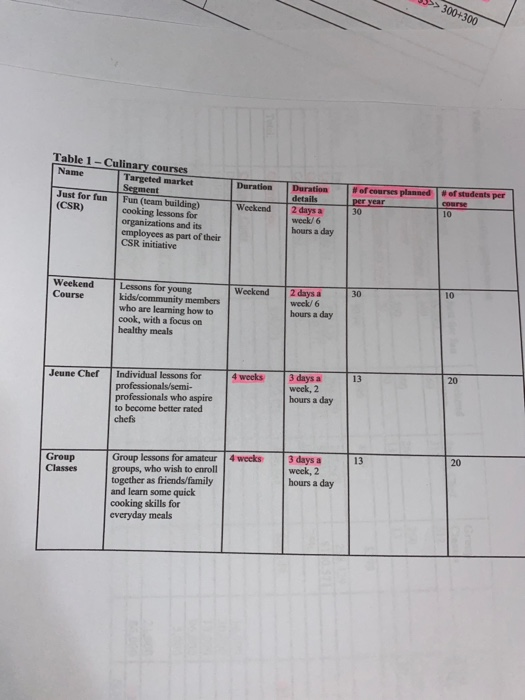
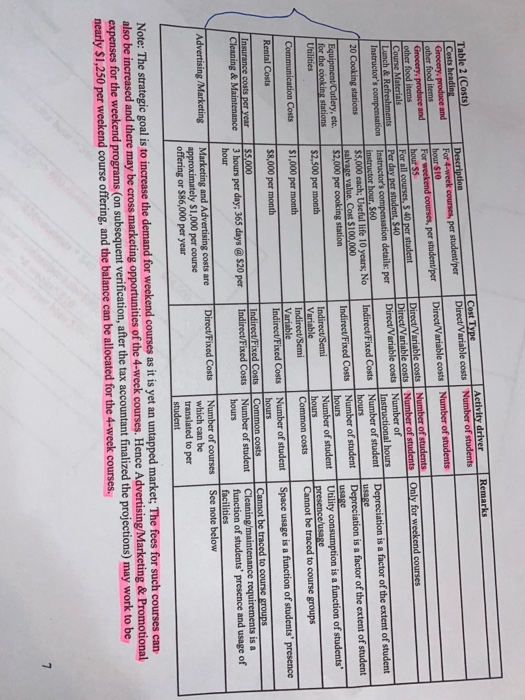
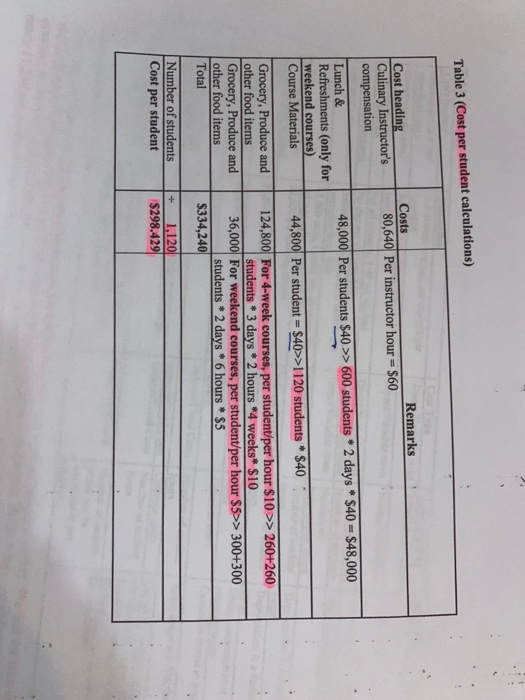
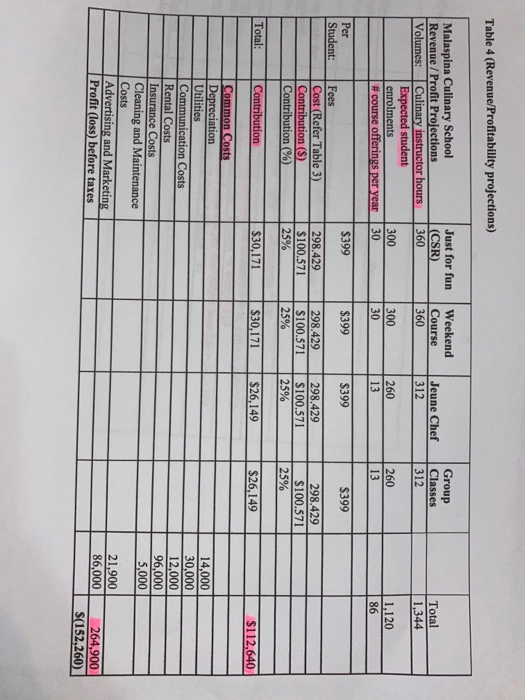
>> 300+300 Duration Table 1 - Culinary courses Name Targeted market Segment Just for fun Fun (team building) (CSR) cooking lessons for organizations and its employees as part of their CSR initiative Duration details 2 days a weck/6 hours a day #of courses planned of students per per year course 30 10 Weekend Weekend Course Weekend 30 10 Lessons for young kids/community members who are learning how to cook, with a focus on healthy meals 2 days a weck/6 hours a day Jeune Cher 4 weeks 20 Individual lessons for professionals/semi- professionals who aspire to become better rated chefs 3 days a week, 2 hours a day Group Classes 4 weeks 20 Group lessons for amateur groups, who wish to enroll together as friends/family and learn some quick cooking skills for everyday meals 3 days a weck, 2 hours a day Remarks Cost Type Activity driver Direct/Variable costs Number of students Direct/Variable costs Number of students Only for weekend courses Table 2 (Costs) Costs heading Grocery produce and other food items Grocery produce and other food items Course Materials Lunch & Refreshments Instructor's compensation 20 Cooking stations Description For 4-week courses, per student per hour SIO For weekend courses, per student per hours For all courses, $ 40 per student Per day per student $40 Instructor's compensation details: per instructor hour, 560 $5,000 cach: Useful life 10 years; No salvare value. Cost $100,000 $2,000 per cooking station Direct/Variable costs Number of students Direct/Variable costs Number of students Direct/Variable costs Number of Instructional hours Indirect Fixed Costs Number of student hours Indirect Fixed Costs Number of student hours Indirect Semi Number of student Variable hours Indirect Semi Common costs Variable Indirect/Fixed Costs Number of student hours Indirect/Fixed Costs Common costs Indirect Fixed Costs Number of student hours Depreciation is a factor of the extent of student usage Depreciation is a factor of the extent of student usage Utility consumption is a function of students' presence/usage Cannot be traced to course groups Equipment/Cutlery, etc. for the cooking stations Utilities $2,500 per month Communication Costs $1,000 per month $8,000 per month Space usage is a function of students' presence Rental Costs Insurance costs per year Cleaning & Maintenance $5,000 3 hours per day, 365 days @ $20 per hour Cannot be traced to course groups Cleaning/maintenance requirements is a function of students' presence and usage of facilities See note below DirectFixed Costs Advertising/Marketing Marketing and Advertising costs are approximately $1,000 per course offering or $86,000 per year Number of courses which can be translated to per student Note: The strategic goal is to increase the demand for weekend courses as it is yet an untapped market; The fees for such courses can also be increased and there may be cross marketing opportunities of the 4-week courses. Hence Advertising/Marketing & Promotional expenses for the weekend programs (on subsequent verification, after the tax accountant finalized the projections) may work to be nearly $1,250 per weekend course offering, and the balance can be allocated for the 4-week courses. 7 Table 3 (Cost per student calculations) Remarks Cost heading Culinary Instructor's compensation Costs 80,640 Per instructor hour = $60 48,000 Per students $40 >> 600 students * 2 days * $40 = $48,000 Lunch & Refreshments (only for weekend courses) Course Materials Grocery, Produce and other food items Grocery, Produce and other food items Total 44,800 Per student = $40>>1120 students * $40 124,800 For 4-week courses, per student/per hour $10 >> 260+260 students * 3 days * 2 hours 4 weeks* $10 36,000 For weekend courses, per student/per hour $5>> 300+300 students * 2 days * 6 hours * $5 $334,240 Number of students Cost per student 1,120 $298.429 Table 4 (Revenue/Profitability projections) Just for fun (CSR) 360 Weekend Course 360 Jeune Chef 312 Group Classes 312 Malaspina Culinary School Revenue / Profit Projections Volumes: Culinary instructor hours Expected student enrolments #course offerings per year Total 1,344 300 30 300 30 260 13 260 13 1,120 86 $399 Per Student: $399 $399 S399 Fees Cost (Refer Table 3) Contribution (S) Contribution (%) 298.429 $100.571 25% 298.429 $100.571 25% 298.429 $100.571 25% 298.429 $100.571 25% Total: Contribution $30,171 $30,171 $26,149 $26,149 $112,640 Common Costs Depreciation Utilities Communication Costs Rental Costs Insurance Costs Cleaning and Maintenance Costs Advertising and Marketing Profit (loss) before taxes 14,000 30,000 12,000 96,000 5,000 21,900 86,000 264,900 S(152,260_ 00) and not related it to the vidual course groups. She also felt that the cost per student around ($298) across all the courses, not appear right. That is when she remembered her dearest high school friend, you. She immediately on phone with you. It was now left in your safe hands to save Sue's worthy culinary school! Required: (100 Marks) Each student is required to submit their files (Word and Excel) to the ACCT 362 D2L Case Part 1 Dropbox no later than 11:55PM, Friday October 30, 2020. No late files will be accepted after the due date time. Please do not wait until the last minute to attach your files and email me if you have any problems. You are expected to prepare a memo for Sue and make recommendations based on your quantitative and qualitative analyses. Critically examine the calculations and projections made by the tax-accountant and address the following: 1. Provide an alternate set of calculations (in contribution format), taking into account, the information in Tables 1 to 4, to provide further insight (if any) to Sue. Make your assumptions explicit, while making these calculations. Note that marks are assigned based on the detailed computations and professional presentation. So even if your final numbers are 100% accurate, marks are deducted if you do not provide the detailed computations and clear assumption to support your final numbers. (60 Marks) {No page limit) 2. Suggest some strategic and operational choices that Sue might have to make, based on clear quantitative and qualitative analyses of her situation, to improve the profitability of MCS and achieve its mission, (15 Marks) {1.5-page limit) 3. Describe the management accounting tool that you may have used to come up with the alternate projections in 1) above. Discuss the benefits and limitations of this tool. (15 Marks) {1.5-page limit 4. Discuss other factors would Sue need to consider before going ahead with the project. (10 Marks) {1-page limit 5 >> 300+300 Duration Table 1 - Culinary courses Name Targeted market Segment Just for fun Fun (team building) (CSR) cooking lessons for organizations and its employees as part of their CSR initiative Duration details 2 days a weck/6 hours a day #of courses planned of students per per year course 30 10 Weekend Weekend Course Weekend 30 10 Lessons for young kids/community members who are learning how to cook, with a focus on healthy meals 2 days a weck/6 hours a day Jeune Cher 4 weeks 20 Individual lessons for professionals/semi- professionals who aspire to become better rated chefs 3 days a week, 2 hours a day Group Classes 4 weeks 20 Group lessons for amateur groups, who wish to enroll together as friends/family and learn some quick cooking skills for everyday meals 3 days a weck, 2 hours a day Remarks Cost Type Activity driver Direct/Variable costs Number of students Direct/Variable costs Number of students Only for weekend courses Table 2 (Costs) Costs heading Grocery produce and other food items Grocery produce and other food items Course Materials Lunch & Refreshments Instructor's compensation 20 Cooking stations Description For 4-week courses, per student per hour SIO For weekend courses, per student per hours For all courses, $ 40 per student Per day per student $40 Instructor's compensation details: per instructor hour, 560 $5,000 cach: Useful life 10 years; No salvare value. Cost $100,000 $2,000 per cooking station Direct/Variable costs Number of students Direct/Variable costs Number of students Direct/Variable costs Number of Instructional hours Indirect Fixed Costs Number of student hours Indirect Fixed Costs Number of student hours Indirect Semi Number of student Variable hours Indirect Semi Common costs Variable Indirect/Fixed Costs Number of student hours Indirect/Fixed Costs Common costs Indirect Fixed Costs Number of student hours Depreciation is a factor of the extent of student usage Depreciation is a factor of the extent of student usage Utility consumption is a function of students' presence/usage Cannot be traced to course groups Equipment/Cutlery, etc. for the cooking stations Utilities $2,500 per month Communication Costs $1,000 per month $8,000 per month Space usage is a function of students' presence Rental Costs Insurance costs per year Cleaning & Maintenance $5,000 3 hours per day, 365 days @ $20 per hour Cannot be traced to course groups Cleaning/maintenance requirements is a function of students' presence and usage of facilities See note below DirectFixed Costs Advertising/Marketing Marketing and Advertising costs are approximately $1,000 per course offering or $86,000 per year Number of courses which can be translated to per student Note: The strategic goal is to increase the demand for weekend courses as it is yet an untapped market; The fees for such courses can also be increased and there may be cross marketing opportunities of the 4-week courses. Hence Advertising/Marketing & Promotional expenses for the weekend programs (on subsequent verification, after the tax accountant finalized the projections) may work to be nearly $1,250 per weekend course offering, and the balance can be allocated for the 4-week courses. 7 Table 3 (Cost per student calculations) Remarks Cost heading Culinary Instructor's compensation Costs 80,640 Per instructor hour = $60 48,000 Per students $40 >> 600 students * 2 days * $40 = $48,000 Lunch & Refreshments (only for weekend courses) Course Materials Grocery, Produce and other food items Grocery, Produce and other food items Total 44,800 Per student = $40>>1120 students * $40 124,800 For 4-week courses, per student/per hour $10 >> 260+260 students * 3 days * 2 hours 4 weeks* $10 36,000 For weekend courses, per student/per hour $5>> 300+300 students * 2 days * 6 hours * $5 $334,240 Number of students Cost per student 1,120 $298.429 Table 4 (Revenue/Profitability projections) Just for fun (CSR) 360 Weekend Course 360 Jeune Chef 312 Group Classes 312 Malaspina Culinary School Revenue / Profit Projections Volumes: Culinary instructor hours Expected student enrolments #course offerings per year Total 1,344 300 30 300 30 260 13 260 13 1,120 86 $399 Per Student: $399 $399 S399 Fees Cost (Refer Table 3) Contribution (S) Contribution (%) 298.429 $100.571 25% 298.429 $100.571 25% 298.429 $100.571 25% 298.429 $100.571 25% Total: Contribution $30,171 $30,171 $26,149 $26,149 $112,640 Common Costs Depreciation Utilities Communication Costs Rental Costs Insurance Costs Cleaning and Maintenance Costs Advertising and Marketing Profit (loss) before taxes 14,000 30,000 12,000 96,000 5,000 21,900 86,000 264,900 S(152,260_ 00) and not related it to the vidual course groups. She also felt that the cost per student around ($298) across all the courses, not appear right. That is when she remembered her dearest high school friend, you. She immediately on phone with you. It was now left in your safe hands to save Sue's worthy culinary school! Required: (100 Marks) Each student is required to submit their files (Word and Excel) to the ACCT 362 D2L Case Part 1 Dropbox no later than 11:55PM, Friday October 30, 2020. No late files will be accepted after the due date time. Please do not wait until the last minute to attach your files and email me if you have any problems. You are expected to prepare a memo for Sue and make recommendations based on your quantitative and qualitative analyses. Critically examine the calculations and projections made by the tax-accountant and address the following: 1. Provide an alternate set of calculations (in contribution format), taking into account, the information in Tables 1 to 4, to provide further insight (if any) to Sue. Make your assumptions explicit, while making these calculations. Note that marks are assigned based on the detailed computations and professional presentation. So even if your final numbers are 100% accurate, marks are deducted if you do not provide the detailed computations and clear assumption to support your final numbers. (60 Marks) {No page limit) 2. Suggest some strategic and operational choices that Sue might have to make, based on clear quantitative and qualitative analyses of her situation, to improve the profitability of MCS and achieve its mission, (15 Marks) {1.5-page limit) 3. Describe the management accounting tool that you may have used to come up with the alternate projections in 1) above. Discuss the benefits and limitations of this tool. (15 Marks) {1.5-page limit 4. Discuss other factors would Sue need to consider before going ahead with the project. (10 Marks) {1-page limit 5