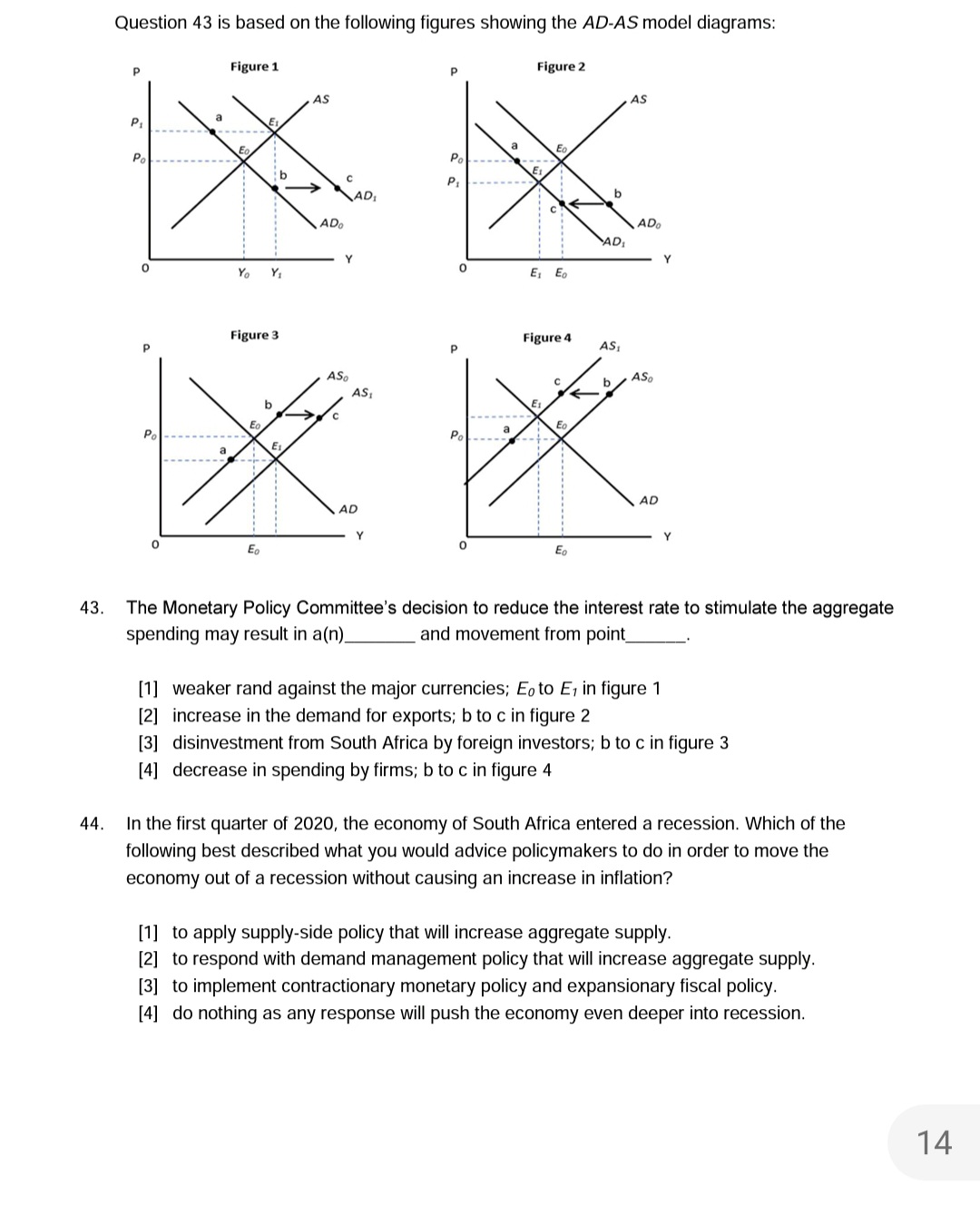
4B. 49. 50. 51. Which of the following best describes a difference between demand-pull ination and cost-push ination? [1] Demand-pull ination occurs when there is a shortage in aggregate demand, while cost- push inflation is the upward pressure on the general price level due to rising cost of production. [2] Cost-push ination can be caused by increases in the cost of wages and intermediate goods. while demand-pull can be caused by increase in exports. [3] Demand-pull ination is triggered by increases in the cost of production, while cost-push ination occurs when the aggregate demand for goods and services increases while aggregate supply remains unchanged. [4] There is no difference between demand-pull inflation and cost-push inflation as they are triggered by the same sources. If inflation accelerates due to the increase in the price of oil (an import), the best policy to combat such inflation in a country with a high unemployment rate. would be to... [1] apply the supply-side policy that will increase aggregate supply. which will be illustrated by a rightward shift of the AS curve. [2] respond with demand management policy that will increase aggregate demand. which will be illustrated by a rightward shift of the AD curve. [3] implement contractionary monetary policy. illustrated by the rightward shift of the AD curve. [4] apply incomes policy. illustrated by a leftward shift of the AS curve. To enter the pool of unemployment, a person must be... [1] any age and looking for ajob. [2] a discouraged work-seeker. [3] economically active. [4] working while searching for better ajob. CONFIDENTIAL 16 Page 11 of 20 ECS161t Manyune 2020 Assume the local currency weakens against the major currencies. This will result in... a) a decrease in the employment level. b) an increase in the net export. c) a fall in the purchasing power of local currency. d) an increase in the purchasing power of local currency. [1] a and b [2] b and c [3] c [4] a and d [5] a, b. c and d 51. Assume the local currency weakens against the major currencies. This will result in... a) a decrease in the employment level. b) an increase in the net export. C) a fall in the purchasing power of local currency. d) an increase in the purchasing power of local currency. [1] a and b [2] b and c [3] C [4] a and d [5] a, b, c and d Questions 52 and 53 are based on the following table showing the key labour market indicators in South Africa: Number of persons ('000) Population 15-64 yrs 38 134 Labour force 22 668 Employed 16 529 Unemployed 6 139 Discouraged work- 2 841 seekers 52. The unemployment rate (using the strict definition) in South Africa is... (rounded to two decimals after the comma). [1] 54,33% [2] 35,20% [3] 37,14% [4] 27,08% 53. The unemployment rate (using expanded definition) in South Africa is... (rounded to two decimals after the comma). [1] 54,33% [2] 35,20% [3] 37,14% [4] 27,08% CONFIDENTIAL Page 18 of 20 ECS1610 May/June 202 17 54. Due to coronavirus pandemic, many education institutions adopted an online teaching method. This meant that all educators must now be able to do teaching online. Mary, a contract educator, was laid off by her employer because she does not know how to use online teaching tools. Until she finds a new job, Mary is... [1] structurally unemployed. [2] cyclically unemployed. [3] seasonally unemployed. [4] frictionally unemployed.43. 44. Question 43 is based on the following figures showing the AD-AS model diagrams: p Figure 1 9 Figure 2 The Monetary Policy Committee's decision to reduce the interest rate to stimulate the aggregate spending may result in a(n) and movement from point ['I] weaker rand against the major currencies; E0 to E 1 in figure 1 [2] increase in the demand for exports: b to c in figure 2 [3] disinvestment from South Africa by foreign investors: b to c in figure 3 [4] decrease in spending by firms; b to c in figure 4 In the first quarter of 2020. the economy of South Africa entered a recession. Which of the following best described what you would advice policymakers to do in order to move the economy out of a recession without causing an increase in inflation? ['l] to apply supply-side policy that will increase aggregate supply. [2] to respond with demand management policy that will increase aggregate supply. [3] to implement contractionary monetary policy and expansionary scal policy. [4] do nothing as any response will push the economy even deeper into recession. 14 Question 45 is based on the following diagram: P 'AS, AS P1 Po AD Y1 Yo 45. According to the AD-AS model, a shift of AS curve from AS to AS, is the result of... [1] a decrease in spending by households. [2] an increase in the cost of production. [3] an increase in the general price level in the economy. [4] a decrease in the cost of production. Question 46 is based on the following table showing the CPI in South Africa, 2016-2020: Year Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Average 2016 94.4 95,7 96.4 97,2 97.4 97,9 98,7 98,6 98,8 99,3 99,6 100,0 97,8 2017 100,6 101,7 102,3 102,4 102,7 102,9 103,2 103,3 103,8 104,1 104,2 104,7 103,0 2018 105,0 105,8 106,2 107,0 107,2 107,6 108,5 108,4 108,9 109,4 109,6 109.4 107,8 2019 109,2 110,1 111,0 111,7 112,0 112,4 112,8 113,1 113,4 113,4 113,5 113,8 112,2 2020 114,1 115,2 115,6 Source: Statistics South Africa (2020). 46. Based on the information in the table, which of the following is true? [1] 2020 is the base year [2] The average annual inflation rate for 2019 was 4,08% [3] Price levels increased by 2,7% between 2016 and 2017 [4] The average annual inflation rate for 2018 is obtained as follows: 107,8-105,0 105,0 x 100 15 CONFIDENTIAL Page 16 of 20 ECS1610 May/June 2020 47. Which one of the following is NOT an effect of higher inflation? [1] Redistribution of wealth from the lender to the borrower. A decrease of the real value of existing savings. [3] An increase in the standard of living. [4] An increase in the cost of living