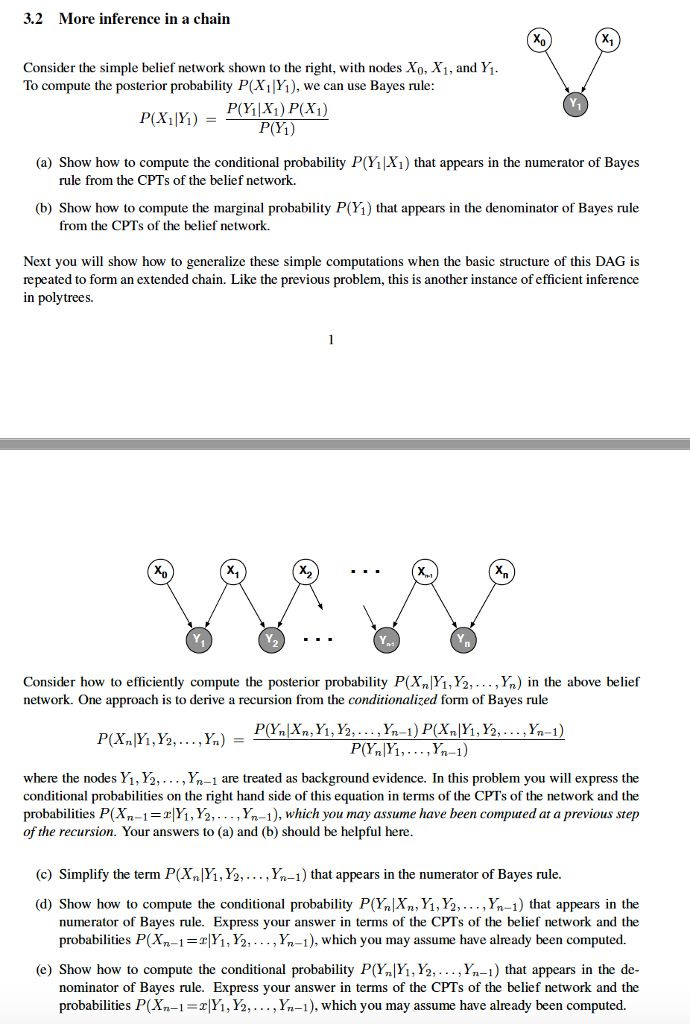
3.2 More inference in a chain X1 Consider the simple belief network shown to the right, with nodes Xo, X1, and Y To compute the posterior probability P(X1 Y), we can use Bayes rule P(Yi) (a) Show how to compute the conditional probability P(Yi|X1) that appears in the numerator of Bayes rule from the CPTs of the belief network. (b) Show how to compute the marginal probability P(1) that appears in the denominator of Bayes rule from the CPTs of the belief network Next you will show how to generalize these simple computations when the basic structure of this DAG is repeated to form an extended chain. Like the previous problem, this is another instance of efficient inference in polytrees. X2 Y. Y. Y. Consider how to efficiently compute the posterior probability PXn|Yi,Y2,... ,Yn) in the above belief network. One approach is to derive a recursion from the conditionalized form of Bayes rule where the nodes Yi, 15. . . . , Yn-1 are treated as background evidence. In this problem you will express the conditional probabilities on the right hand side of this equation in terms of the CPTs of the network and the probabilities P(Xn-1-rlY1,Y2,... ,Yn-1), which you may assume have been computed at a previous step of the recursion. Your answers to (a) and (b) should be helpful here (c) Simplify the term P(Xn[Yi, Y2,..., Yn-1) that appears in the numerator of Bayes rule. (d) Show how to compute the conditional probability P(YnXn, Y1,Y2,... , Yn-1) that appears in the numerator of Bayes rule. Express your answer in terms of the CPTs of the belief network and the probabilities P(Xn-1-TY1, Y2,...,Yn-1), which you may assume have already been computed. (e) Show how to compute the conditional probability P(Y,Y, Y2, , Yn-1) that appears in the de nominator of Bayes rule. Express your answer in terms of the CPTs of the belief network and the probabilities P(Xn-i-r|Yi, Y2,...,Yn-i), which you may assume have already been computed. 3.2 More inference in a chain X1 Consider the simple belief network shown to the right, with nodes Xo, X1, and Y To compute the posterior probability P(X1 Y), we can use Bayes rule P(Yi) (a) Show how to compute the conditional probability P(Yi|X1) that appears in the numerator of Bayes rule from the CPTs of the belief network. (b) Show how to compute the marginal probability P(1) that appears in the denominator of Bayes rule from the CPTs of the belief network Next you will show how to generalize these simple computations when the basic structure of this DAG is repeated to form an extended chain. Like the previous problem, this is another instance of efficient inference in polytrees. X2 Y. Y. Y. Consider how to efficiently compute the posterior probability PXn|Yi,Y2,... ,Yn) in the above belief network. One approach is to derive a recursion from the conditionalized form of Bayes rule where the nodes Yi, 15. . . . , Yn-1 are treated as background evidence. In this problem you will express the conditional probabilities on the right hand side of this equation in terms of the CPTs of the network and the probabilities P(Xn-1-rlY1,Y2,... ,Yn-1), which you may assume have been computed at a previous step of the recursion. Your answers to (a) and (b) should be helpful here (c) Simplify the term P(Xn[Yi, Y2,..., Yn-1) that appears in the numerator of Bayes rule. (d) Show how to compute the conditional probability P(YnXn, Y1,Y2,... , Yn-1) that appears in the numerator of Bayes rule. Express your answer in terms of the CPTs of the belief network and the probabilities P(Xn-1-TY1, Y2,...,Yn-1), which you may assume have already been computed. (e) Show how to compute the conditional probability P(Y,Y, Y2, , Yn-1) that appears in the de nominator of Bayes rule. Express your answer in terms of the CPTs of the belief network and the probabilities P(Xn-i-r|Yi, Y2,...,Yn-i), which you may assume have already been computed







