4-26 & 4-60
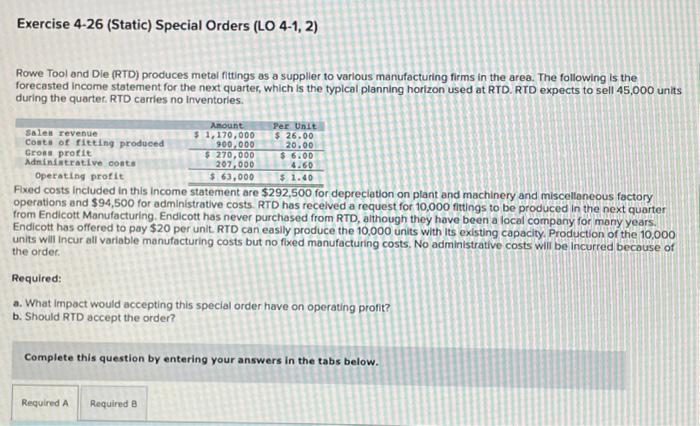
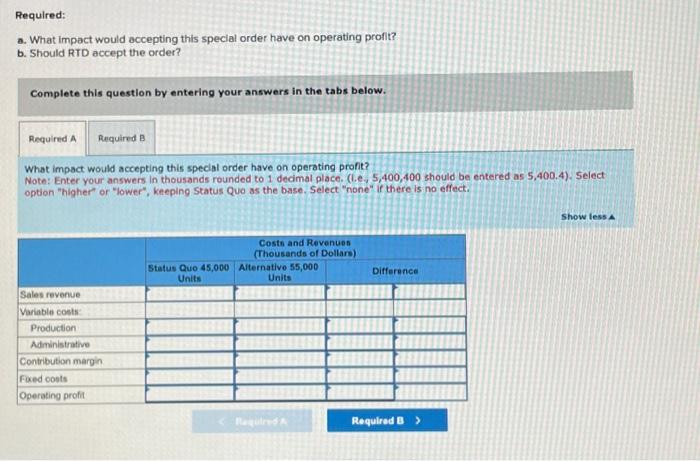
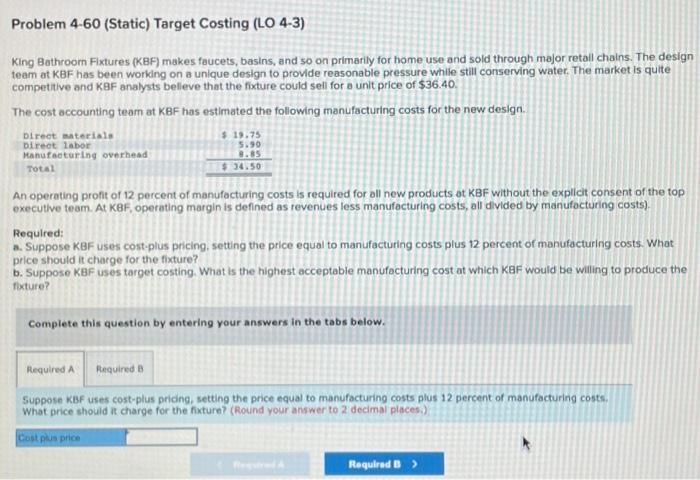
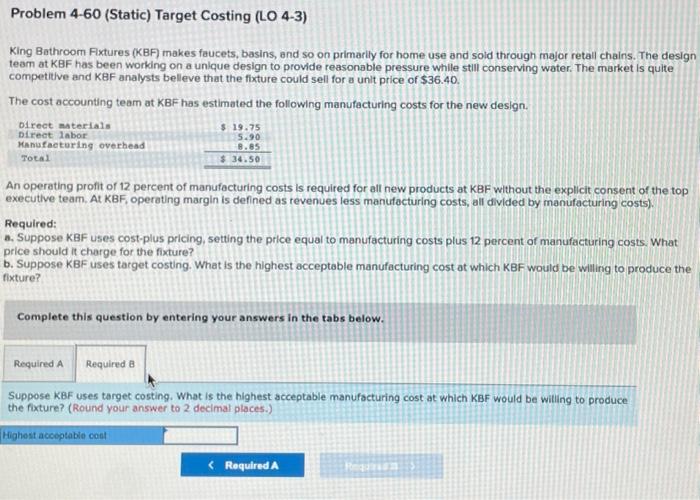
Required: a. What impact would accepting this special order have on operating profit? b. Should RTD accept the order? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. What impact would accepting this special order have on operating profit? Note: Enter your answers in thousands rounded to 1 decimal place. (1.e, 5,400,400 should be entered as 5,400,4). 5elect option "higher" or "lower", keeping Status Quo as the base. Select "none" if there is no effect. Exercise 4-26 (Static) Special Orders (LO 4-1, 2) Rowe Tool and Die (RTD) produces metal fittings as a suppller to varlous manufacturing firms in the area. The following is the forecasted income statement for the next quarter, which is the typlcal planning horizon used at RTD. RTD expects to sell 45,000 units during the quarter. RTD carries no inventories. rowed costs inciuded in this income statement are $292,500 for depreciation on plant and machinery and miscellaneous factory operations and $94,500 for administrative costs. RTD has recelved a request for 10,000 fittings to be produced in the next quarter from Endicott Manufacturing. Endicott has never purchased from RTD, although they have been a local company for many years. Endicott has offered to pay $20 per unit. RTD can easily produce the 10,000 units with its existing capacity. Production of the 10,000 units will incur all variable manufacturing costs but no fixed manufacturing costs. No administrative costs wili be incurred because of the order. Required: a. What impact would accepting this special order have on operating profit? b. Should RTD accept the order? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Problem 4-60 (Static) Target Costing (LO 4-3) King Bathroom Fxtures (KBF) makes faucets, basins, and so on primarily for home use and sold through major retall chains. The design team at KBF has been working on a unlque design to provide reasonable pressure whille still conserving water. The market is quite. competitve and KBF analysts belleve that the fixture could sell for a unit price of $36.40. The cost accounting team at KBF has estimated the following manufacturing costs for the new design. An operating profit of 12 percent of manufacturing costs is required for all new products at KBF without the explicit consent of the top executive team. At KBF, operating margin is defined as revenues less manufacturing costs, all divided by manufacturing costs). Required: a. Suppose KBF uses cost-plus pricing, setting the price equal to manufacturing costs plus 12 percent of manufacturing costs. What price should it charge for the fixture? b. Suppose KBF uses target costing. What is the highest acceptable manufacturing cost at which KBF would be willing to produce the flxture? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Suppose KBF uses target costing. What is the highest acceptable manufacturing cost at which KBF would be willing to produce the foxture? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) King Bathroom Fixtures (KBF) makes faucets, basins, and so on primarily for home use and sold through major retall chains. The design team at KBF has been working on a unique design to provide reasonable pressure while still conserving water. The market is quite competitive and KBF analysts belleve that the fixture could sell for a unit price of $36.40. The cost accounting team at KBF has estimated the following manufacturing costs for the new design. An operating profit of 12 percent of manufacturing costs is required for all new products ot KBF without the explicit consent of the top executlve team. At KBF, operating margin is defined as revenues less manufacturing costs, all divided by manufocturing costs). Required: a. Suppose KBF uses cost-plus pricing, setting the price equal to manufacturing costs plus 12 percent of manufacturing costs. What price should it charge for the fixture? b. Suppose KBF uses target costing. What is the highest acceptable manufacturing cost at which KBF would be willing to produce the fixture? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Suppose KBf uses cost-plus priding, setting the price equal to manufacturing costs plus 12 percent of manufacturing costs. What price should it charge for the fixture? (Round your answer to 2 decimai places.)