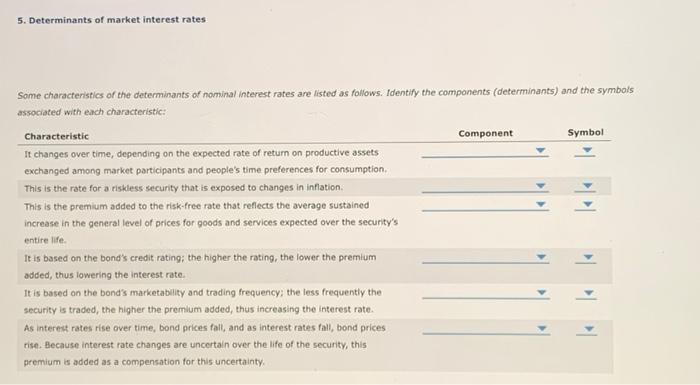
5. Determinants of market interest rates Some characteristics of the determinants of nominal interest rates are listed as follows. Identify the components (determinants) and the symbols associated with each characteristic: Characteristic Component Symbol It changes over time, depending on the expected rate of return on productive assets exchanged among market participants and people's time preferences for consumption This is the rate for a riskless security that is exposed to changes in inflation This is the premium added to the risk-free rate that reflects the average sustained increase in the general level of prices for goods and services expected over the security's entire life. It is based on the band's credit rating; the higher the rating, the lower the premium added, thus lowering the interest rate. It is based on the bond's marketability and trading frequency, the less frequently the security is traded, the higher the premium added, thus increasing the interest rate. As interest rates rise over time, bond prices fall, and as interest rates fall, bond prices rise. Because interest rate changes are uncertain over the life of the security, this premium is added as a compensation for this uncertainty 5. Determinants of market interest rates Some characteristics of the determinants of nominal interest rates are listed as follows. Identify the components (determinants) and the symbols associated with each characteristic: Characteristic Component Symbol It changes over time, depending on the expected rate of return on productive assets exchanged among market participants and people's time preferences for consumption This is the rate for a riskless security that is exposed to changes in inflation This is the premium added to the risk-free rate that reflects the average sustained increase in the general level of prices for goods and services expected over the security's entire life. It is based on the band's credit rating; the higher the rating, the lower the premium added, thus lowering the interest rate. It is based on the bond's marketability and trading frequency, the less frequently the security is traded, the higher the premium added, thus increasing the interest rate. As interest rates rise over time, bond prices fall, and as interest rates fall, bond prices rise. Because interest rate changes are uncertain over the life of the security, this premium is added as a compensation for this uncertainty