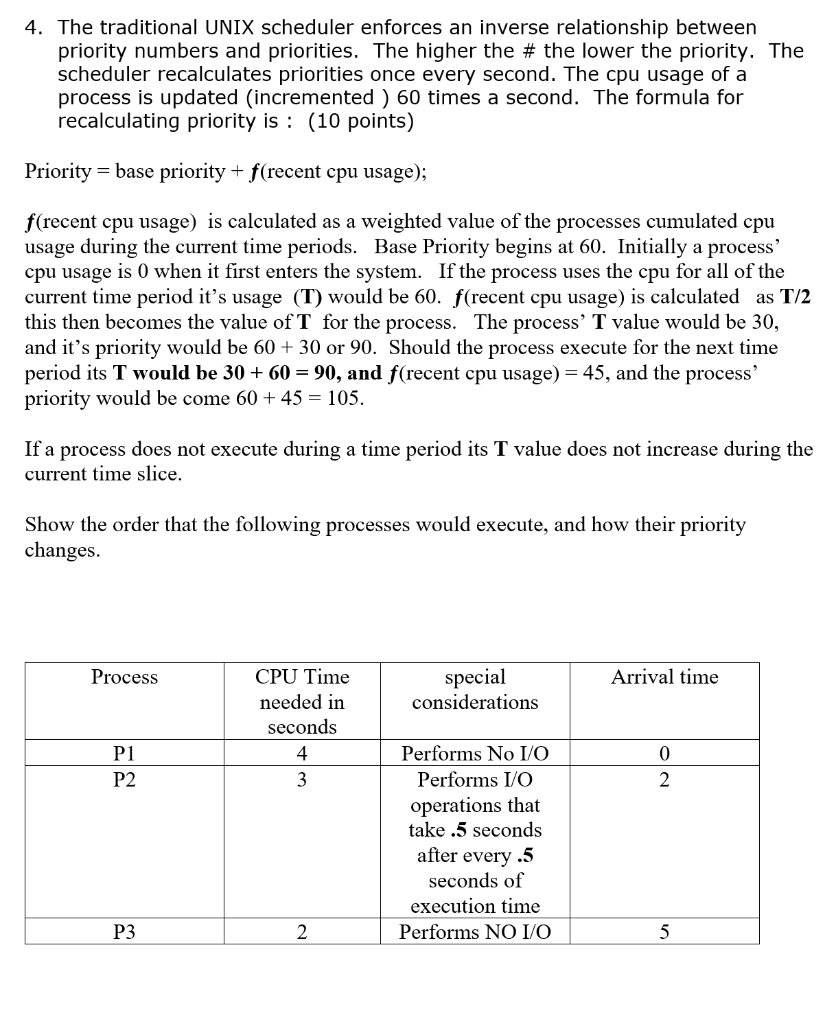
4. The traditional UNIX scheduler enforces an inverse relationship between priority numbers and priorities. The higher the # the lower the priority. The scheduler recalculates priorities once every second. The cpu usage of a process is updated (incremented) 60 times a second. The formula for recalculating priority is: (10 points) Priority -base priority + f(recent cpu usage); f(recent cpu usage) is calculated as a weighted value of the processes cumulated cpu usage during the current time periods. Base Priority begins at 60. Initially a process' cpu usage is 0 when it first enters the system. If the process uses the cpu for all of the current time period it's usage (T) would be 60. f(recent cpu usage) is calculated as T/2 this then becomes the value ofT for the process. The process' T value would be 30, and it's priority would be 60 +30 or 90. Should the process execute for the next time period its T would be 30 + 60 -90, and f(recent cpu usage)-45, and the process' priority would be come 60 + 45-105. If a process does not execute during a time period its T value does not increase during the current time slice. Show the order that the following processes would execute, and how their priority changes CPU Time needed in seconds 4 Process special Arrival time considerations Performs No I/O Performs I/O operations that take .5 seconds after every .5 seconds of execution time P1 P2 0 P3 Performs NO I/O 4. The traditional UNIX scheduler enforces an inverse relationship between priority numbers and priorities. The higher the # the lower the priority. The scheduler recalculates priorities once every second. The cpu usage of a process is updated (incremented) 60 times a second. The formula for recalculating priority is: (10 points) Priority -base priority + f(recent cpu usage); f(recent cpu usage) is calculated as a weighted value of the processes cumulated cpu usage during the current time periods. Base Priority begins at 60. Initially a process' cpu usage is 0 when it first enters the system. If the process uses the cpu for all of the current time period it's usage (T) would be 60. f(recent cpu usage) is calculated as T/2 this then becomes the value ofT for the process. The process' T value would be 30, and it's priority would be 60 +30 or 90. Should the process execute for the next time period its T would be 30 + 60 -90, and f(recent cpu usage)-45, and the process' priority would be come 60 + 45-105. If a process does not execute during a time period its T value does not increase during the current time slice. Show the order that the following processes would execute, and how their priority changes CPU Time needed in seconds 4 Process special Arrival time considerations Performs No I/O Performs I/O operations that take .5 seconds after every .5 seconds of execution time P1 P2 0 P3 Performs NO I/O







