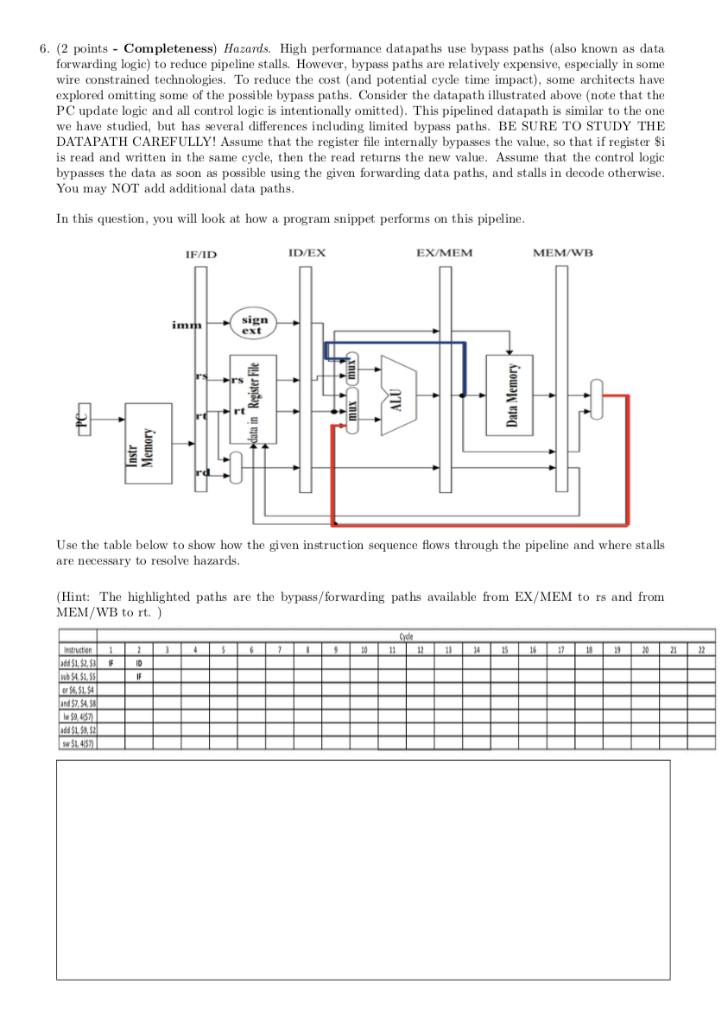
6. (2 points Completeness) Hazards. High performance datapaths use bypass paths (also known as data forwarding logic) to reduce pipeline stalls. However, bypass paths are relatively expensive, especially in some wire constrained technologies. To reduce the cost (and potential cycle time impact), some architects have explored omitting some of the possible bypass paths. Consider the datapath illustrated above (note that the PC update logic and all control logic is intentionally omitted). This pipelined datapath is similar to the one we have studied, but has several differences including limited bypass paths. BE SURE TO STUDY THE DATAPATH CAREFULLY! Assume that the register file internally bypasses the value, so that if register Si is read and written in the same cycle, then the read returns the new value. Assume that the control logic bypasses the data as soon as possible using the given forwarding data paths, and stalls in decode otherwise You may NOT add additional data paths In this question, you will look at how a program snippet performs on this pipeline IF/ID ID/EX EX/MEM MEM/WB sign ext rt Use the table below to show how the given instruction sequence flows through the pipeline and where stalls are necessary to resolve hazards. Hint: The highlighted paths are the bypass/forwarding paths available from EX/MEM to rs and from MEM/WB to rt.) etncter 19 and 57,S 6. (2 points Completeness) Hazards. High performance datapaths use bypass paths (also known as data forwarding logic) to reduce pipeline stalls. However, bypass paths are relatively expensive, especially in some wire constrained technologies. To reduce the cost (and potential cycle time impact), some architects have explored omitting some of the possible bypass paths. Consider the datapath illustrated above (note that the PC update logic and all control logic is intentionally omitted). This pipelined datapath is similar to the one we have studied, but has several differences including limited bypass paths. BE SURE TO STUDY THE DATAPATH CAREFULLY! Assume that the register file internally bypasses the value, so that if register Si is read and written in the same cycle, then the read returns the new value. Assume that the control logic bypasses the data as soon as possible using the given forwarding data paths, and stalls in decode otherwise You may NOT add additional data paths In this question, you will look at how a program snippet performs on this pipeline IF/ID ID/EX EX/MEM MEM/WB sign ext rt Use the table below to show how the given instruction sequence flows through the pipeline and where stalls are necessary to resolve hazards. Hint: The highlighted paths are the bypass/forwarding paths available from EX/MEM to rs and from MEM/WB to rt.) etncter 19 and 57,S







