6. CSK Auto recognizes income taxes based on pretax income.
a. What financial effects did CSK record to recognize income taxes in 2000?
b. Has CSK Auto reported more or less income to its shareholders cumulatively through February 4, 2001, than to the tax authorities? How much more or less?
7. On February 4, 2001, CSK Autos share price closed at $6.10 per share. Using the residual income valu-ation model, calculate the equity value of the company. Assume that the companys cost of equity is approximately 10.4 percent. Top management thinks the share price should be considerably higher. How would you explain the situation to management?
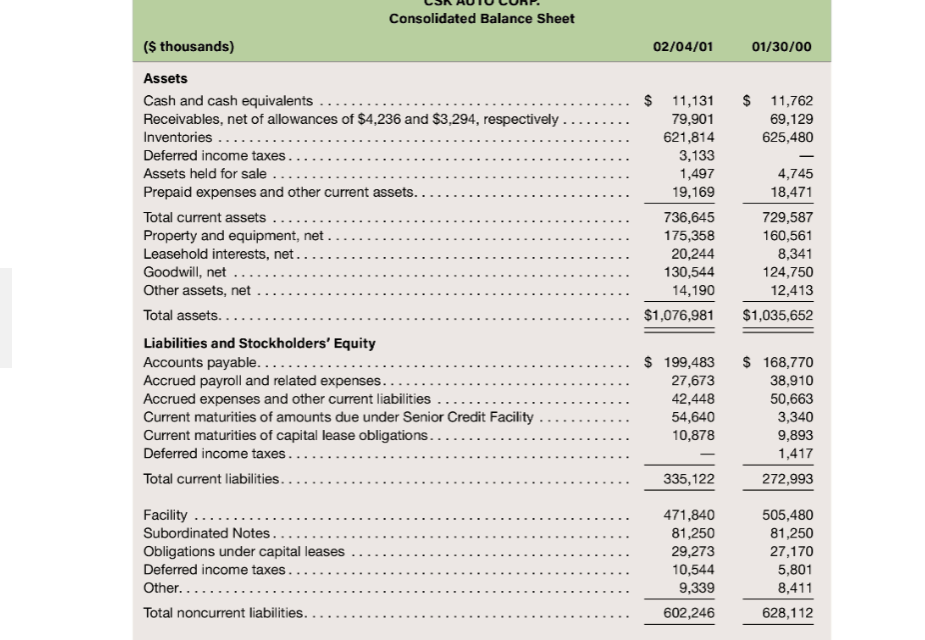
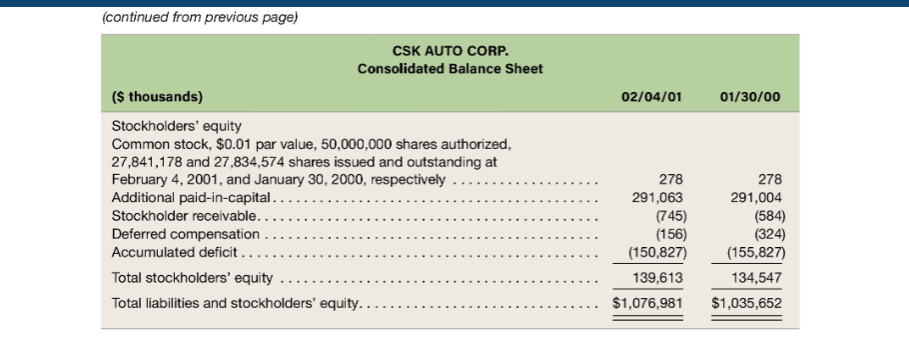
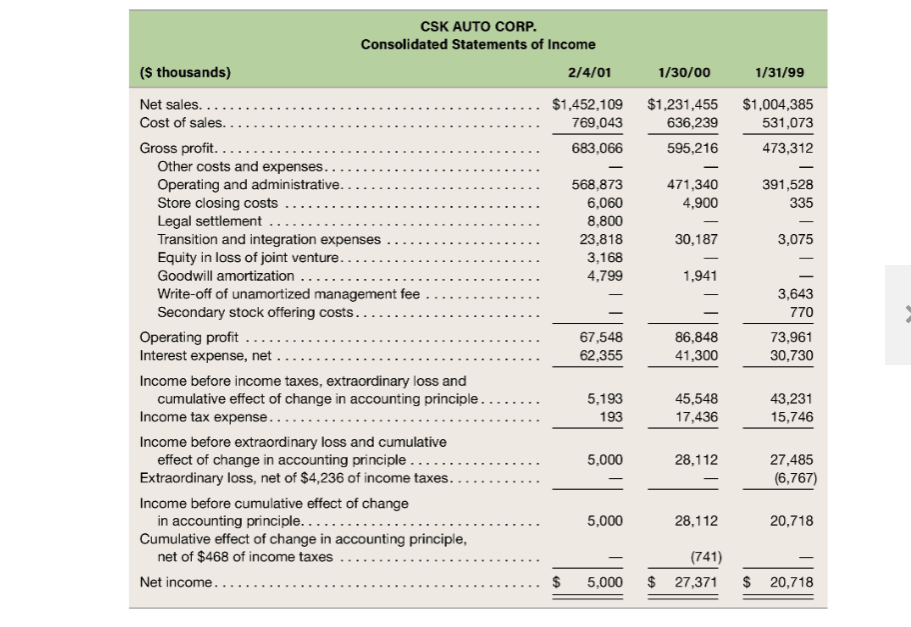
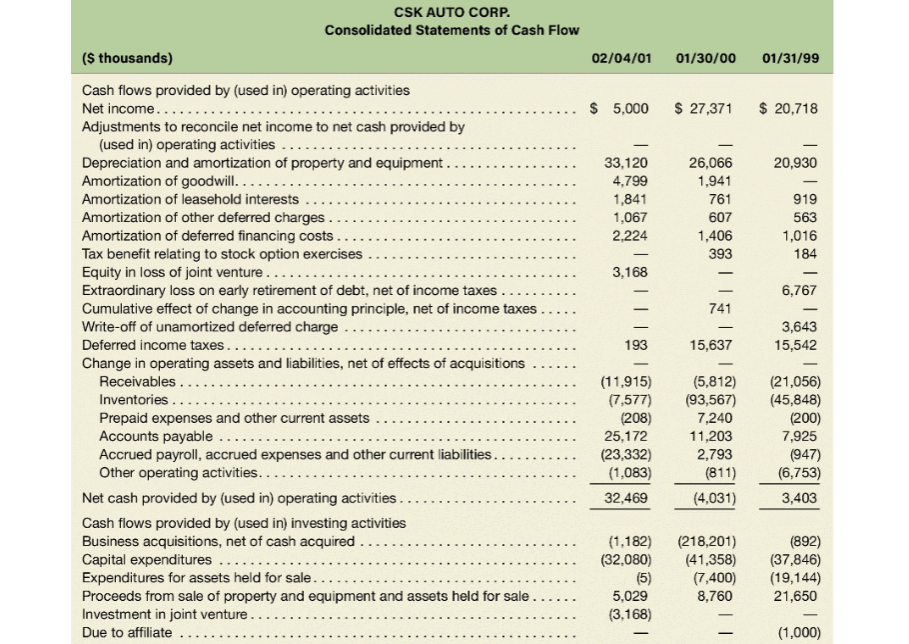
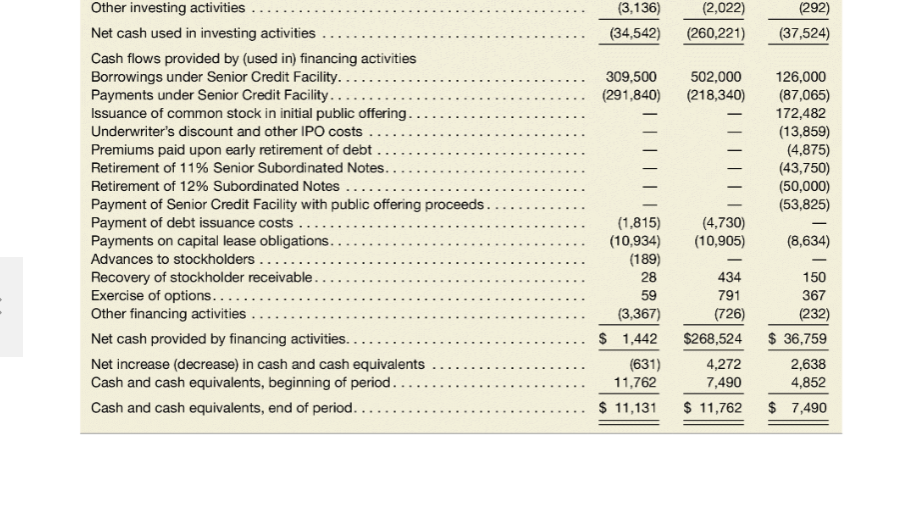
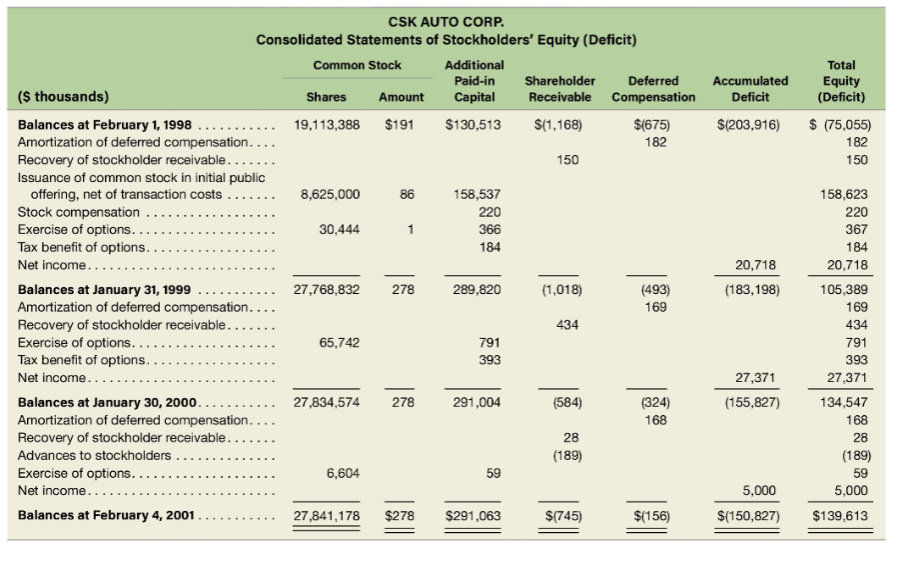
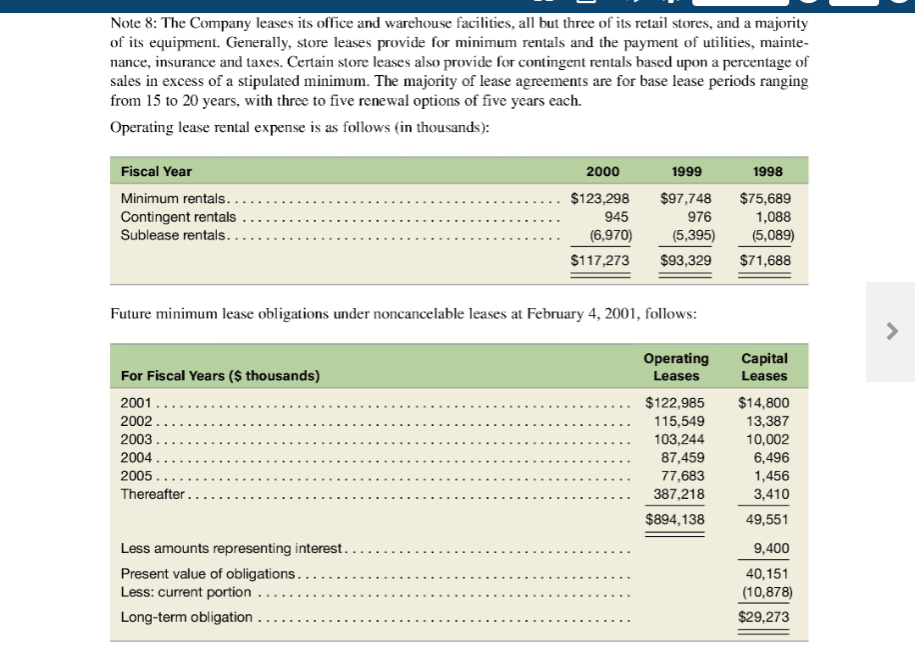
LSN HUIULUR. Consolidated Balance Sheet ($ thousands) 02/04/01 01/30/00 $ 11,762 69,129 625,480 O Sale ........ . Assets Cash and cash equivalents ..... Receivables, net of allowances of $4,236 and $3,294, respectively Inventories .. Deferred income taxes.... Assets held for sale. Prepaid expenses and other current assets. Total current assets ..... Property and equipment, net.... Leasehold interests, net........ Goodwill, net ............. Other assets, net ......... Total assets. Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Accounts payable.... Accrued payroll and related expenses Accrued expenses and other current liabilities ... Current maturities of amounts due under Senior Credit Facility Current maturities of capital lease obligations.... Deferred income taxes. Total current liabilities. $ 11,131 79,901 621,814 3,133 1,497 19,169 736,645 175,358 20,244 130,544 14,190 $1,076,981 4,745 18,471 729,587 160,561 8,341 124,750 12,413 $1,035,652 .. $ $ 199,483 27,673 42,448 54,640 10,878 168,770 38,910 50,663 3,340 9,893 1,417 272,993 335,122 Facility ........ Subordinated Notes... Obligations under capital leases ...... Deferred income taxes... Other............ Total noncurrent liabilities 471,840 81,250 29,273 10,544 9,339 602,246 505,480 81,250 27,170 5,801 8,411 628,112 (continued from previous page) CSK AUTO CORP. Consolidated Balance Sheet ($ thousands) 02/04/01 01/30/00 278 Stockholders' equity Common stock, $0.01 par value, 50,000,000 shares authorized, 27,841,178 and 27,834,574 shares issued and outstanding at February 4, 2001, and January 30, 2000, respectively ...... Additional paid-in-capital. Stockholder receivable....... Deferred compensation ..., Accumulated deficit Total stockholders' equity ... Total liabilities and stockholders' equity.. 291,063 (745) (156) (150,827) 139,613 $1,076,981 278 291,004 (584) (324) (155,827) 134,547 $1,035,652 CSK AUTO CORP. Consolidated Statements of Income 2/4/01 ($ thousands) 1/30/00 1 /31/99 $1,452,109 769,043 683,066 $1,231,455 636,239 595,216 - 471,340 4,900 $1,004,385 531,073 473,312 391,528 335 568,873 6,060 8,800 23,818 3,168 4,799 30,187 3,075 1,941 Net sales................... Cost of sales... Gross profit. ........ Other costs and expenses.... Operating and administrative.. Store closing costs ........ Legal settlement ........ Transition and integration expenses. Equity in loss of joint venture. ... Goodwill amortization .. Write-off of unamortized management fee. Secondary stock offering costs.... Operating profit .... Interest expense, net ......... Income before income taxes, extraordinary loss and cumulative effect of change in accounting principle....... Income tax expense.... Income before extraordinary loss and cumulative effect of change in accounting principle ........ Extraordinary loss, net of $4,236 of income taxes........ Income before cumulative effect of change in accounting principle....... Cumulative effect of change in accounting principle, net of $468 of income taxes .. 3,643 770 73,961 30,730 67,548 62,355 86,848 41,300 5,193 193 45,548 17,436 43,231 15,746 5,000 28,112 27,485 (6,767) 5,000 28,112 20,718 (741) 27,371 Net income......... $ 5,000 $ $ 20,718 CSK AUTO CORP. Consolidated Statements of Cash Flow (s thousands) 02/04/01 01/30/00 01/31/99 $ 5,000 $ 27,371 $ 20,718 20,930 33,120 4,799 1,841 1,067 2,224 26,066 1,941 761 607 1,406 919 563 1,016 184 393 3,168 6,767 741 15,637 3,643 15,542 Cash flows provided by (used in) operating activities Net income.......... Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by (used in) operating activities ... Depreciation and amortization of property and equipment ....... Amortization of goodwill.... Amortization of leasehold interests ................. Amortization of other deferred charges ........... Amortization of deferred financing costs ........... Tax benefit relating to stock option exercises ........... Equity in loss of joint venture........ Extraordinary loss on early retirement of debt, net of income taxes Cumulative effect of change in accounting principle, net of income taxes Write-off of unamortized deferred charge ...... Deferred income taxes..... Change in operating assets and liabilities, net of effects of acquisitions Receivables ........ Inventories ........................................ Prepaid expenses and other current assets .......... Accounts payable ....... Accrued payroll, accrued expenses and other current liabilities Other operating activities.. Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities Cash flows provided by (used in) investing activities Business acquisitions, net of cash acquired ....... Capital expenditures ....... Expenditures for assets held for sale.... Proceeds from sale of property and equipment and assets held for sale Investment in joint venture...... Due to affiliate ......... (11,915) (7,577) (208) 25,172 (23,332) (1,083) 32,469 (5,812) (93,567) 7,240 11,203 2,793 (811) (4,031) (21,056) (45,848) (200) 7,925 (947) (6,753) 3,403 (1,182) (32,080) (5) 5.029 (3,168) - (218.201) (41,358) (7,400) 8,760 (892) (37,846) (19,144) 21,650 (1,000) (3,136) (34,542) (2,022) (260,221) (292) (37,524) 309,500 (291,840) 502,000 (218,340) Other investing activities .............. Net cash used in investing activities ..... Cash flows provided by (used in) financing activities Borrowings under Senior Credit Facility. Payments under Senior Credit Facility. ...... Issuance of common stock in initial public offering ...... Underwriter's discount and other IPO costs Premiums paid upon early retirement of debt ... Retirement of 11% Senior Subordinated Notes................ Retirement of 12% Subordinated Notes. Payment of Senior Credit Facility with public offering proceeds ..... Payment of debt issuance costs. Payments on capital lease obligations ..................... Advances to stockholders Recovery of stockholder receivable..... Exercise of options...... Other financing activities .. Net cash provided by financing activities. Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of period. Cash and cash equivalents, end of period. .... 126,000 (87,065) 172,482 (13,859) (4,875) (43,750) (50,000) (53,825) - (4,730) (10,905) (8,634) (1,815) (10,934) (189) 28 59 (3,367) 1,442 (631) 11,762 $ 11,131 434 791 (726) $268,524 4,272 7,490 $ 11,762 150 367 (232) $ 36,759 2,638 4,852 $ 7,490 Note 8: The Company leases its office and warehouse facilities, all but three of its retail stores, and a majority of its equipment. Generally, store leases provide for minimum rentals and the payment of utilities, mainte- nance, insurance and taxes. Certain store leases also provide for contingent rentals based upon a percentage of sales in excess of a stipulated minimum. The majority of lease agreements are for base lease periods ranging from 15 to 20 years, with three to five renewal options of five years each. Operating lease rental expense is as follows (in thousands): Fiscal Year Minimum rentals........... Contingent rentals .............. Sublease rentals.. 2000 $123,298 945 (6,970) 1999 $97,748 9 76 (5,395) $93,329 1998 $75,689 1,088 (5,089) $71,688 Future minimum lease obligations under noncancelable leases at February 4, 2001, follows: Operating Leases Capital Leases ................ ................. For Fiscal Years ($ thousands) 2001.. 2002....... 2003..... 2004...... 2005...... Thereafter ....... $122,985 115,549 103,244 87,459 77,683 387,218 $894,138 $14,800 13,387 10,002 6,496 1,456 3,410 49,551 9,400 Less amounts representing interest Present value of obligations. Less: current portion ..... Long-term obligation .......... 40,151 (10,878) $29,273 LSN HUIULUR. Consolidated Balance Sheet ($ thousands) 02/04/01 01/30/00 $ 11,762 69,129 625,480 O Sale ........ . Assets Cash and cash equivalents ..... Receivables, net of allowances of $4,236 and $3,294, respectively Inventories .. Deferred income taxes.... Assets held for sale. Prepaid expenses and other current assets. Total current assets ..... Property and equipment, net.... Leasehold interests, net........ Goodwill, net ............. Other assets, net ......... Total assets. Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Accounts payable.... Accrued payroll and related expenses Accrued expenses and other current liabilities ... Current maturities of amounts due under Senior Credit Facility Current maturities of capital lease obligations.... Deferred income taxes. Total current liabilities. $ 11,131 79,901 621,814 3,133 1,497 19,169 736,645 175,358 20,244 130,544 14,190 $1,076,981 4,745 18,471 729,587 160,561 8,341 124,750 12,413 $1,035,652 .. $ $ 199,483 27,673 42,448 54,640 10,878 168,770 38,910 50,663 3,340 9,893 1,417 272,993 335,122 Facility ........ Subordinated Notes... Obligations under capital leases ...... Deferred income taxes... Other............ Total noncurrent liabilities 471,840 81,250 29,273 10,544 9,339 602,246 505,480 81,250 27,170 5,801 8,411 628,112 (continued from previous page) CSK AUTO CORP. Consolidated Balance Sheet ($ thousands) 02/04/01 01/30/00 278 Stockholders' equity Common stock, $0.01 par value, 50,000,000 shares authorized, 27,841,178 and 27,834,574 shares issued and outstanding at February 4, 2001, and January 30, 2000, respectively ...... Additional paid-in-capital. Stockholder receivable....... Deferred compensation ..., Accumulated deficit Total stockholders' equity ... Total liabilities and stockholders' equity.. 291,063 (745) (156) (150,827) 139,613 $1,076,981 278 291,004 (584) (324) (155,827) 134,547 $1,035,652 CSK AUTO CORP. Consolidated Statements of Income 2/4/01 ($ thousands) 1/30/00 1 /31/99 $1,452,109 769,043 683,066 $1,231,455 636,239 595,216 - 471,340 4,900 $1,004,385 531,073 473,312 391,528 335 568,873 6,060 8,800 23,818 3,168 4,799 30,187 3,075 1,941 Net sales................... Cost of sales... Gross profit. ........ Other costs and expenses.... Operating and administrative.. Store closing costs ........ Legal settlement ........ Transition and integration expenses. Equity in loss of joint venture. ... Goodwill amortization .. Write-off of unamortized management fee. Secondary stock offering costs.... Operating profit .... Interest expense, net ......... Income before income taxes, extraordinary loss and cumulative effect of change in accounting principle....... Income tax expense.... Income before extraordinary loss and cumulative effect of change in accounting principle ........ Extraordinary loss, net of $4,236 of income taxes........ Income before cumulative effect of change in accounting principle....... Cumulative effect of change in accounting principle, net of $468 of income taxes .. 3,643 770 73,961 30,730 67,548 62,355 86,848 41,300 5,193 193 45,548 17,436 43,231 15,746 5,000 28,112 27,485 (6,767) 5,000 28,112 20,718 (741) 27,371 Net income......... $ 5,000 $ $ 20,718 CSK AUTO CORP. Consolidated Statements of Cash Flow (s thousands) 02/04/01 01/30/00 01/31/99 $ 5,000 $ 27,371 $ 20,718 20,930 33,120 4,799 1,841 1,067 2,224 26,066 1,941 761 607 1,406 919 563 1,016 184 393 3,168 6,767 741 15,637 3,643 15,542 Cash flows provided by (used in) operating activities Net income.......... Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by (used in) operating activities ... Depreciation and amortization of property and equipment ....... Amortization of goodwill.... Amortization of leasehold interests ................. Amortization of other deferred charges ........... Amortization of deferred financing costs ........... Tax benefit relating to stock option exercises ........... Equity in loss of joint venture........ Extraordinary loss on early retirement of debt, net of income taxes Cumulative effect of change in accounting principle, net of income taxes Write-off of unamortized deferred charge ...... Deferred income taxes..... Change in operating assets and liabilities, net of effects of acquisitions Receivables ........ Inventories ........................................ Prepaid expenses and other current assets .......... Accounts payable ....... Accrued payroll, accrued expenses and other current liabilities Other operating activities.. Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities Cash flows provided by (used in) investing activities Business acquisitions, net of cash acquired ....... Capital expenditures ....... Expenditures for assets held for sale.... Proceeds from sale of property and equipment and assets held for sale Investment in joint venture...... Due to affiliate ......... (11,915) (7,577) (208) 25,172 (23,332) (1,083) 32,469 (5,812) (93,567) 7,240 11,203 2,793 (811) (4,031) (21,056) (45,848) (200) 7,925 (947) (6,753) 3,403 (1,182) (32,080) (5) 5.029 (3,168) - (218.201) (41,358) (7,400) 8,760 (892) (37,846) (19,144) 21,650 (1,000) (3,136) (34,542) (2,022) (260,221) (292) (37,524) 309,500 (291,840) 502,000 (218,340) Other investing activities .............. Net cash used in investing activities ..... Cash flows provided by (used in) financing activities Borrowings under Senior Credit Facility. Payments under Senior Credit Facility. ...... Issuance of common stock in initial public offering ...... Underwriter's discount and other IPO costs Premiums paid upon early retirement of debt ... Retirement of 11% Senior Subordinated Notes................ Retirement of 12% Subordinated Notes. Payment of Senior Credit Facility with public offering proceeds ..... Payment of debt issuance costs. Payments on capital lease obligations ..................... Advances to stockholders Recovery of stockholder receivable..... Exercise of options...... Other financing activities .. Net cash provided by financing activities. Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of period. Cash and cash equivalents, end of period. .... 126,000 (87,065) 172,482 (13,859) (4,875) (43,750) (50,000) (53,825) - (4,730) (10,905) (8,634) (1,815) (10,934) (189) 28 59 (3,367) 1,442 (631) 11,762 $ 11,131 434 791 (726) $268,524 4,272 7,490 $ 11,762 150 367 (232) $ 36,759 2,638 4,852 $ 7,490 Note 8: The Company leases its office and warehouse facilities, all but three of its retail stores, and a majority of its equipment. Generally, store leases provide for minimum rentals and the payment of utilities, mainte- nance, insurance and taxes. Certain store leases also provide for contingent rentals based upon a percentage of sales in excess of a stipulated minimum. The majority of lease agreements are for base lease periods ranging from 15 to 20 years, with three to five renewal options of five years each. Operating lease rental expense is as follows (in thousands): Fiscal Year Minimum rentals........... Contingent rentals .............. Sublease rentals.. 2000 $123,298 945 (6,970) 1999 $97,748 9 76 (5,395) $93,329 1998 $75,689 1,088 (5,089) $71,688 Future minimum lease obligations under noncancelable leases at February 4, 2001, follows: Operating Leases Capital Leases ................ ................. For Fiscal Years ($ thousands) 2001.. 2002....... 2003..... 2004...... 2005...... Thereafter ....... $122,985 115,549 103,244 87,459 77,683 387,218 $894,138 $14,800 13,387 10,002 6,496 1,456 3,410 49,551 9,400 Less amounts representing interest Present value of obligations. Less: current portion ..... Long-term obligation .......... 40,151 (10,878) $29,273













