Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
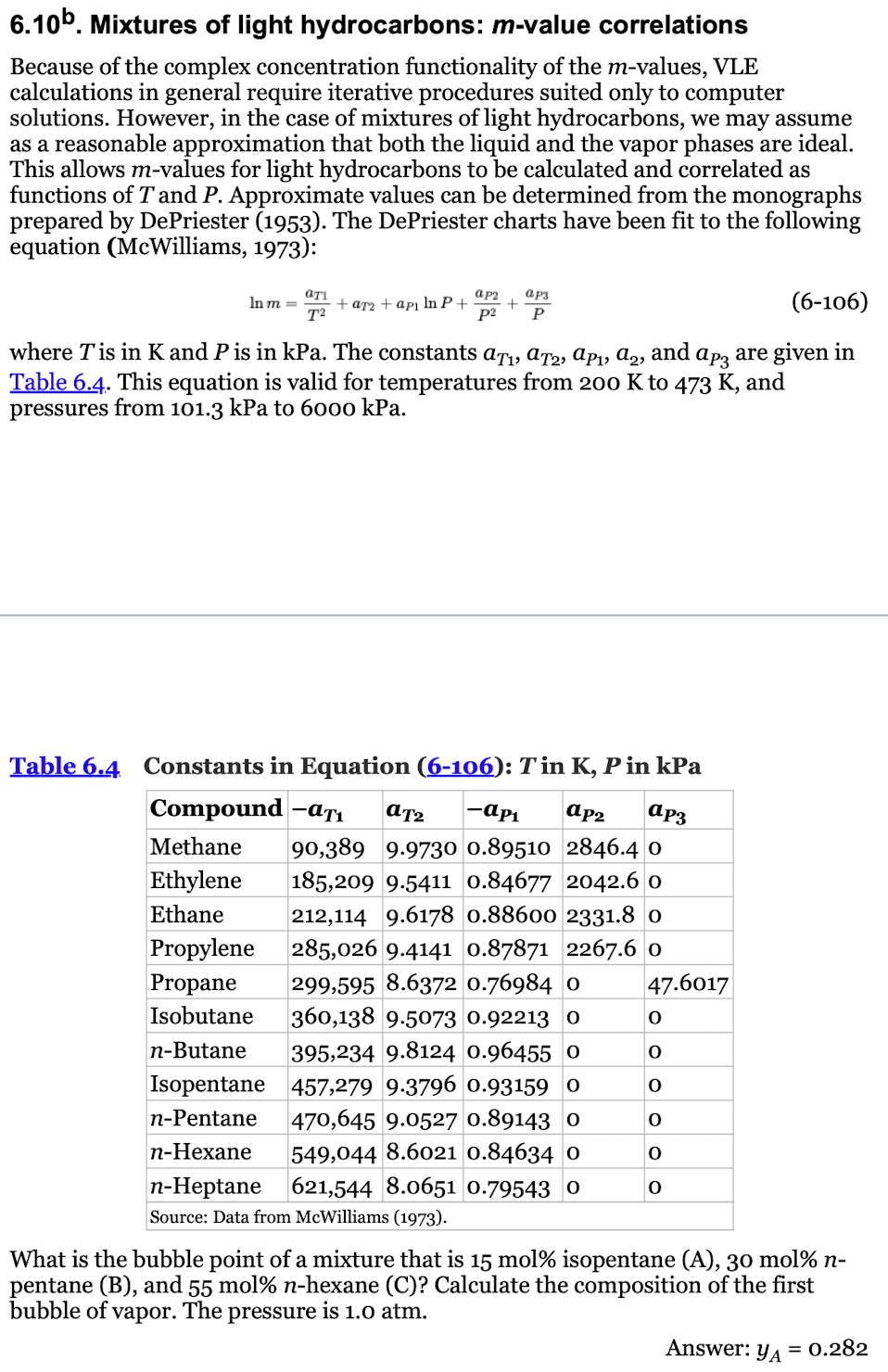
6 . 1 0 b . Mixtures of light hydrocarbons: m - value correlations Because of the complex concentration functionality of the m - values,
Mixtures of light hydrocarbons: value correlations
Because of the complex concentration functionality of the values, VLE
calculations in general require iterative procedures suited only to computer
solutions. However, in the case of mixtures of light hydrocarbons, we may assume
as a reasonable approximation that both the liquid and the vapor phases are ideal.
This allows values for light hydrocarbons to be calculated and correlated as
functions of and Approximate values can be determined from the monographs
prepared by DePriester The DePriester charts have been fit to the following
equation McWilliams:
where is in and is in kPa. The constants and are given in
Table This equation is valid for temperatures from to and
pressures from kPa to kPa.
Table Constants in Equation : in in kPa
What is the bubble point of a mixture that is mol isopentane Amol
pentane B and molhexane C Calculate the composition of the first
bubble of vapor. The pressure is atm.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


