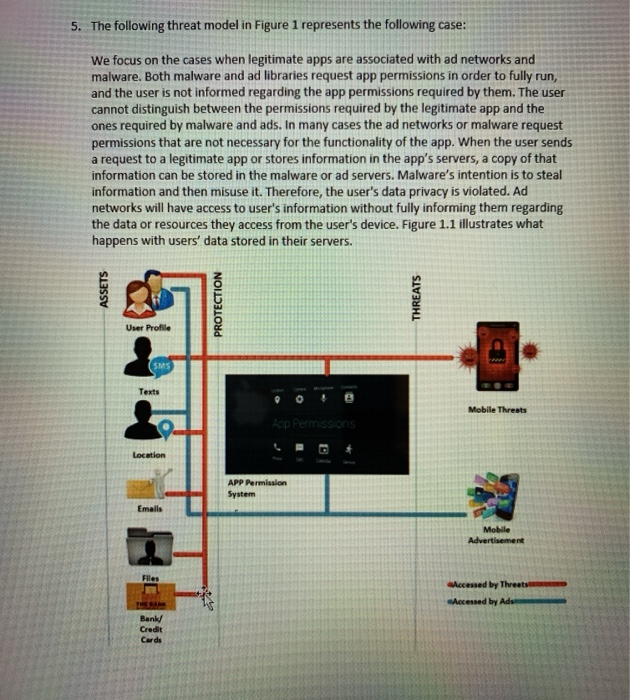
5. The following threat model in Figure 1 represents the following case: We focus on the cases when legitimate apps are associated with ad networks and malware. Both malware and ad libraries request app permissions in order to fully run, and the user is not informed regarding the app permissions required by them. The user cannot distinguish between the permissions required by the legitimate app and the ones required by malware and ads. In many cases the ad networks or malware request permissions that are not necessary for the functionality of the app. When the user sends a request to a legitimate app or stores information in the app's servers, a copy of that information can be stored in the malware or ad servers. Malware's intention is to steal information and then misuse it. Therefore, the user's data privacy is violated. Ad networks will have access to user's information without fully informing them regarding the data or resources they access from the user's device. Figure 1.1 illustrates what happens with users' data stored in their servers. ASSETS PROTECTION THREATS User Profile Texts Mobile Threats App Permissions Location APP Permission Emails Mobile Advertisement Files Accessed by Threats Accessed by Ads Bank/ Credit Cards Figure 1. Threat Model Showing the flow of Sensitive Information between the User of an App that might be Associated with Ad Networks or Malware. a. Identify the list of all legitimate users that have access on the mobile platform, especially accessing apps. (7 points) b. Identify the privileges of each user, which can access all the assets identified in the threat mode. (8 points) 5. The following threat model in Figure 1 represents the following case: We focus on the cases when legitimate apps are associated with ad networks and malware. Both malware and ad libraries request app permissions in order to fully run, and the user is not informed regarding the app permissions required by them. The user cannot distinguish between the permissions required by the legitimate app and the ones required by malware and ads. In many cases the ad networks or malware request permissions that are not necessary for the functionality of the app. When the user sends a request to a legitimate app or stores information in the app's servers, a copy of that information can be stored in the malware or ad servers. Malware's intention is to steal information and then misuse it. Therefore, the user's data privacy is violated. Ad networks will have access to user's information without fully informing them regarding the data or resources they access from the user's device. Figure 1.1 illustrates what happens with users' data stored in their servers. ASSETS PROTECTION THREATS User Profile Texts Mobile Threats App Permissions Location APP Permission Emails Mobile Advertisement Files Accessed by Threats Accessed by Ads Bank/ Credit Cards Figure 1. Threat Model Showing the flow of Sensitive Information between the User of an App that might be Associated with Ad Networks or Malware. a. Identify the list of all legitimate users that have access on the mobile platform, especially accessing apps. (7 points) b. Identify the privileges of each user, which can access all the assets identified in the threat mode. (8 points)