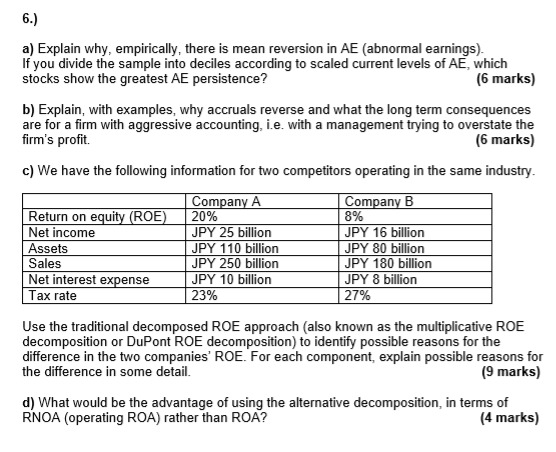
6.) 8% a) Explain why, empirically, there is mean reversion in AE abnormal earnings) If you divide the sample into deciles according to scaled current levels of AE, which stocks show the greatest AE persistence? (6 marks) b) Explain, with examples, why accruals reverse and what the long term consequences are for a firm with aggressive accounting, i.e. with a management trying to overstate the firm's profit (6 marks) c) We have the following information for two competitors operating in the same industry. Company A Company B Return on equity (ROE) 20% Net income JPY 25 billion JPY 16 billion Assets JPY 110 billion JPY 80 billion Sales JPY 250 billion JPY 180 billion Net interest expense JPY 10 billion JPY 8 billion Tax rate 23% 27% Use the traditional decomposed ROE approach (also known as the multiplicative ROE decomposition or DuPont ROE decomposition) to identify possible reasons for the difference in the two companies' ROE. For each component, explain possible reasons for the difference in some detail. (9 marks) d) What would be the advantage of using the alternative decomposition, in terms of RNOA (operating ROA) rather than ROA? (4 marks) 6.) 8% a) Explain why, empirically, there is mean reversion in AE abnormal earnings) If you divide the sample into deciles according to scaled current levels of AE, which stocks show the greatest AE persistence? (6 marks) b) Explain, with examples, why accruals reverse and what the long term consequences are for a firm with aggressive accounting, i.e. with a management trying to overstate the firm's profit (6 marks) c) We have the following information for two competitors operating in the same industry. Company A Company B Return on equity (ROE) 20% Net income JPY 25 billion JPY 16 billion Assets JPY 110 billion JPY 80 billion Sales JPY 250 billion JPY 180 billion Net interest expense JPY 10 billion JPY 8 billion Tax rate 23% 27% Use the traditional decomposed ROE approach (also known as the multiplicative ROE decomposition or DuPont ROE decomposition) to identify possible reasons for the difference in the two companies' ROE. For each component, explain possible reasons for the difference in some detail. (9 marks) d) What would be the advantage of using the alternative decomposition, in terms of RNOA (operating ROA) rather than ROA? (4 marks)







