Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
4. Specialization and trade When a country has a comparative advantage in the production of a good, it means that it can produce this good
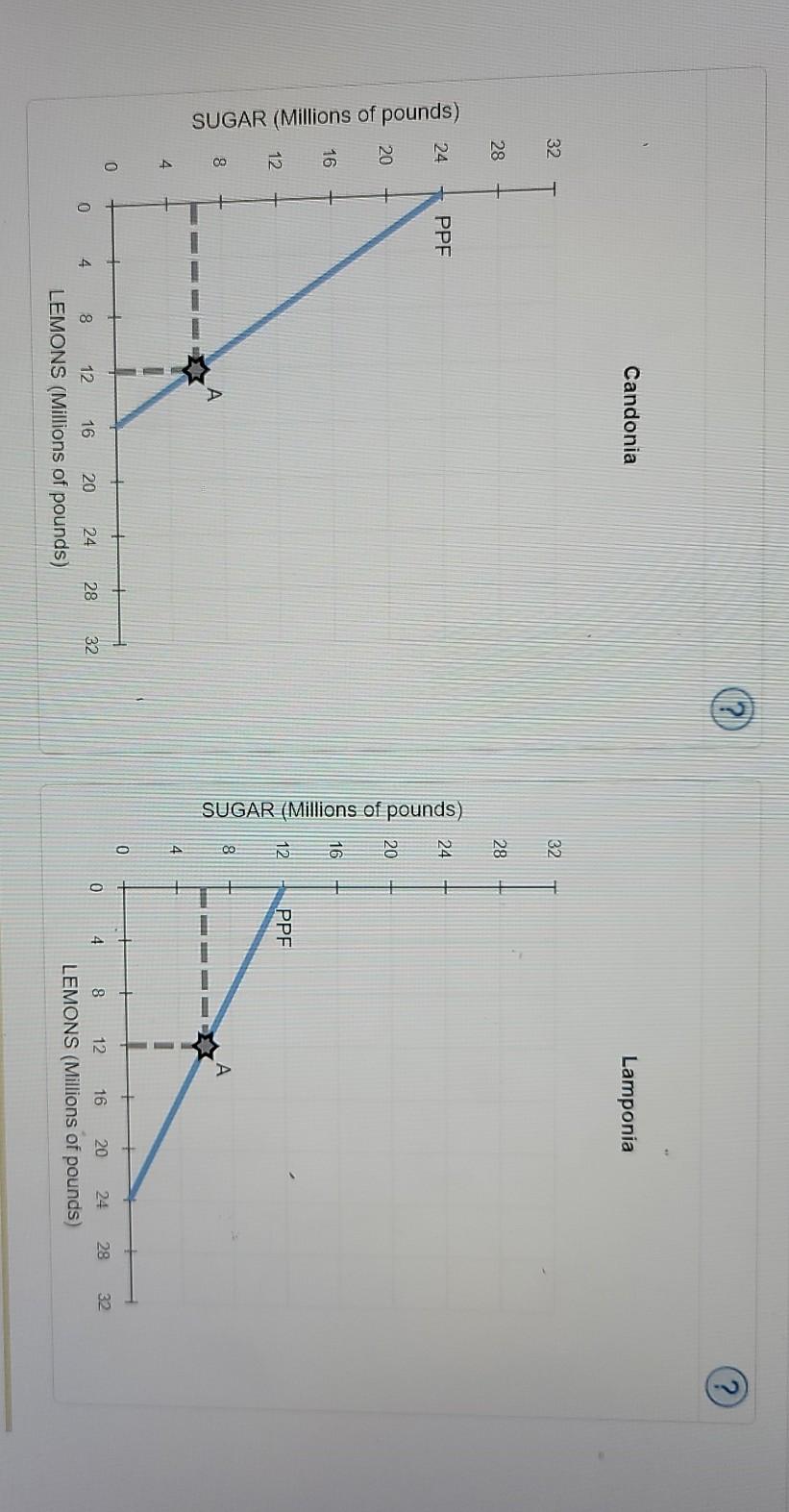
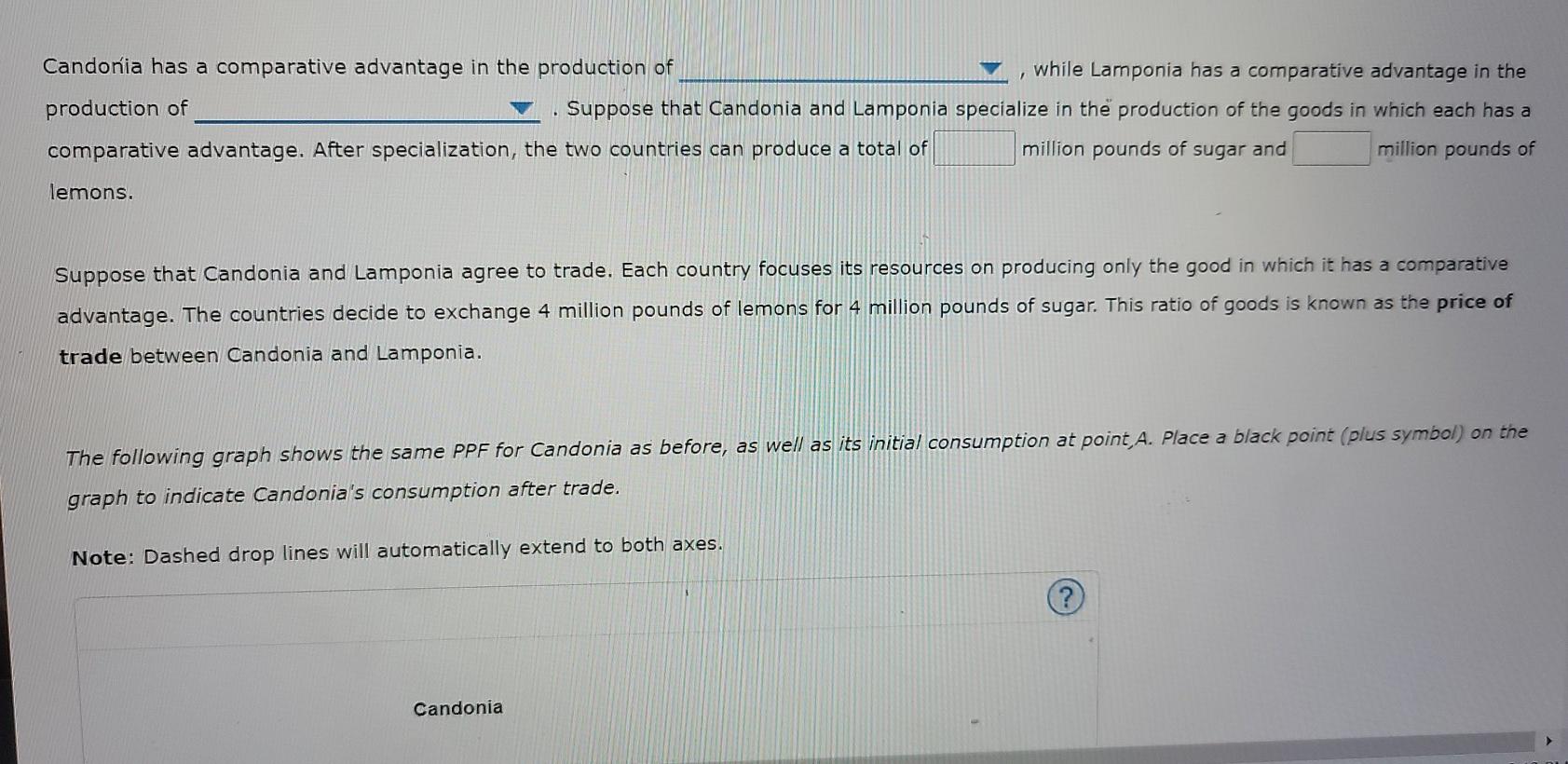
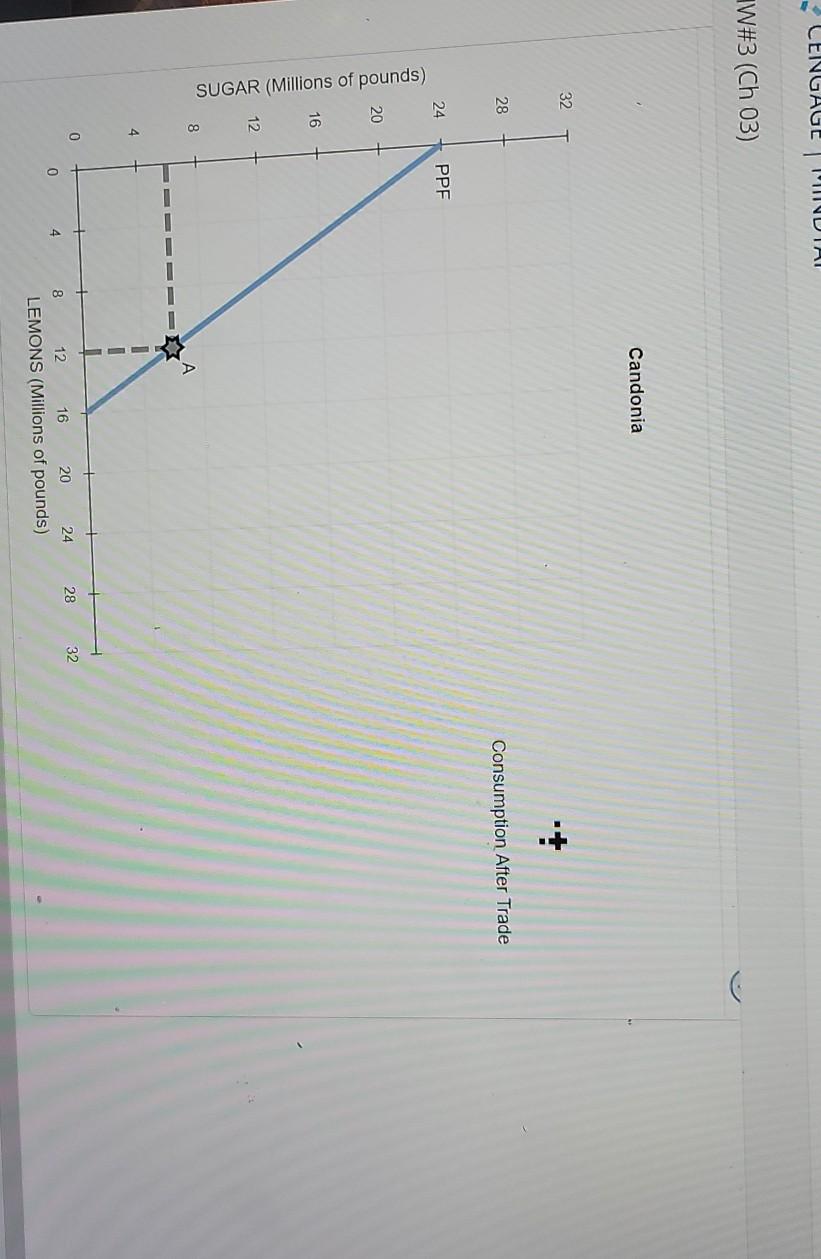
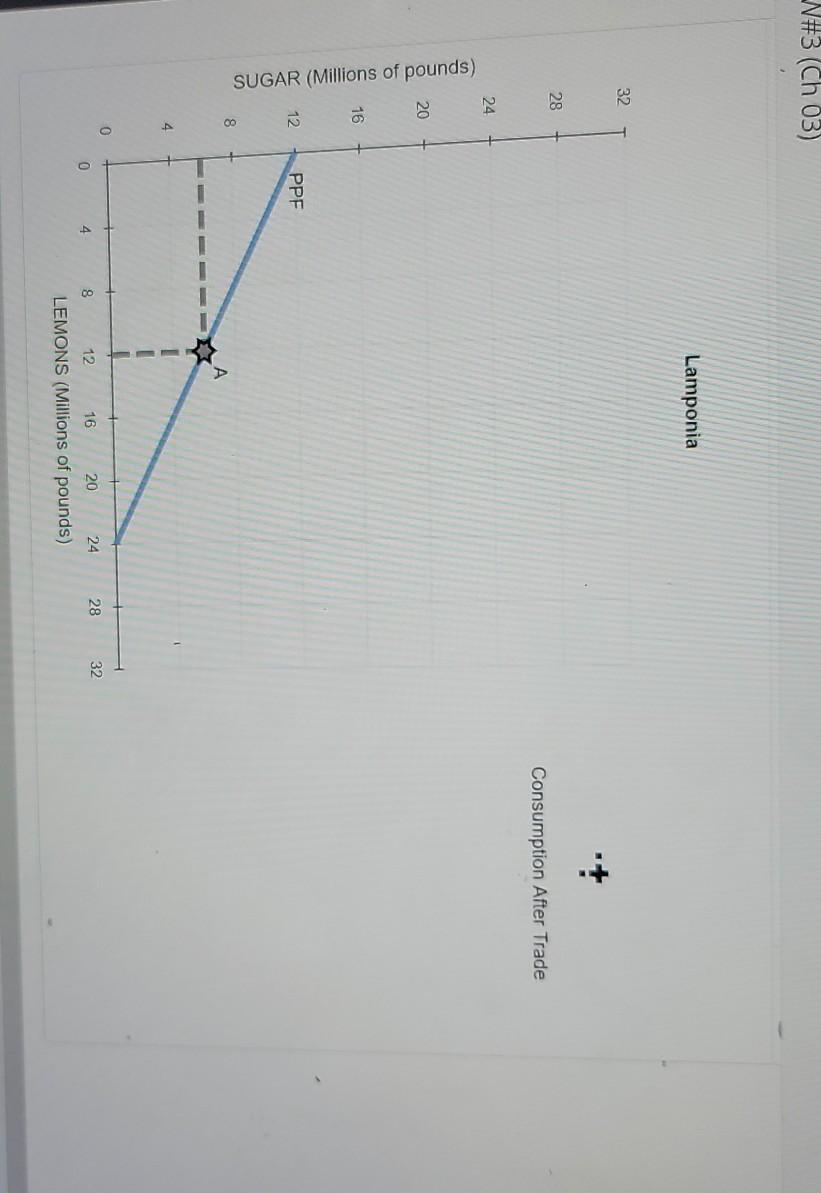
4. Specialization and trade When a country has a comparative advantage in the production of a good, it means that it can produce this good at a lower opportunity cost than its trading partner. Then the country will specialize in the production of this good and trade it for other goods. The following graphs show the production possibilities frontiers (PPFs) for Candonia and Lamponia. Both countries produce lemons and sugar, each initially (i.e., before specialization and trade) producing 12 million pounds of lemons and 6 million pounds of sugar, as indicated by the grey stars marked with the letter A. (?) Candonia Lamponia 32 32 28 28 24 24 PPF unds) Candonia has a comparative advantage in the production of while Lamponia has a comparative advantage in the production of Suppose that Candonia and Lamponia specialize in the production of the goods in which each has a comparative advantage. After specialization, the two countries can produce a total of million pounds of sugar and million pounds of lemons. Suppose that Candonia and Lamponia agree to trade. Each country focuses its resources on producing only the good in which it has a comparative advantage. The countries decide to exchange 4 million pounds of lemons for 4 million pounds of sugar. This ratio of goods is known as the price of trade between Candonia and Lamponia. The following graph shows the same PPF for Candonia as before, as well as its initial consumption at point, A. Place a black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate Candonia's consumption after trade. Note: Dashed drop lines will automatically extend to both axes. (? Candonia CENGAGE WITVDIA W#3 (Ch 03) Candonia 32 28 Consumption After Trade 24 PPF 20 SUGAR (Millions of pounds) A - - 4 0 28 32 0 8 12 16 20 24 LEMONS (Millions of pounds) -NH3 (Ch 03) Lamponia 32 28 Consumption After Trade 24 20 SUGAR (Millions of pounds) 16 12. PPF 8 1 - - 4 0 24 12 28 20 16 4 0 32 8 LEMONS (Millions of pounds) LEMONS (Millions of pounds) True or False: Without engaging in international trade, Candonia and Lamponia would not have been able to consume at the after-trade consumption bundles. (Hint: Base this question on the answers you previously entered on this page.) True False
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


