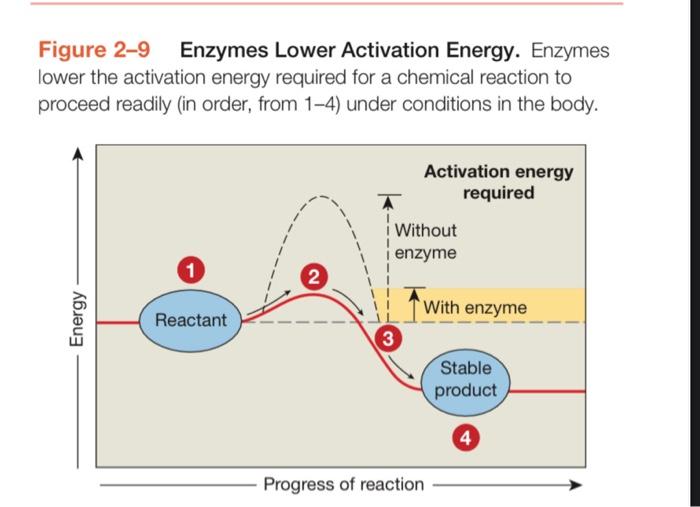
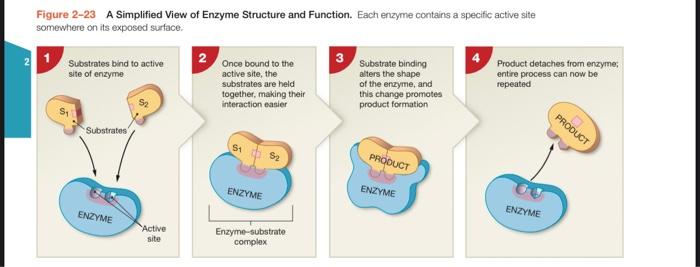
4. ENZYMES and CHEMICAL REACTIONS The textbook illustrates an enzymatic reaction in Figure 2-23, A Simplified View of Enzymatic Structure and Function. While this is in the next section, understanding this process helps you to understand Figure 2-9, Enzymes Lower Activation Energy. (The authors should have positioned these diagrams closer together to help you understand them.). Study both figures, read the following, and draw a labeled diagram to answer this question Enzymes facilitate a majority of reactions in the body, allowing them to occur under normal homeostatic conditions. (In other words, we don't need to heat things up to get reactions to occur!) Some of the reactions are synthesis reactions (anabolic reactions), as shown in Figure 2-23. Others are decomposition reactions catabolic reactions). Enzymes can play a role in both types of reactions, but the book doesn't make that clear. To demonstrate that you understand how enzymes can work in both synthesis and decomposition reactions, draw and label a diagram that shows the REVERSE of Figure 2-23, A Simplified View of Enzyme Structure and Function. a. Draw a decomposition reaction mediated by an enzyme. Label the following: the enzyme the substrate (notice this is singular) the enzyme-substrate complex the products (notice this is plural) Your diagram should have 3 (or 4) parts to illustrate each step. Figure 2-9 Enzymes Lower Activation Energy. Enzymes lower the activation energy required for a chemical reaction to proceed readily (in order, from 1-4) under conditions in the body. Activation energy required Without enzyme 1 2 Energy Reactant With enzyme 3 Stable product 4 Progress of reaction Figure 2-23 A Simplified View of Enzyme Structure and Function. Each enzyme contains a specific active site somewhere on its exposed surface. Substrates bind to active site of enzyme Once bound to the active site, the substrates are held together, making their interaction easier Substrate binding alters the shape of the enzyme, and this change promotes product formation Product detaches from enzyme entire process can now be repeated PRODUCT Substrates PRODUCT ENZYME ENZYME ENZYME ENZYME Active site Enzyme-substrate complex