should ignore integer problems: a fractional number of firms is permissible. e. Suppose the market comprises 300 consumers and the government wants there to be exactly 70 firms in the industry when it is in long-run equilibrium. In order to implement this policy, the government requires firms to purchase a license for selling gizmos. Once a firm purchases a license, it can sell as many gizmos as it wants, but a firm without a license cannot sell any gizmos. Firms may not share licenses. How much should the government charge for the license?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


