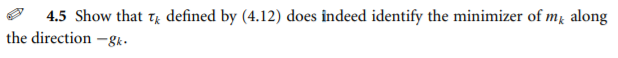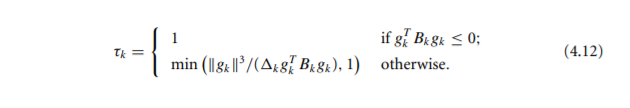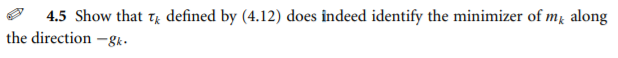

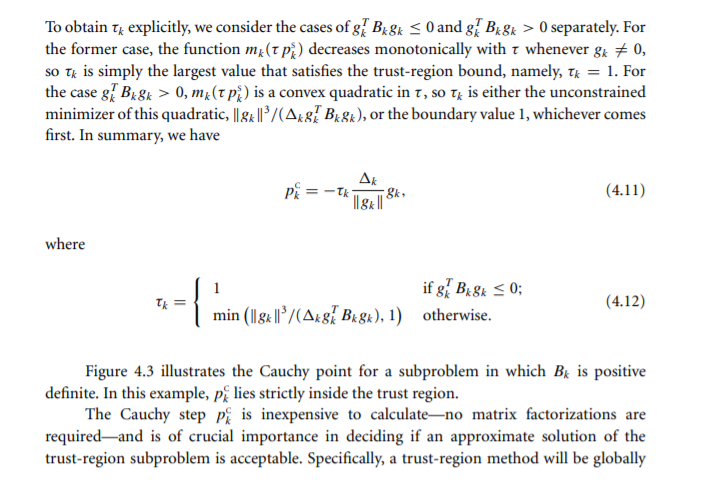
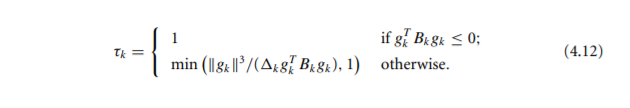
4.5 Show that Tk defined by (4.12) does indeed identify the minimizer of me along the direction - gk. Algorithm 4.2 (Cauchy Point Calculation). Find the vector p, that solves a linear version of (4.3), that is, p = arg min fx + gp s.t. ||p| 0 that minimizes m(t p) subject to satisfying the trust-region bound, that is, Ik = arg min m (1 p.) s.t. || 1 pill separately. For the former case, the function m (p) decreases monotonically with t whenever gk # 0, SO Tk is simply the largest value that satisfies the trust-region bound, namely, tk = 1. For the case g Bx&k > 0, m (Tp) is a convex quadratic in t, so Tt is either the unconstrained minimizer of this quadratic, | 84 /(Ax8} Bx8k), or the boundary value 1, whichever comes first. In summary, we have PE =-Tk Ak 18x 10 (4.11) where Tk if 87 Bk8k = 0; min (1884 11/(Axsh Bkgk), 1) otherwise. (4.12) Figure 4.3 illustrates the Cauchy point for a subproblem in which Bk is positive definite. In this example, p lies strictly inside the trust region. The Cauchy step pi is inexpensive to calculateno matrix factorizations are requiredand is of crucial importance in deciding if an approximate solution of the trust-region subproblem is acceptable. Specifically, a trust-region method will be globally 1 T = = { if g Bkgk 0 that minimizes m(t p) subject to satisfying the trust-region bound, that is, Ik = arg min m (1 p.) s.t. || 1 pill separately. For the former case, the function m (p) decreases monotonically with t whenever gk # 0, SO Tk is simply the largest value that satisfies the trust-region bound, namely, tk = 1. For the case g Bx&k > 0, m (Tp) is a convex quadratic in t, so Tt is either the unconstrained minimizer of this quadratic, | 84 /(Ax8} Bx8k), or the boundary value 1, whichever comes first. In summary, we have PE =-Tk Ak 18x 10 (4.11) where Tk if 87 Bk8k = 0; min (1884 11/(Axsh Bkgk), 1) otherwise. (4.12) Figure 4.3 illustrates the Cauchy point for a subproblem in which Bk is positive definite. In this example, p lies strictly inside the trust region. The Cauchy step pi is inexpensive to calculateno matrix factorizations are requiredand is of crucial importance in deciding if an approximate solution of the trust-region subproblem is acceptable. Specifically, a trust-region method will be globally 1 T = = { if g Bkgk