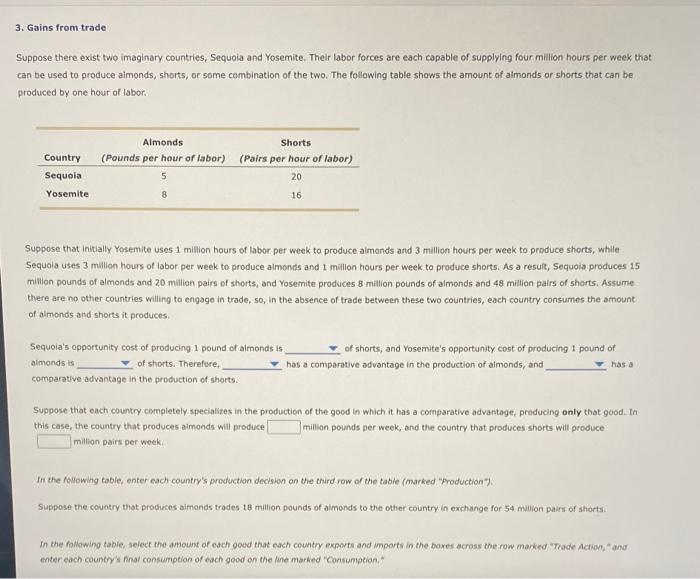
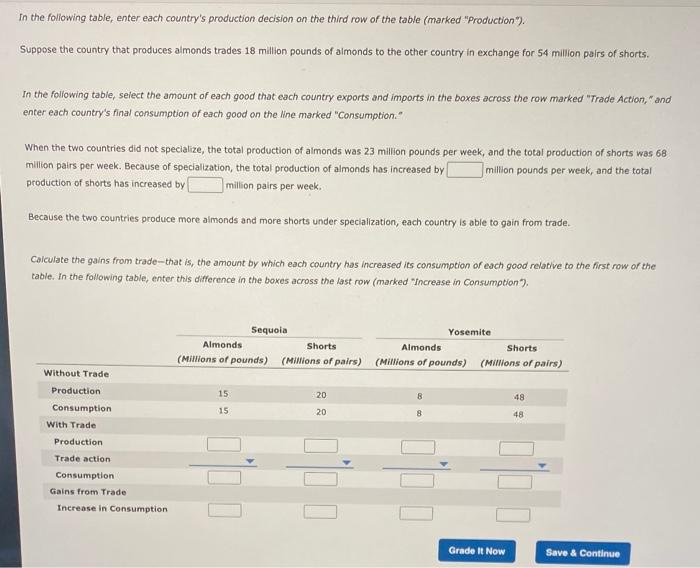
3. Gains from trade Suppose there exist two imaginary countries, Sequoia and Yosemite. Their labor forces are each capable of supplying four million hours per week that can be used to produce aimonds, shorts, or some combination of the two. The following table shows the amount of aimonds or shorts that can be produced by one hour of Iabor. Suppose that initially Yosemite uses 1 million hours of labor per week to produce aimonds and 3 million hours per week to produce shorts, while Sequoia uses 3 million hours of labor per week to produce almonds and 1 millon hours per week to produce shorts. As a resuit, Sequoia produces 15 mililion pounds of almonds and 20 milion pairs of shorts, and Yosemite produces 8 million pounds of aimonds and 48 million pairs of shorts. Assume there are no other countries willing to engage in trade, so, in the absence of trade between these two countries, each country consumes the amount of almonds and shorts it produces. Sequoia's opportunity cost of producing 1 pound of aimonds is of shorts, and Yosemite's opportunity cost of producing 1 pound of almonds is of shorts. Therefore, has a comparative advantage in the production of almonds, and has a comparative advantage in the production of shorts. Suppose that each country completely specializes in the production of the good in which it has a comparative advantoge, producing only that good. In this case, the country that produces aimonds will produce million pounds per week, and the country that produces shorts will produce million pairs per week; In the following table, enter each country's production decision on the third row of the table (marked "Production"). Suppose the country that produces aimonds trades 18 million pounds of almonds to the other country in exchange for 54 million pairs of shorts. In the following tabie, seiect the anount of each pood that each country exports and imports in the bores across the row marked "Trade Action, "and enter each country's final consumption of each good on the line marked "Consumption," in the following table, enter each country's production decision on the third row of the table (marked "Production"). Suppose the country that produces almonds trades 18 million pounds of almonds to the other country in exchange for 54 million pairs of shorts. In the following table, select the amount of each good that each country exports and imports in the boxes across the row marked "Irade Action, "and enter each country's final consumption of each good on the line marked "Consumption." When the two countries did not specialize, the total production of almonds was 23 million pounds per week, and the total production of shorts was 68 milition pairs per week. Because of specialization, the total production of almonds has increased by million pounds per week, and the total production of shorts has increased by million pairs per week. Because the two countries produce more almonds and more shorts under specialization, each country is able to gain from trade. Calculate the gains from trade-that is, the amount by which each country has increased its consumption of each good relative to the first row of the table. In the following table, enter this difference in the boxes across the last row (marked "Increase in Consumption