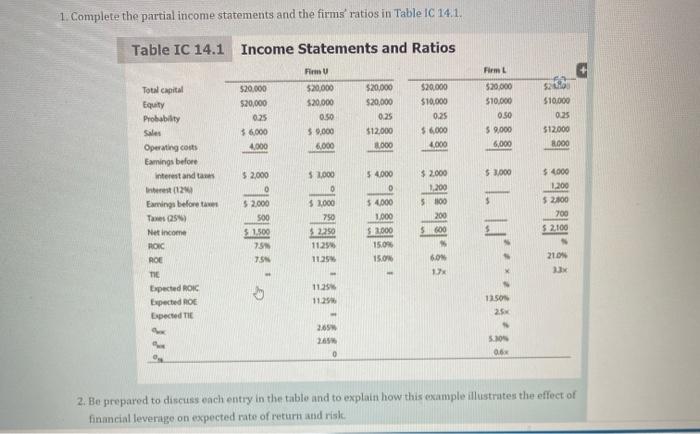
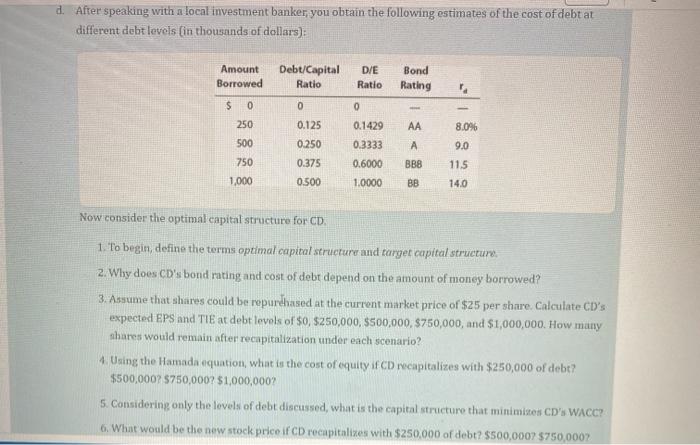
5. OPTIMAL. CAPITAL.STRUCTURE Assume thatyou have just been hired as business manager of Campus Deli (CD), which is located adjacent to the campus. Sales were $1,100,000 last year; variable costs were 60% of sales, and fixed costs were $40,000. Therefore, EBIT totaled $400,000. Because the university's enrollment is capped, EBIT is expected to be constant over time. Because no expansion capital is required, CD distributes all earnings as dividends. Invested capital is $2 million, and 80,000 shares are outstanding. The management group owns about 50% of the stock, which is traded in the over-the-counter market. CD currently has no debt - it is an all-equity firm - and its 80,000 shares outstanding sell at a price of $25 per share, which is also the book value. The firm's federal-plus-state tax rate is 25%. On the basis of statements made in your finance text, you believe that CD's shareholders would be better off if some debt financing were used. When you suggested this to your new boss, she encouraged you to pursue the idea but to provide support: for the suggestion. Note that CD is a small firm, so it is exempt from the interest deduction limitation. In today's tharket, the risk-free rate, RRP, is 7,5%, and the market risk premium, RPM, is 6%. CD's unlevered beta, bu, is 1.25. CD currently has no debt, so its cost of equity (and WACC) is 15%. If the firm was recapitalized, debt would be issued, and the borrowed funds Iwould be used to repurchase stock. Stockholders, in turn, would use funds provided by the repurchase to buy equities in other fast-food companies similar to CD. You plin to complete your report by asking and then answering the following questions. a. 1. What is business risk? What factors influence a firm's business risk? 2. What is operating leverage, and how does it affect a firm's business risk? 3. What is the firm's return on invested capital (ROIC)? 1. What do the terms financial leverage and financial risk mean? 2. How does financial risk differ from business risk? c. To develop an example that can be presented to CD's management as an illustration, consider two small hypothetical firms: Firm U with zero debt financing and Firm L with $10,000 of 12% debt. Both firms have $20,000 in invested capital and a 25% federal-plus-state tax rate, and they have the following EBIT probability distribution for next year: 1. Complete the partial income statements and the firms' ratios in Table iC 14.1. 2. Be prepared to discuss each entry in the table and to explain how this cxample illustrates the effect of financial leverige on expected rate of return and risle. 1. Afrer speaking with a local investment banker, you obtain-the following estimates of the cost of debt at different debt levels (in thousands of dollars): Now consider the optimal capital structure for CD. 1. To begin, define the terms optimal capital strueture and target capital structure: 2. Why does CD's bond rating and cost of debt depend on the amount of money borrowed? 3. Assume that shares could be repurehased at the current market price of $25 per share. Calculate CD's expected EPS and TIE at debt levels of $0,$250,000,$500,000,$750,000, and $1,000,000. How many ahares would remain after recapitalization under each scenario? 4. Using the Hamada nquation, what is the cost of equity if CD necapitalizes with $250,000 of debt? $500,000?$750,000?$1,000,000? 5. Considering only the levels of debt discussed, what is the capital structure that minimistes CD' WACC? 6. What would be the new stock price if CD recapitalizes with $250,000 of debt? $500,0007$750,000 ? 5. OPTIMAL. CAPITAL.STRUCTURE Assume thatyou have just been hired as business manager of Campus Deli (CD), which is located adjacent to the campus. Sales were $1,100,000 last year; variable costs were 60% of sales, and fixed costs were $40,000. Therefore, EBIT totaled $400,000. Because the university's enrollment is capped, EBIT is expected to be constant over time. Because no expansion capital is required, CD distributes all earnings as dividends. Invested capital is $2 million, and 80,000 shares are outstanding. The management group owns about 50% of the stock, which is traded in the over-the-counter market. CD currently has no debt - it is an all-equity firm - and its 80,000 shares outstanding sell at a price of $25 per share, which is also the book value. The firm's federal-plus-state tax rate is 25%. On the basis of statements made in your finance text, you believe that CD's shareholders would be better off if some debt financing were used. When you suggested this to your new boss, she encouraged you to pursue the idea but to provide support: for the suggestion. Note that CD is a small firm, so it is exempt from the interest deduction limitation. In today's tharket, the risk-free rate, RRP, is 7,5%, and the market risk premium, RPM, is 6%. CD's unlevered beta, bu, is 1.25. CD currently has no debt, so its cost of equity (and WACC) is 15%. If the firm was recapitalized, debt would be issued, and the borrowed funds Iwould be used to repurchase stock. Stockholders, in turn, would use funds provided by the repurchase to buy equities in other fast-food companies similar to CD. You plin to complete your report by asking and then answering the following questions. a. 1. What is business risk? What factors influence a firm's business risk? 2. What is operating leverage, and how does it affect a firm's business risk? 3. What is the firm's return on invested capital (ROIC)? 1. What do the terms financial leverage and financial risk mean? 2. How does financial risk differ from business risk? c. To develop an example that can be presented to CD's management as an illustration, consider two small hypothetical firms: Firm U with zero debt financing and Firm L with $10,000 of 12% debt. Both firms have $20,000 in invested capital and a 25% federal-plus-state tax rate, and they have the following EBIT probability distribution for next year: 1. Complete the partial income statements and the firms' ratios in Table iC 14.1. 2. Be prepared to discuss each entry in the table and to explain how this cxample illustrates the effect of financial leverige on expected rate of return and risle. 1. Afrer speaking with a local investment banker, you obtain-the following estimates of the cost of debt at different debt levels (in thousands of dollars): Now consider the optimal capital structure for CD. 1. To begin, define the terms optimal capital strueture and target capital structure: 2. Why does CD's bond rating and cost of debt depend on the amount of money borrowed? 3. Assume that shares could be repurehased at the current market price of $25 per share. Calculate CD's expected EPS and TIE at debt levels of $0,$250,000,$500,000,$750,000, and $1,000,000. How many ahares would remain after recapitalization under each scenario? 4. Using the Hamada nquation, what is the cost of equity if CD necapitalizes with $250,000 of debt? $500,000?$750,000?$1,000,000? 5. Considering only the levels of debt discussed, what is the capital structure that minimistes CD' WACC? 6. What would be the new stock price if CD recapitalizes with $250,000 of debt? $500,0007$750,000