Question
3. Researchers studying the enzyme glucosamine-6-phosphate synthase have measured the dissociation constant for d-glucosamine-6-phosphate [3.8 x 10 -4 M] and 2-deoxy- d -glucose-6-phosphate [4.6 (0.7)
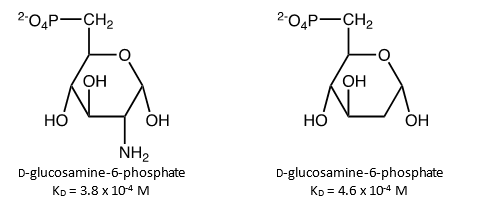
3. Researchers studying the enzyme glucosamine-6-phosphate synthase have measured the dissociation constant for d-glucosamine-6-phosphate [3.8 x 10-4 M] and 2-deoxy- d -glucose-6-phosphate [4.6 (0.7) x 10-2]. Are these values consistent with the hypothesis that the enzyme makes a hydrogen bond with the amino group of glucosamine and that water cannot replace the amine when 2-deoxy- d -glucose-6-phosphate binds? Draw the structures of these sugar derivatives bound to glucosamine-6-phosphate synthase and explain how you came to your conclusion. A typical hydrogen bond in a biomolecule has an energy of ~15 kJ/mol.
Suggestion: Write out the two dissociation reactions. Combine them to show one substrate swapping for the other and determine the free energy change associated with that.
cosamine-6-phosphate D-glucosamine-6-phosphate KD=3.8104M KD=4.6104MStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


