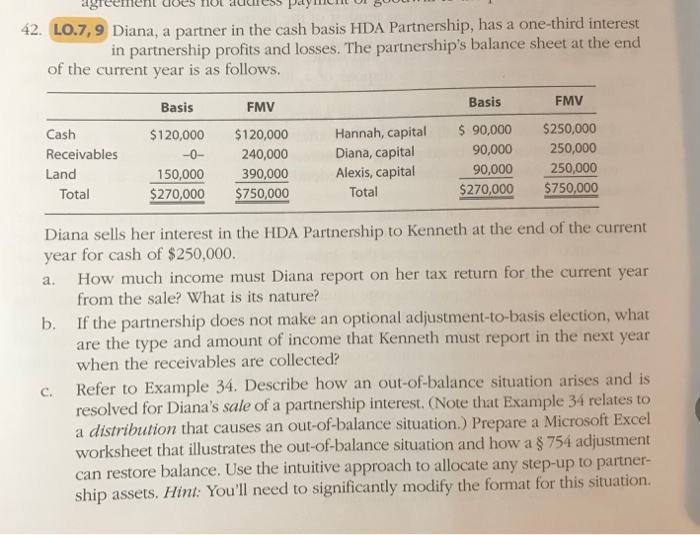
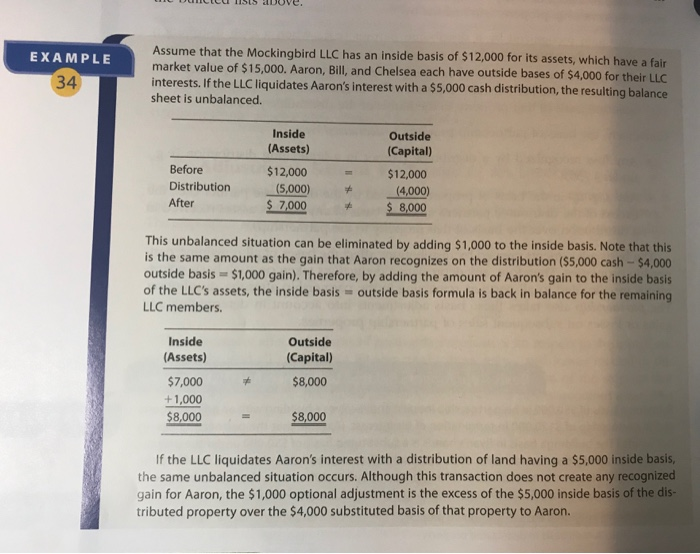
42. LO.7, 9 Diana, a partner in the cash basis HDA Partnership, has a one-third interest in partnership profits and losses. The partnership's balance sheet at the end of the current year is as follows. FMV Basis FMV Cash Receivables Land Total Basis $120,000 -0- 150,000 $270,000 $120,000 240,000 390,000 $750,000 Hannah, capital Diana, capital Alexis, capital Total $ 90,000 90,000 90,000 $270,000 $250,000 250,000 250,000 $750,000 a. Diana sells her interest in the HDA Partnership to Kenneth at the end of the current year for cash of $250,000. How much income must Diana report on her tax return for the current year from the sale? What is its nature? b. If the partnership does not make an optional adjustment-to-basis election, what are the type and amount of income that Kenneth must report in the next year when the receivables are collected? Refer to Example 34. Describe how an out-of-balance situation arises and is resolved for Diana's sale of a partnership interest. (Note that Example 34 relates to a distribution that causes an out-of-balance situation.) Prepare a Microsoft Excel worksheet that illustrates the out-of-balance situation and how a $ 754 adjustment can restore balance. Use the intuitive approach to allocate any step-up to partner- ship assets. Hint: You'll need to significantly modify the format for this situation. c. d. If the partnership did make an optional adjustment-to-basis election, what are the type and amount of income that Kenneth would report in the next year when the receivables are collected? If the land (which is used in the HDA Part- nership's business) was sold for $420,000? Assume that no other transactions occurred that year. EXAMPLE 34 Assume that the Mockingbird LLC has an inside basis of $12,000 for its assets, which have a fair market value of $15,000. Aaron, Bill, and Chelsea each have outside bases of $4,000 for their LLC interests. If the LLC liquidates Aaron's interest with a $5,000 cash distribution, the resulting balance sheet is unbalanced. Inside (Assets) Before Distribution After $12,000 (5,000) $ 7,000 Outside (Capital) $12,000 (4,000) $ 8,000 This unbalanced situation can be eliminated by adding $1,000 to the inside basis. Note that this is the same amount as the gain that Aaron recognizes on the distribution ($5,000 cash - $4,000 outside basis = $1,000 gain). Therefore, by adding the amount of Aaron's gain to the inside basis of the LLC's assets, the inside basis - outside basis formula is back in balance for the remaining LLC members. Inside (Assets) $7,000 +1,000 $8,000 Outside (Capital) $8,000 $8,000 If the LLC liquidates Aaron's interest with a distribution of land having a $5,000 inside basis, the same unbalanced situation occurs. Although this transaction does not create any recognized gain for Aaron, the $1,000 optional adjustment is the excess of the $5,000 inside basis of the dis- tributed property over the $4,000 substituted basis of that property to Aaron