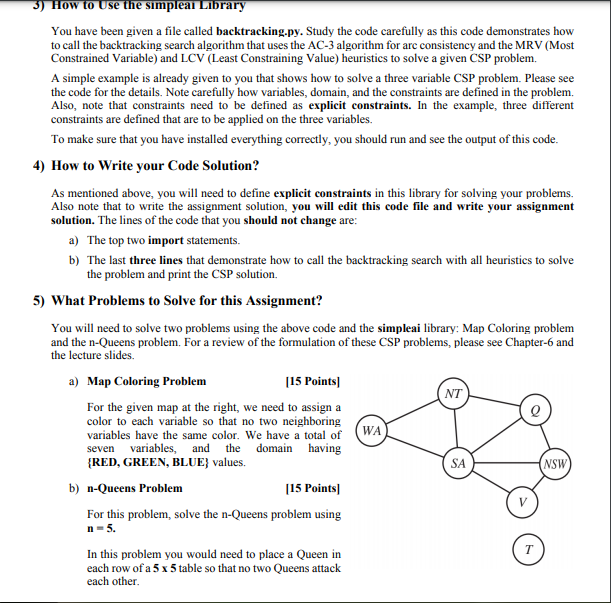
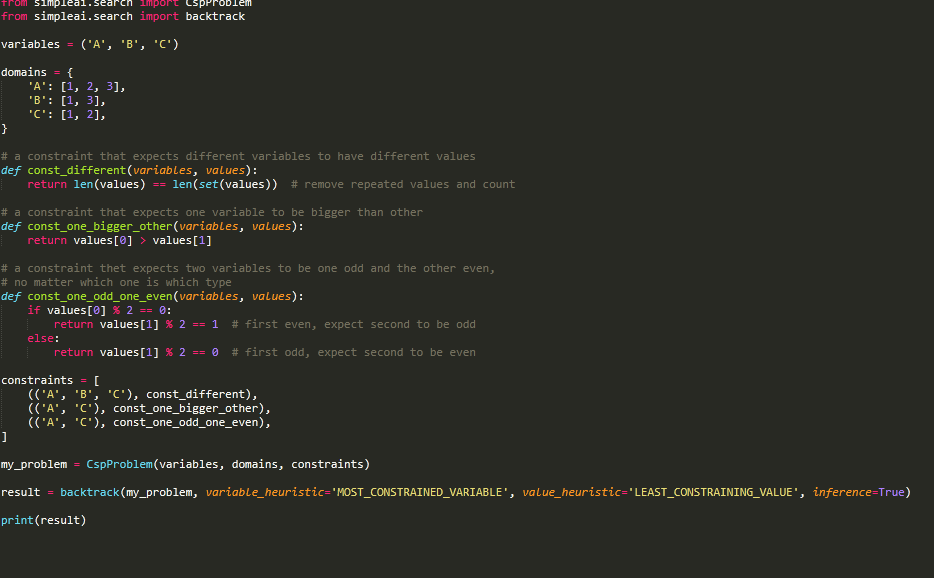
3) How to Use the simpleal Library You have been given a file called backtracking.py. Study the code carefully as this code demonstrates how to call the backtracking search algorithm that uses the AC-3 algorithm for are consistency and the MRV (Most Constrained Variable) and LCV (Least Constraining Value) heuristics to solve a given CSP problem. A simple example is already given to you that shows how to solve a three variable CSP problem. Please see the code for the details. Note carefully how variables, domain, and the constraints are defined in the problem. Also, note that constraints need to be defined as explicit constraints. In the example, three different constraints are defined that are to be applied on the three variables. To make sure that you have installed everything correctly, you should run and see the output of this code. 4) How to Write your Code Solution? As mentioned above, you will need to define explicit constraints in this library for solving your problems. Also note that to write the assignment solution, you will edit this code file and write your assignment solution. The lines of the code that you should not change are: a) The top two import statements. b) The last three lines that demonstrate how to call the backtracking search with all heuristics to solve the problem and print the CSP solution. 5) What Problems to Solve for this Assignment? You will need to solve two problems using the above code and the simpleai library: Map Coloring problem and the n-Queens problem. For a review of the formulation of these CSP problems, please see Chapter-6 and the lecture slides. a) Map Coloring Problem [15 Points NT For the given map at the right, we need to assign a color to each variable so that no two neighboring variables have the same color. We have a total of WA seven variables, and the domain having {RED, GREEN, BLUE) values. SA b) n-Queens Problem [15 Points) For this problem, solve the n-Queens problem using n-5. In this problem you would need to place a Queen in T each row of a 5 x 5 table so that no two Queens attack each other NSW) V pieal.search blem from simpleai.search import backtrack variables = ('A', 'B', 'C") domains { 'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [1, 3], "C': [1, 2], } # a constraint that expects different variables to have different values def const_different (variables, values): return len(values) == len(set(values)) # remove repeated values and count # a constraint that expects one variable to be bigger than other def const_one_bigger_other(variables, values): return values[@] > values[1] # a constraint thet expects two variables to be one odd and the other even, # no matter which one is which type def const_one_odd_one_even(variables, values): if values[@] % 2 == 0: return values[1] % 2 == 1 # first even, expect second to be odd else: return values[1] % 2 == 0 # first odd, expect second to be even constraints = [ (('A', 'B', 'C'), const_different), (('A', 'C"), const_one_bigger_other), (('A', 'C"), const_one_odd_one_even), ] my_problem CspProblem(variables, domains, constraints) result = backtrack(my_problem, variable_heuristic="MOST_CONSTRAINED_VARIABLE', value_heuristic='LEAST_CONSTRAINING_VALUE', inference=True) print(result) 3) How to Use the simpleal Library You have been given a file called backtracking.py. Study the code carefully as this code demonstrates how to call the backtracking search algorithm that uses the AC-3 algorithm for are consistency and the MRV (Most Constrained Variable) and LCV (Least Constraining Value) heuristics to solve a given CSP problem. A simple example is already given to you that shows how to solve a three variable CSP problem. Please see the code for the details. Note carefully how variables, domain, and the constraints are defined in the problem. Also, note that constraints need to be defined as explicit constraints. In the example, three different constraints are defined that are to be applied on the three variables. To make sure that you have installed everything correctly, you should run and see the output of this code. 4) How to Write your Code Solution? As mentioned above, you will need to define explicit constraints in this library for solving your problems. Also note that to write the assignment solution, you will edit this code file and write your assignment solution. The lines of the code that you should not change are: a) The top two import statements. b) The last three lines that demonstrate how to call the backtracking search with all heuristics to solve the problem and print the CSP solution. 5) What Problems to Solve for this Assignment? You will need to solve two problems using the above code and the simpleai library: Map Coloring problem and the n-Queens problem. For a review of the formulation of these CSP problems, please see Chapter-6 and the lecture slides. a) Map Coloring Problem [15 Points NT For the given map at the right, we need to assign a color to each variable so that no two neighboring variables have the same color. We have a total of WA seven variables, and the domain having {RED, GREEN, BLUE) values. SA b) n-Queens Problem [15 Points) For this problem, solve the n-Queens problem using n-5. In this problem you would need to place a Queen in T each row of a 5 x 5 table so that no two Queens attack each other NSW) V pieal.search blem from simpleai.search import backtrack variables = ('A', 'B', 'C") domains { 'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [1, 3], "C': [1, 2], } # a constraint that expects different variables to have different values def const_different (variables, values): return len(values) == len(set(values)) # remove repeated values and count # a constraint that expects one variable to be bigger than other def const_one_bigger_other(variables, values): return values[@] > values[1] # a constraint thet expects two variables to be one odd and the other even, # no matter which one is which type def const_one_odd_one_even(variables, values): if values[@] % 2 == 0: return values[1] % 2 == 1 # first even, expect second to be odd else: return values[1] % 2 == 0 # first odd, expect second to be even constraints = [ (('A', 'B', 'C'), const_different), (('A', 'C"), const_one_bigger_other), (('A', 'C"), const_one_odd_one_even), ] my_problem CspProblem(variables, domains, constraints) result = backtrack(my_problem, variable_heuristic="MOST_CONSTRAINED_VARIABLE', value_heuristic='LEAST_CONSTRAINING_VALUE', inference=True) print(result)








