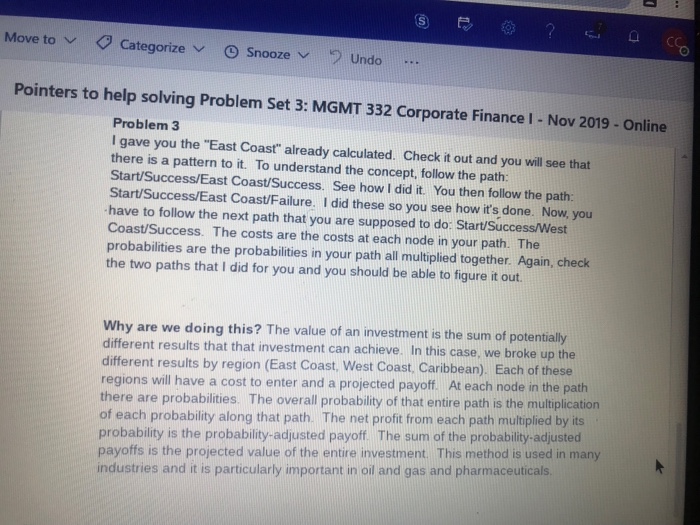
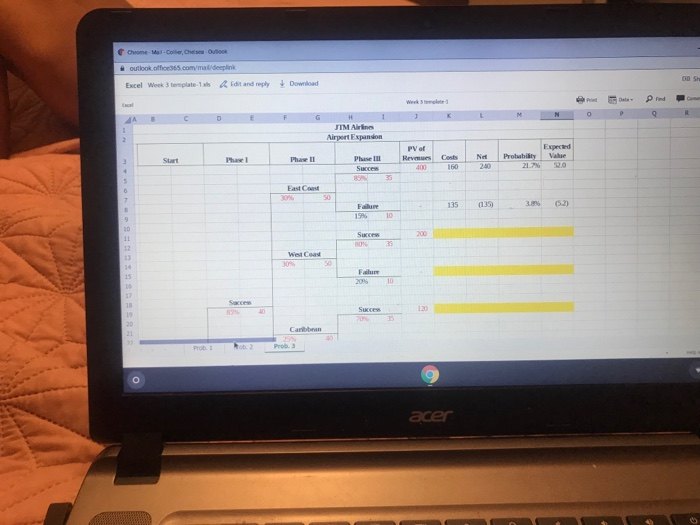
4. you compare the price of the call option as calculated using the BSO formula with the NPV in the No Real Options scenario. With this, you can decide whether or not the $1M option is worth it or not. Is it? Problem 3 - Decision Tree JTM really liked your work on the option pricing of the gates, so they ask you to look at their 3-phase expansion at their home airport. The three phases are: 1. upon purchase of the new gates, start a marketing program to promote JTM's routes to the East Coast, West Coast, and the Caribbean. It all goes well and the market is receptive, they will go on to phase 2 2. phase 2 has JTM invest in new routes to the three sets of destinations listed. If at any time. JTM finds that this is not going to work, they will pull the plug on phase 2 and scratch the project 3. phase 3 has JTM start the new routes to the destinations listed. If things don't go well on any of the three destinations, they will pull the plug on phase 3 and scratch that destination out After much work with other departments, you generate enough data to calculate the NPV of the 3-phase expansion. Before you have a chance to save all your work, there is a power spike in the building and you lose part of your work. You have to go back and complete it so you can present it to your manager. Please use the template to complete problem 3 Problem Set 1 Rubric (3) Criteria Ratings Pts acer Move to Categorize Snooze Undo Pointers to help solving Problem Set 3: MGMT 332 Corporate Finance I - Nov 2019 - Online Problem 3 I gave you the "East Coast" already calculated. Check it out and you will see that there is a pattern to it. To understand the concept, follow the path Start/Success/East Coast/Success. See how I did it. You then follow the path Start/Success/East Coast/Failure. I did these so you see how it's done. Now, you have to follow the next path that you are supposed to do: Start/Success/West Coast/Success. The costs are the costs at each node in your path. The probabilities are the probabilities in your path all multiplied together. Again, check the two paths that I did for you and you should be able to figure it out. Why are we doing this? The value of an investment is the sum of potentially different results that that investment can achieve. In this case, we broke up the different results by region (East Coast, West Coast, Caribbean). Each of these regions will have a cost to enter and a projected payoff. At each node in the path there are probabilities. The overall probability of that entire path is the multiplication of each probability along that path. The net profit from each path multiplied by its probability is the probability-adjusted payoff. The sum of the probability-adjusted payoffs is the projected value of the entire investment. This method is used in many industries and it is particularly important in oil and gas and pharmaceuticals Chrome Matches Otok outlook off .com mat deeplink Excel Week 3 torplatens Edit and reply Download JIM Airlines Airport Expansion Expected Value Phasell Phase III Net Probabilly acer 4. you compare the price of the call option as calculated using the BSO formula with the NPV in the No Real Options scenario. With this, you can decide whether or not the $1M option is worth it or not. Is it? Problem 3 - Decision Tree JTM really liked your work on the option pricing of the gates, so they ask you to look at their 3-phase expansion at their home airport. The three phases are: 1. upon purchase of the new gates, start a marketing program to promote JTM's routes to the East Coast, West Coast, and the Caribbean. It all goes well and the market is receptive, they will go on to phase 2 2. phase 2 has JTM invest in new routes to the three sets of destinations listed. If at any time. JTM finds that this is not going to work, they will pull the plug on phase 2 and scratch the project 3. phase 3 has JTM start the new routes to the destinations listed. If things don't go well on any of the three destinations, they will pull the plug on phase 3 and scratch that destination out After much work with other departments, you generate enough data to calculate the NPV of the 3-phase expansion. Before you have a chance to save all your work, there is a power spike in the building and you lose part of your work. You have to go back and complete it so you can present it to your manager. Please use the template to complete problem 3 Problem Set 1 Rubric (3) Criteria Ratings Pts acer Move to Categorize Snooze Undo Pointers to help solving Problem Set 3: MGMT 332 Corporate Finance I - Nov 2019 - Online Problem 3 I gave you the "East Coast" already calculated. Check it out and you will see that there is a pattern to it. To understand the concept, follow the path Start/Success/East Coast/Success. See how I did it. You then follow the path Start/Success/East Coast/Failure. I did these so you see how it's done. Now, you have to follow the next path that you are supposed to do: Start/Success/West Coast/Success. The costs are the costs at each node in your path. The probabilities are the probabilities in your path all multiplied together. Again, check the two paths that I did for you and you should be able to figure it out. Why are we doing this? The value of an investment is the sum of potentially different results that that investment can achieve. In this case, we broke up the different results by region (East Coast, West Coast, Caribbean). Each of these regions will have a cost to enter and a projected payoff. At each node in the path there are probabilities. The overall probability of that entire path is the multiplication of each probability along that path. The net profit from each path multiplied by its probability is the probability-adjusted payoff. The sum of the probability-adjusted payoffs is the projected value of the entire investment. This method is used in many industries and it is particularly important in oil and gas and pharmaceuticals Chrome Matches Otok outlook off .com mat deeplink Excel Week 3 torplatens Edit and reply Download JIM Airlines Airport Expansion Expected Value Phasell Phase III Net Probabilly acer