
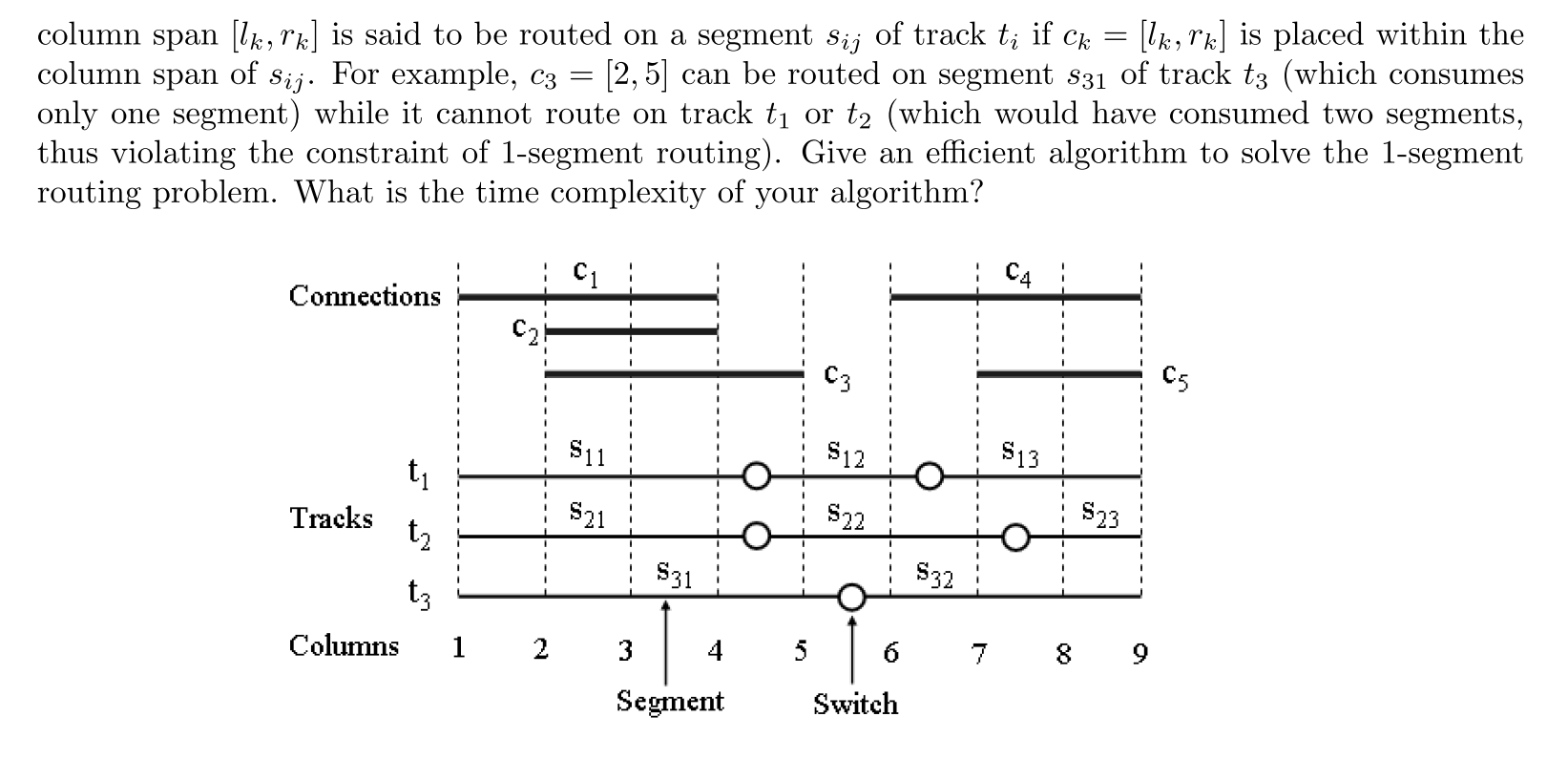
5. The figure below shows a segmented routing structure in a row-based field-programmable gate array (FPGA). There are five connections, c1, c2, ..., C5, to be routed on three segmented tracks, t1, t2, and t3, with eight segments s11, 812, of segments by using switches. If a switch incident on two adjacent segments is "ON", then the two segments are electrically connected; otherwise, the two segments can be used independently. You are asked to route (place) the five connections on the three segmented tracks. Suppose each connection can use at most one segment for routing, i.e., 1-segment routing. In other words, a connection Ck of the ., S32 in the row-based FPGA. A track can be partitioned into a set column span [lk,rk] is said to be routed on a segment s;ij of track t; if Ck = [lk,rk] is placed within the column of For example, c 2, 5| can be routed on segment s31 Of track t3 (which consumes span Sij. only one segment) while it cannot route on track t1 or t2 (which would have consumed two segments, thus violating the constraint of 1-segment routing). Give an efficient algorithm to solve the 1-segment routing problem. What is the time complexity of your algorithm? C4 Connections C5 $11 $12 $13 t1 $23 $21 S22 Tracks t2 S32 $31 t3 Columns 2 3 4 5 Segment Switch 5. The figure below shows a segmented routing structure in a row-based field-programmable gate array (FPGA). There are five connections, c1, c2, ..., C5, to be routed on three segmented tracks, t1, t2, and t3, with eight segments s11, 812, of segments by using switches. If a switch incident on two adjacent segments is "ON", then the two segments are electrically connected; otherwise, the two segments can be used independently. You are asked to route (place) the five connections on the three segmented tracks. Suppose each connection can use at most one segment for routing, i.e., 1-segment routing. In other words, a connection Ck of the ., S32 in the row-based FPGA. A track can be partitioned into a set column span [lk,rk] is said to be routed on a segment s;ij of track t; if Ck = [lk,rk] is placed within the column of For example, c 2, 5| can be routed on segment s31 Of track t3 (which consumes span Sij. only one segment) while it cannot route on track t1 or t2 (which would have consumed two segments, thus violating the constraint of 1-segment routing). Give an efficient algorithm to solve the 1-segment routing problem. What is the time complexity of your algorithm? C4 Connections C5 $11 $12 $13 t1 $23 $21 S22 Tracks t2 S32 $31 t3 Columns 2 3 4 5 Segment Switch








