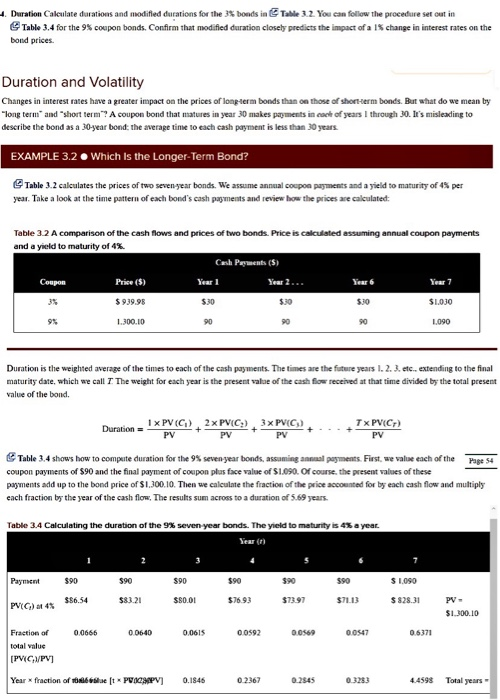
4. Duration Calculate durations and modified durations for the 35 bonds in Table 3.2. You can follow the procedure set out in Table 3.4 for the 9% coupon bonds. Confirm that modified duration closely predicts the impact of a 15 change in interest rates on the bond prices Duration and Volatility Changes in interest rates have a greater impact on the prices of long-term bonds than on those of short-term bonds. But what do we mean by "long terms and short term"? A coupon bond that matures in year 30 makes payments in care of years I through 30. It's misleading to describe the bond as a 30-year bond, the average time to each cash payment is less than 30 years EXAMPLE 3.2. Which is the Longer-Term Bond? Table 3.2 calculates the prices of two seven year bonds. We assume annual coupon payments and a yield to maturity of 4% per year. Take a look at the time pattern of each bond's cash payments and review how the prices are calculated: Table 3.2 A comparison of the cash flows and prices of two bonds. Price is calculated assuming annual coupon payments and a yield to maturity of 4%. Cash Perments (5) Coupon Price ($) Year 1 Year 2, Year 6 Year 7 35 $99.98 $30 $.30 $30 SIOJO 9% 1.300.10 90 90 90 1.090 Duration is the weighted average of the times to each of the cash payments. The times are the future years I. 2. 3. etc.. extending to the final maturits date, which we call The weight for each year is the present value of the cash flow received at that time divided by the total present value of the bond. 1 x PV(C) 2x PVC;)3 PV(C) Duration TX PVC) PV PV PV PV Table 3.4 shows how to compete duration for the 9% seven year bonds, assuming annual payments. First, we value each of the Page 54 coupon payments of $90 and the final payment of coupon plus face value of $1.090. Of course, the present values of these payments add up to the bond price of $1.300.10. Then we calculate the fraction of the price accounted for by each cash flow and multiply each fraction by the year of the cash flow. The results sum across to a duration of 5.69 years. Table 3.4 Calculating the duration of the 9% seven year bonds. The yield to maturity is 4% a year Payment $90 $90 $90 $90 $90 590 $ 1.090 $$6.54 $83.21 $80.01 $76.93 $73.97 $71.13 $828.31 PV(C) 4% PV- $1.300.10 0.0666 0.0640 0.0615 0.0592 0.0569 0.0547 0.6371 Fraction of total value [PVC/PV] Year fraction of oft PVC PV] 0.1846 0.2367 0.2545 0.3293 4.4598 Total years