Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
3. In Figure 3, the spring is initially at the static equilibrium position. Solve the following problems: (a) Select coordinates and obtain kinematic constraint
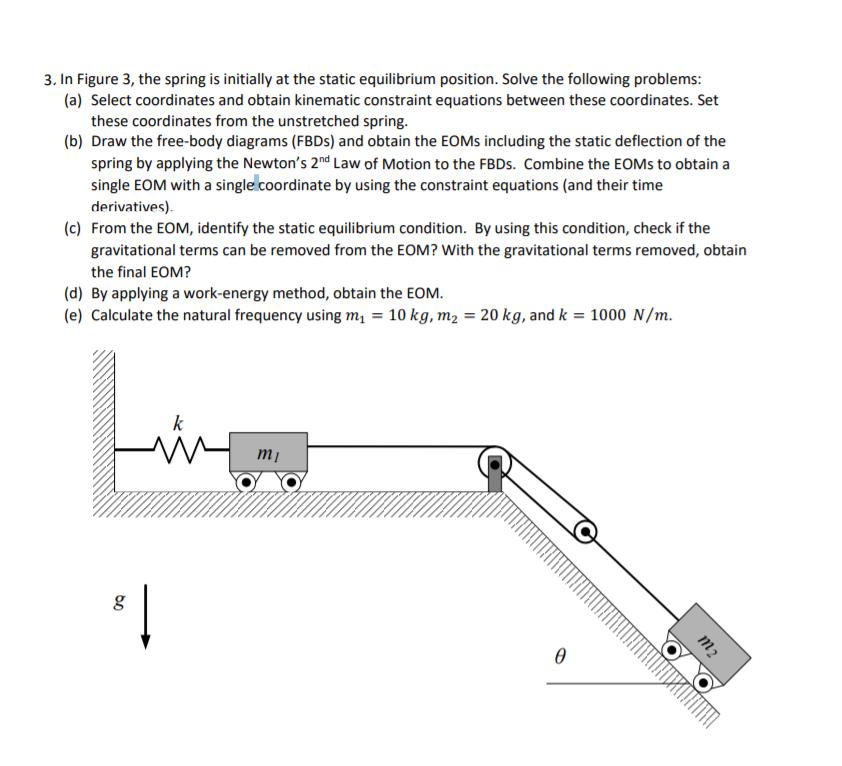
3. In Figure 3, the spring is initially at the static equilibrium position. Solve the following problems: (a) Select coordinates and obtain kinematic constraint equations between these coordinates. Set these coordinates from the unstretched spring. (b) Draw the free-body diagrams (FBDs) and obtain the EOMS including the static deflection of the spring by applying the Newton's 2nd Law of Motion to the FBDs. Combine the EOMs to obtain a single EOM with a single coordinate by using the constraint equations (and their time derivatives). (c) From the EOM, identify the static equilibrium condition. By using this condition, check if the gravitational terms can be removed from the EOM? With the gravitational terms removed, obtain the final EOM? (d) By applying a work-energy method, obtain the EOM. (e) Calculate the natural frequency using m = 10 kg, m = 20 kg, and k = 1000 N/m. g k m 0 m2
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.39 Rating (152 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
a 6 K Lo Mi x 48 mass m moves by x my will move negoud static defl...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


