Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
3. Using Excel (or Google sheets), calculate the average and standard deviation of the Virtual Lab and the Real-Life Lab data. You should report


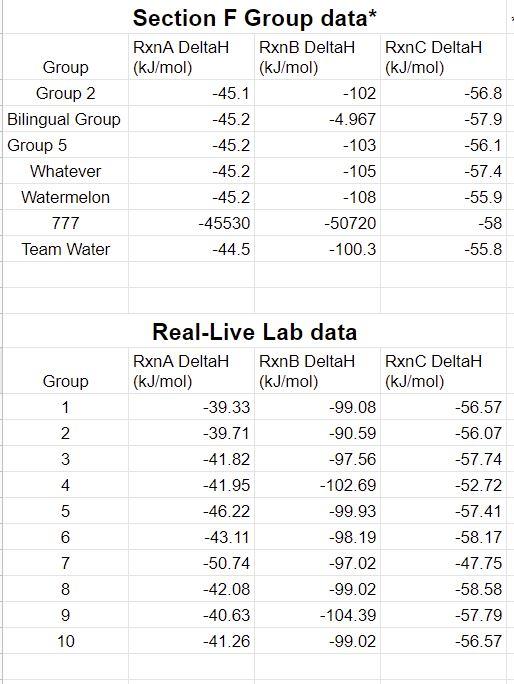
3. Using Excel (or Google sheets), calculate the average and standard deviation of the Virtual Lab and the Real-Life Lab data. You should report your calculated values as "Avg StDev" (don't forget units) Table 2. Class Data for Hess's Law Rxn A Virtual Lab AHrxn Avg StDev Real-Life Lab AHrxn Avg StDev OVERALL AHrxn Avg StDev -45.0667+0.280476 kJ/mol -42.6853.249225 kJ/mol -87.75167+3.529701 kJ/mol Least precise is reaction B. Most precise is reaction A. Rxn B -87.211177+40.3783 kJ/mol -98.849+3.44689 kJ/mol -186.0602+43.82519 kJ/mol NaOH(aq) NaOH(s) NaOH(aq) + HC1 (aq) NaC1 (aq) + H2O(1) So, AHrxn B - AHxn A = AHrxn C Rxn C -56.84286+0.939605 kJ/mol -55.8373.089579 kJ/mol 4. Consider the standard deviations computed above. Overall, which reaction was least precise? Most precise? Comment on the precision of the class results. -112.6799+4.029184 kJ/mol For reaction B, it is least precise because there is a group who got the answer too low than others' group, which lead the standard deviation been too high that have affected the overall result. Otherwise, everything else is great. 5. Examine the three reaction equations and determine the relationship between them. Demonstrate this relationship by combining the chemical reactions in a manner consistent with Hess's Law. (Figure out a way to sum reactions A and B to produce reaction C and show it in this space. If you are typing, be sure to use Equation Editor. Or you may handwrite this section (it must be legible) Heat change for a reaction remains same weather a reaction occurs in single step or multiple steps. Reaction A: NaOH(s) NaOH(aq) Reaction B: NaOH(s) + HC1 (aq) NaC1 (aq) + H2O(1) Reaction B - Reaction A = Reaction C NaOH(s) + HC1 (aq) NaC1 (aq) + H2O(1) 6. Using the overall averages above as the experimental AHrxn for reactions A and B, calculate the predicted value for reaction C by applying Hess's Law. Show your calculation here and record the result below. Then calculate a %error between this predicted AHrxn and the experimental AHrxn (the class average) for reaction C. Here, since both values are based on experimental results, consider the class average value to be the "accepted" value since it is likely to have less error. 7. Was Hess's Law validated? Explain briefly. 8. Calculate the "true" AHrxn value for all three NET IONIC reactions. (Use the standard enthalpies of formation found in Appendix B in your textbook) Note that for aqueous ionic compounds, you must look up each ion separately. i.e., for NaCl(aq), look up Na+ (aq) and Cl- (aq). Calculate the %error comparing the experimental class average to the "true" value for each of the three reactions. If you are typing, be sure to use Equation Editor. Or you may handwrite this section (it must be legible) Show your calculations below. True AH(kJ/mol): Using the equation editor, Insert --> Equation, show your work in this box. RxnA % Error: RxnB True AH(kJ/mol): %Error: Using the equation editor, Insert --> Equation, show your work in this box. RxnC True AH(kJ/mol): Using the equation editor, Insert --> Equation, show your work in this box. %Error: Chemistry 161 9. Which reaction was least accurate? Comment briefly on the accuracy of the overall data. Group Group 2 Bilingual Group Group 5 Whatever Watermelon 777 Team Water Group 1 2 W N 3 45 6 7 8 9 10 Section F Group data* RxnB DeltaH (kJ/mol) RxnA DeltaH (kJ/mol) -45.1 -45.2 -45.2 -45.2 -45.2 -45530 -44.5 -102 -4.967 -103 -105 -108 -50720 -100.3 Real-Live Lab data RxnA DeltaH RxnB DeltaH (kJ/mol) (kJ/mol) -39.33 -39.71 -41.82 -41.95 -46.22 -43.11 -50.74 -42.08 -40.63 -41.26 -99.08 -90.59 -97.56 -102.69 -99.93 -98.19 -97.02 -99.02 -104.39 -99.02 RxnC DeltaH (kJ/mol) -56.8 -57.9 -56.1 -57.4 -55.9 -58 -55.8 RxnC DeltaH (kJ/mol) -56.57 -56.07 -57.74 -52.72 -57.41 -58.17 -47.75 -58.58 -57.79 -56.57
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.42 Rating (152 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
To calculate the average and standard deviation of the Virtual Lab and RealLife Lab data in Excel yo...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


