Question
3. Variable levies The following graph shows the market for wheat in the European Union (EU). The world price of wheat is $2.00 per bushel,
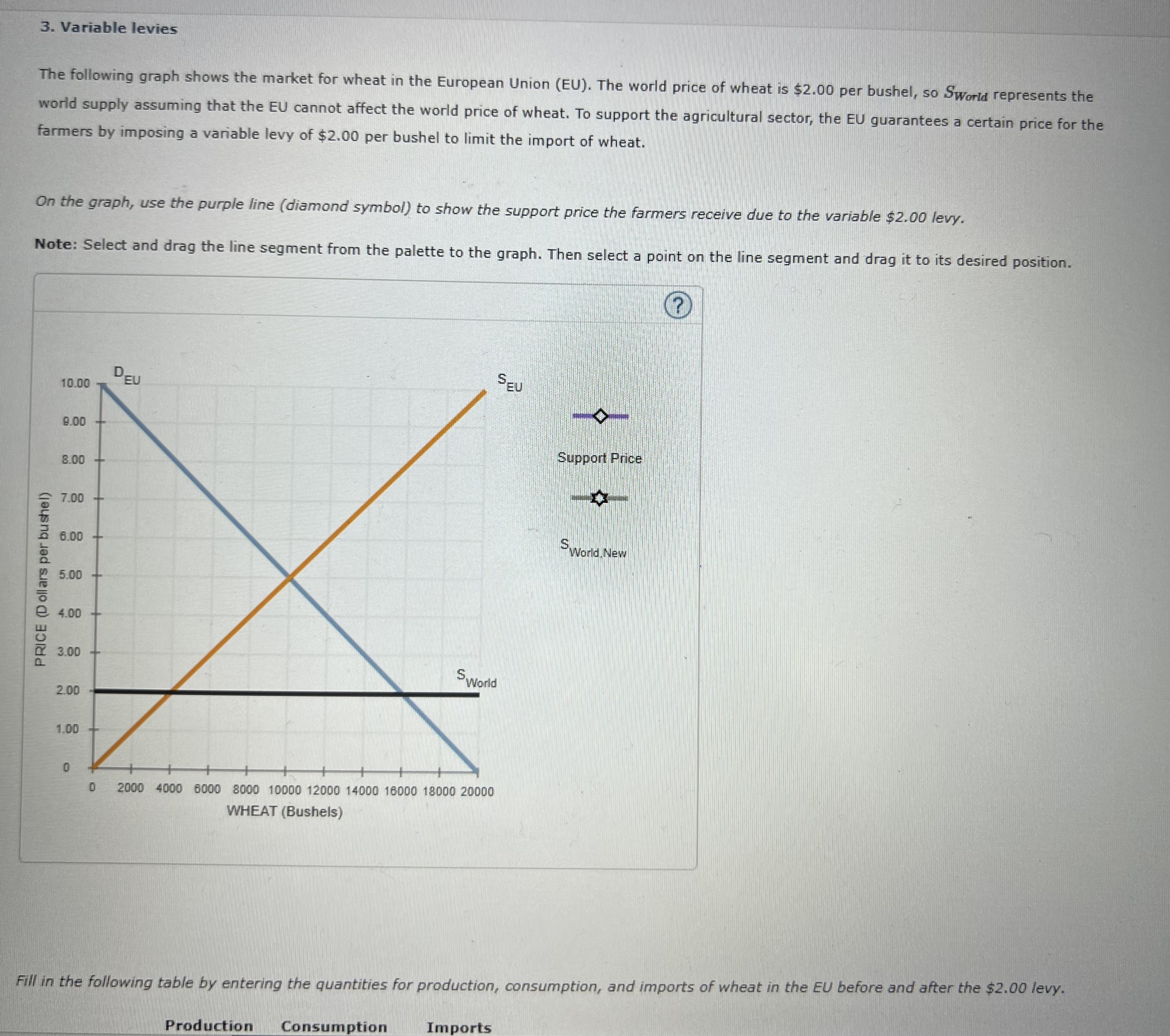
3. Variable levies
The following graph shows the market for wheat in the European Union (EU). The world price of wheat is $2.00 per bushel, so SWorld?Worldrepresents the world supply assuming that the EU cannot affect the world price of wheat. To support the agricultural sector, the EU guarantees a certain price for the farmers by imposing a variable levy of $2.00 per bushel to limit the import of wheat.
On the graph, use the purple line (diamond symbol) to show the support price the farmers receive due to the variable $2.00 levy.
Note: Select and drag the line segment from the palette to the graph. Then select a point on the line segment and drag it to its desired position.
Support PriceSWorld,New0200040006000800010000120001400016000180002000010.009.008.007.006.005.004.003.002.001.000PRICE (Dollars per bushel)WHEAT (Bushels)DEUSEUSWorld
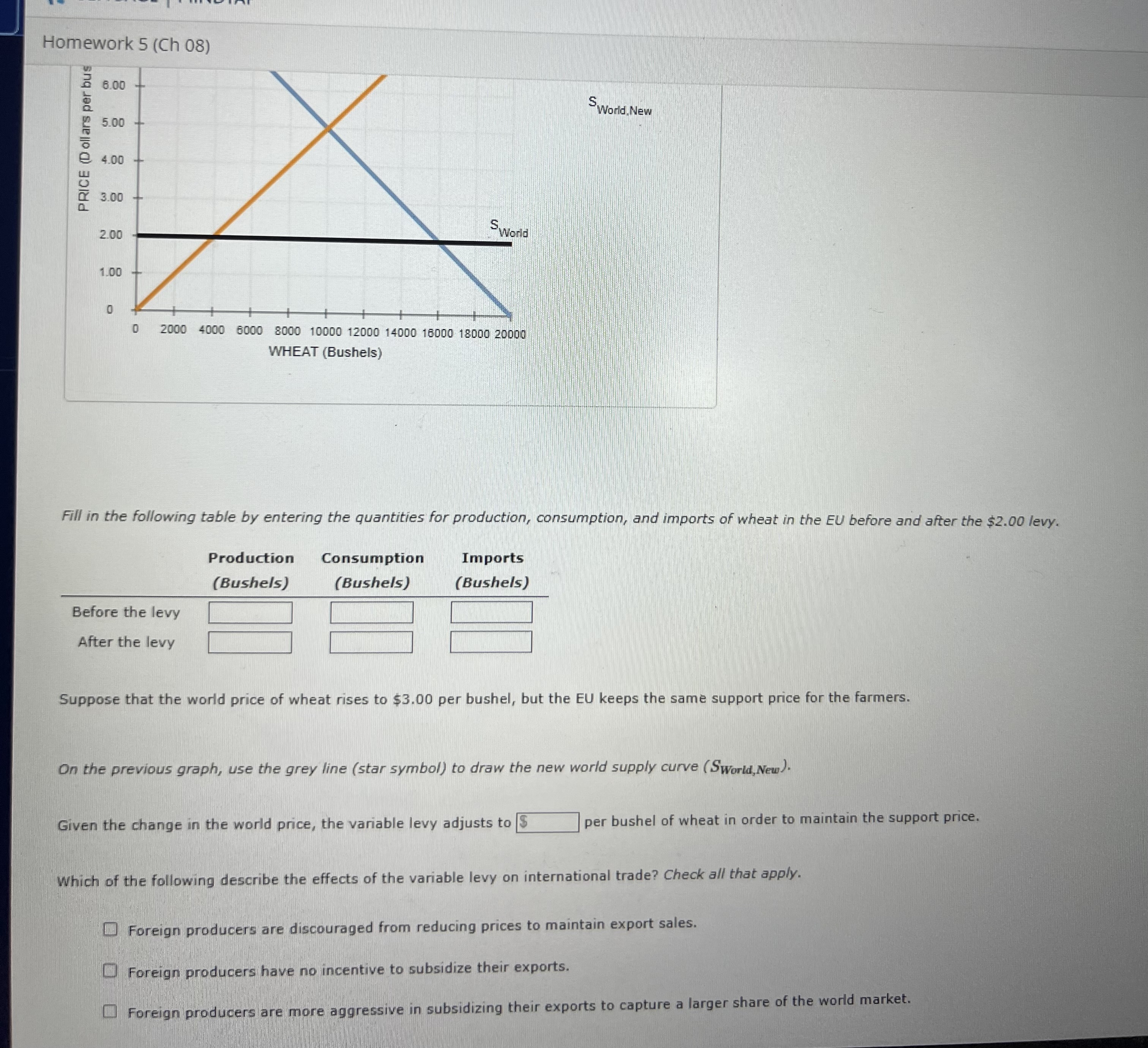
Fill in the following table by entering the quantities for production, consumption, and imports of wheat in the EU before and after the $2.00 levy.
| Production | Consumption | Imports | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (Bushels) | (Bushels) | (Bushels) | |
| Before the levy | |||
| After the levy |
Suppose that the world price of wheat rises to $3.00 per bushel, but the EU keeps the same support price for the farmers.
On the previous graph, use the grey line (star symbol) to draw the new world supply curve (SWorld,New?World,New).
Given the change in the world price, the variable levy adjusts to
per bushel of wheat in order to maintain the support price.
Which of the following describe the effects of the variable levy on international trade?Check all that apply.
Foreign producers are discouraged from reducing prices to maintain export sales.
Foreign producers have no incentive to subsidize their exports.
Foreign producers are more aggressive in subsidizing their exports to capture a larger share of the world market.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


