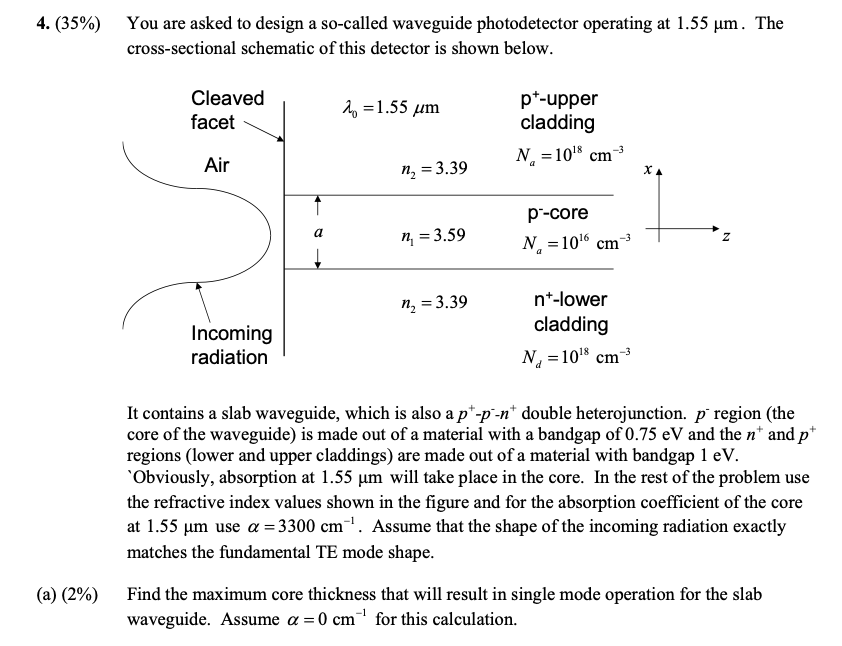


4. (35%) You are asked to design a so-called waveguide photodetector operating at 1.55 um. The cross-sectional schematic of this detector is shown below. Cleaved facet 2n =1.55 um p*-upper cladding Ne = 1018 cm Air n2 = 3.39 a p-core N = 10 cm N n = 3.59 n2 = 3.39 Incoming radiation nt-lower cladding N. = 10 cm + It contains a slab waveguide, which is also a pt-p-nt double heterojunction. p region (the core of the waveguide) is made out of a material with a bandgap of 0.75 eV and the nt and p regions (lower and upper claddings) are made out of a material with bandgap 1 eV. "Obviously, absorption at 1.55 um will take place in the core. In the rest of the problem use the refractive index values shown in the figure and for the absorption coefficient of the core at 1.55 um use a = 3300 cm!. Assume that the shape of the incoming radiation exactly matches the fundamental TE mode shape. (a) (2%) Find the maximum core thickness that will result in single mode operation for the slab waveguide. Assume a = 0 cm-' for this calculation. (b) (3%) For the actual core thickness, use 76% of the maximum thickness you found in part (a). What is the effective index of the fundamental TE mode at 1.55 um? What are the electric and magnetic field components that exist for this mode? Assume a =0 cm for this calculation. () (5%) Find an expression for the E,(x,z) component of the fundamental TE mode in the core and in the cladding? Note that E, (x,z) can be expressed as E, (x,z) = Acos(kx)etes for (xlsx Aco(. mjetila for [s] 2= Determine all the constants involved except the effective absorption coefficient a and the mode amplitude A. Assume a =0 cm for this calculation. (d) (7%) Since absorption only takes place in the core only the part of the power in the core is absorbed. Find the fraction of the power in the core, which is |,(x,z)]* dx E, (x,x)E,(x,z)' dx 18, (27) de S|, (3,2))*dx E, (x,z)E,(x,z) dx Assume a = 0 cm for this calculation. () (3%) The power absorption in the detector can be written as e-raz. Calculate the detector length required for total absorption if T=0.75. Assume a = 3300 cm~' for this calculation. (f) (3%) Calculate the reverse bias needed to keep the electric field above 5x104 V/cm in the pregion (core of the waveguide). Assume that the built-in potential is 0.6 V and relative dielectric constant of core and claddings is , =13. (g) (3%) Calculate the capacitance of the detector assuming the waveguide is only 3 um wide. Note that this is not the core thickness a calculated above. Core thickness a is used to calculate the capacitance per unit area. The area of the detector is its width multiplied by its length. Length is the length needed for total absorption calculated in part (e) above. What is the RC limited bandwidth if the load resistor is 1 k 2? (h) (3%) Estimate the transit time limited bandwidth of this detector. Assume electron and hole velocities saturate if the field in the pregion is above 5x10* V/cm. Use 10 cm/sec and 10 cm/sec for electron and hole saturated velocities respectively. (i) (3%) Incoming light will reflect from the input facet of the detector. We can approximate this reflection using the plane wave reflection formula under normal incidence. Since radiation will be incident from the air side index of one side is the index of the air. Use the effective index of the mode for the waveguide side and determine the power reflection. Calculate the responsivity of this detector assuming 100% internal quantum efficiency. Describe how you could improve the responsivity. 6) (2%) (k) (1%) 4. (35%) You are asked to design a so-called waveguide photodetector operating at 1.55 um. The cross-sectional schematic of this detector is shown below. Cleaved facet 2n =1.55 um p*-upper cladding Ne = 1018 cm Air n2 = 3.39 a p-core N = 10 cm N n = 3.59 n2 = 3.39 Incoming radiation nt-lower cladding N. = 10 cm + It contains a slab waveguide, which is also a pt-p-nt double heterojunction. p region (the core of the waveguide) is made out of a material with a bandgap of 0.75 eV and the nt and p regions (lower and upper claddings) are made out of a material with bandgap 1 eV. "Obviously, absorption at 1.55 um will take place in the core. In the rest of the problem use the refractive index values shown in the figure and for the absorption coefficient of the core at 1.55 um use a = 3300 cm!. Assume that the shape of the incoming radiation exactly matches the fundamental TE mode shape. (a) (2%) Find the maximum core thickness that will result in single mode operation for the slab waveguide. Assume a = 0 cm-' for this calculation. (b) (3%) For the actual core thickness, use 76% of the maximum thickness you found in part (a). What is the effective index of the fundamental TE mode at 1.55 um? What are the electric and magnetic field components that exist for this mode? Assume a =0 cm for this calculation. () (5%) Find an expression for the E,(x,z) component of the fundamental TE mode in the core and in the cladding? Note that E, (x,z) can be expressed as E, (x,z) = Acos(kx)etes for (xlsx Aco(. mjetila for [s] 2= Determine all the constants involved except the effective absorption coefficient a and the mode amplitude A. Assume a =0 cm for this calculation. (d) (7%) Since absorption only takes place in the core only the part of the power in the core is absorbed. Find the fraction of the power in the core, which is |,(x,z)]* dx E, (x,x)E,(x,z)' dx 18, (27) de S|, (3,2))*dx E, (x,z)E,(x,z) dx Assume a = 0 cm for this calculation. () (3%) The power absorption in the detector can be written as e-raz. Calculate the detector length required for total absorption if T=0.75. Assume a = 3300 cm~' for this calculation. (f) (3%) Calculate the reverse bias needed to keep the electric field above 5x104 V/cm in the pregion (core of the waveguide). Assume that the built-in potential is 0.6 V and relative dielectric constant of core and claddings is , =13. (g) (3%) Calculate the capacitance of the detector assuming the waveguide is only 3 um wide. Note that this is not the core thickness a calculated above. Core thickness a is used to calculate the capacitance per unit area. The area of the detector is its width multiplied by its length. Length is the length needed for total absorption calculated in part (e) above. What is the RC limited bandwidth if the load resistor is 1 k 2? (h) (3%) Estimate the transit time limited bandwidth of this detector. Assume electron and hole velocities saturate if the field in the pregion is above 5x10* V/cm. Use 10 cm/sec and 10 cm/sec for electron and hole saturated velocities respectively. (i) (3%) Incoming light will reflect from the input facet of the detector. We can approximate this reflection using the plane wave reflection formula under normal incidence. Since radiation will be incident from the air side index of one side is the index of the air. Use the effective index of the mode for the waveguide side and determine the power reflection. Calculate the responsivity of this detector assuming 100% internal quantum efficiency. Describe how you could improve the responsivity. 6) (2%) (k) (1%)









