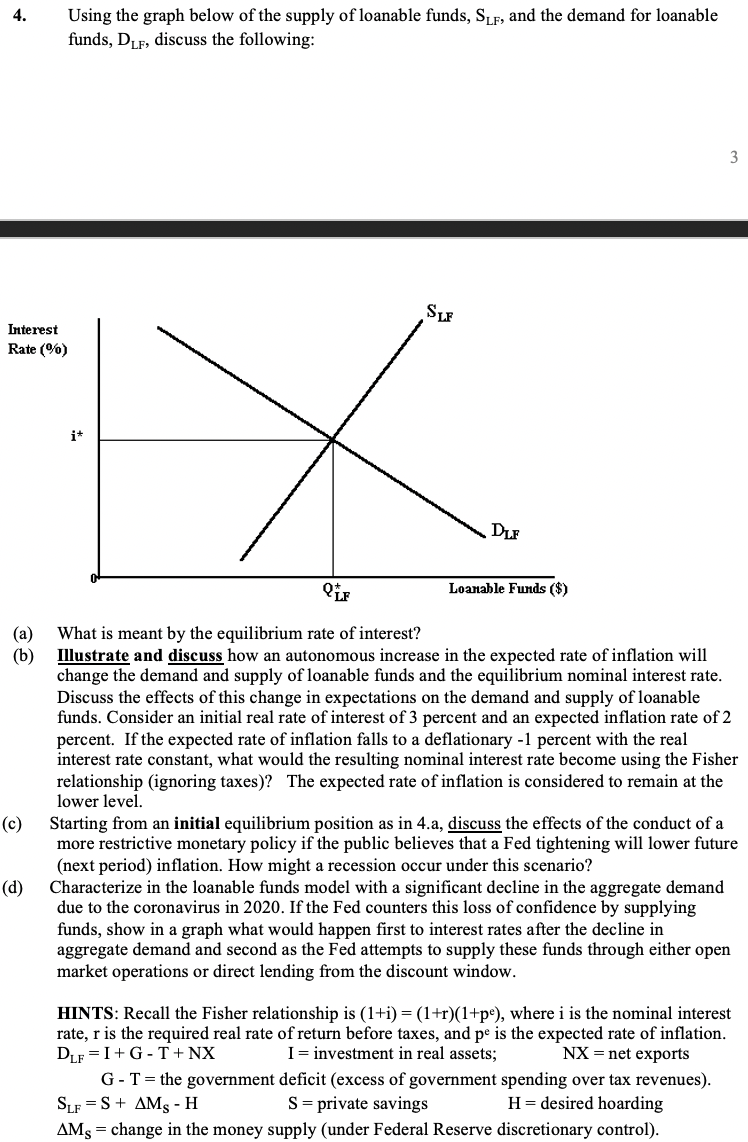
4. Using the graph below of the supply of loanable funds, Slf, and the demand for loanable funds, Dlf, discuss the following: 3 SLF Interest Rate(%) it X DLF Loanable Funds ($) (a) (b) What is meant by the equilibrium rate of interest? Illustrate and discuss how an autonomous increase in the expected rate of inflation will change the demand and supply of loanable funds and the equilibrium nominal interest rate. Discuss the effects of this change in expectations on the demand and supply of loanable funds. Consider an initial real rate of interest of 3 percent and an expected inflation rate of 2 percent. If the expected rate of inflation falls to a deflationary -1 percent with the real interest rate constant, what would the resulting nominal interest rate become using the Fisher relationship (ignoring taxes)? The expected rate of inflation is considered to remain at the lower level. Starting from an initial equilibrium position as in 4.a, discuss the effects of the conduct of a more restrictive monetary policy if the public believes that a Fed tightening will lower future (next period) inflation. How might a recession occur under this scenario? Characterize in the loanable funds model with a significant decline in the aggregate demand due to the coronavirus in 2020. If the Fed counters this loss of confidence by supplying funds, show in a graph what would happen first to interest rates after the decline in aggregate demand and second as the Fed attempts to supply these funds through either open market operations or direct lending from the discount window. (d) HINTS: Recall the Fisher relationship is (1+i)= (1+r)(1+p), where i is the nominal interest rate, r is the required real rate of return before taxes, and pe is the expected rate of inflation. DLF = I+G-T+ NX I= investment in real assets; NX = net exports G-T= the government deficit (excess of government spending over tax revenues). SLF = S + AMS - H S = private savings H= desired hoarding AMs = change in the money supply (under Federal Reserve discretionary control). 4. Using the graph below of the supply of loanable funds, Slf, and the demand for loanable funds, Dlf, discuss the following: 3 SLF Interest Rate(%) it X DLF Loanable Funds ($) (a) (b) What is meant by the equilibrium rate of interest? Illustrate and discuss how an autonomous increase in the expected rate of inflation will change the demand and supply of loanable funds and the equilibrium nominal interest rate. Discuss the effects of this change in expectations on the demand and supply of loanable funds. Consider an initial real rate of interest of 3 percent and an expected inflation rate of 2 percent. If the expected rate of inflation falls to a deflationary -1 percent with the real interest rate constant, what would the resulting nominal interest rate become using the Fisher relationship (ignoring taxes)? The expected rate of inflation is considered to remain at the lower level. Starting from an initial equilibrium position as in 4.a, discuss the effects of the conduct of a more restrictive monetary policy if the public believes that a Fed tightening will lower future (next period) inflation. How might a recession occur under this scenario? Characterize in the loanable funds model with a significant decline in the aggregate demand due to the coronavirus in 2020. If the Fed counters this loss of confidence by supplying funds, show in a graph what would happen first to interest rates after the decline in aggregate demand and second as the Fed attempts to supply these funds through either open market operations or direct lending from the discount window. (d) HINTS: Recall the Fisher relationship is (1+i)= (1+r)(1+p), where i is the nominal interest rate, r is the required real rate of return before taxes, and pe is the expected rate of inflation. DLF = I+G-T+ NX I= investment in real assets; NX = net exports G-T= the government deficit (excess of government spending over tax revenues). SLF = S + AMS - H S = private savings H= desired hoarding AMs = change in the money supply (under Federal Reserve discretionary control)







