Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
4. Inter-Domain Routing-BGP (14 marks) a. (6 marks) (Refer to the Figure below) Consider the network shown below. Here a customer (represented by AS100)
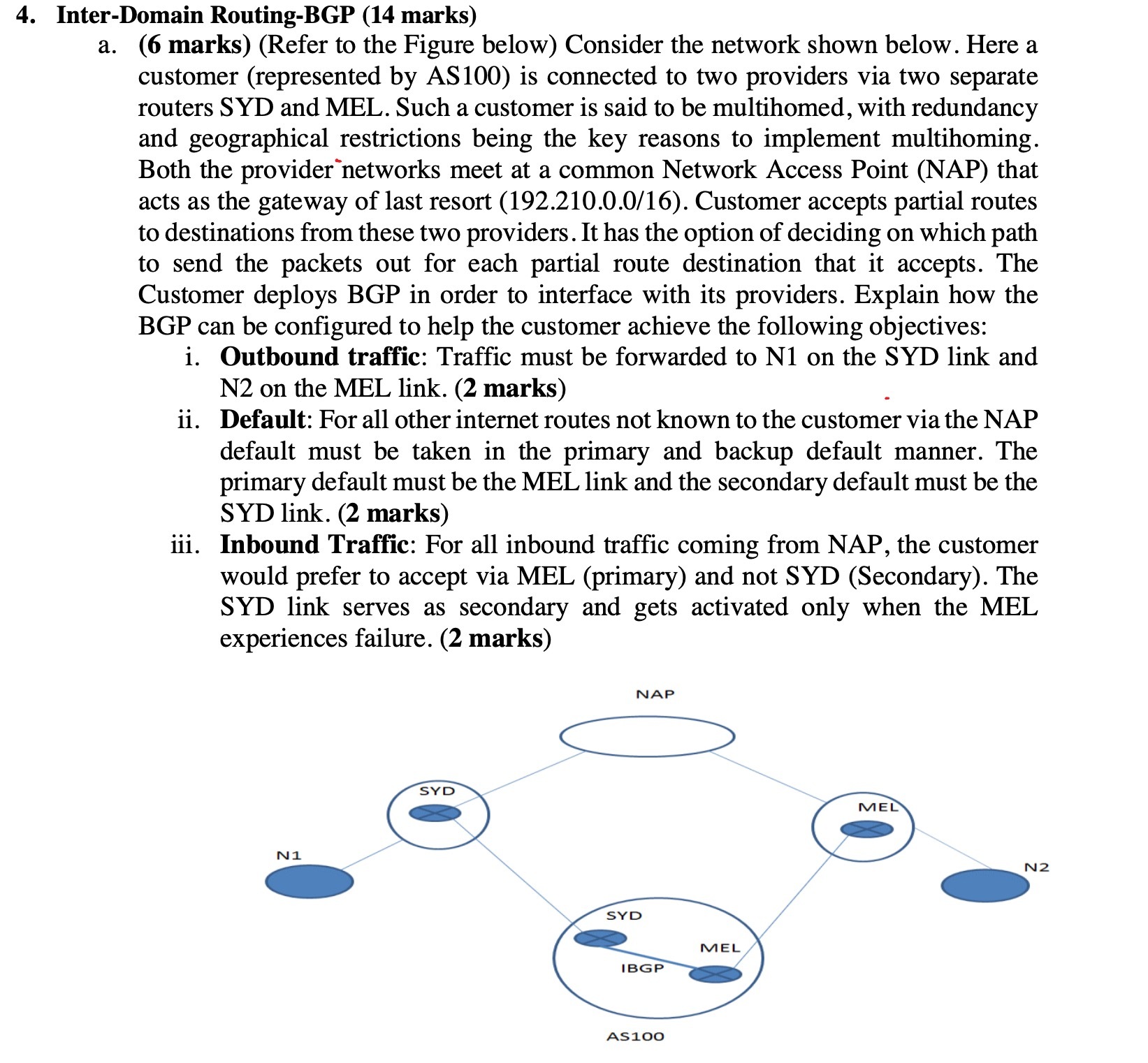
4. Inter-Domain Routing-BGP (14 marks) a. (6 marks) (Refer to the Figure below) Consider the network shown below. Here a customer (represented by AS100) is connected to two providers via two separate routers SYD and MEL. Such a customer is said to be multihomed, with redundancy and geographical restrictions being the key reasons to implement multihoming. Both the provider networks meet at a common Network Access Point (NAP) that acts as the gateway of last resort (192.210.0.0/16). Customer accepts partial routes to destinations from these two providers. It has the option of deciding on which path to send the packets out for each partial route destination that it accepts. The Customer deploys BGP in order to interface with its providers. Explain how the BGP can be configured to help the customer achieve the following objectives: i. Outbound traffic: Traffic must be forwarded to N1 on the SYD link and N2 on the MEL link. (2 marks) ii. Default: For all other internet routes not known to the customer via the NAP default must be taken in the primary and backup default manner. The primary default must be the MEL link and the secondary default must be the SYD link. (2 marks) iii. Inbound Traffic: For all inbound traffic coming from NAP, the customer would prefer to accept via MEL (primary) and not SYD (Secondary). The SYD link serves as secondary and gets activated only when the MEL experiences failure. (2 marks) N1 SYD SYD NAP MEL IBGP AS100 MEL N2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


