
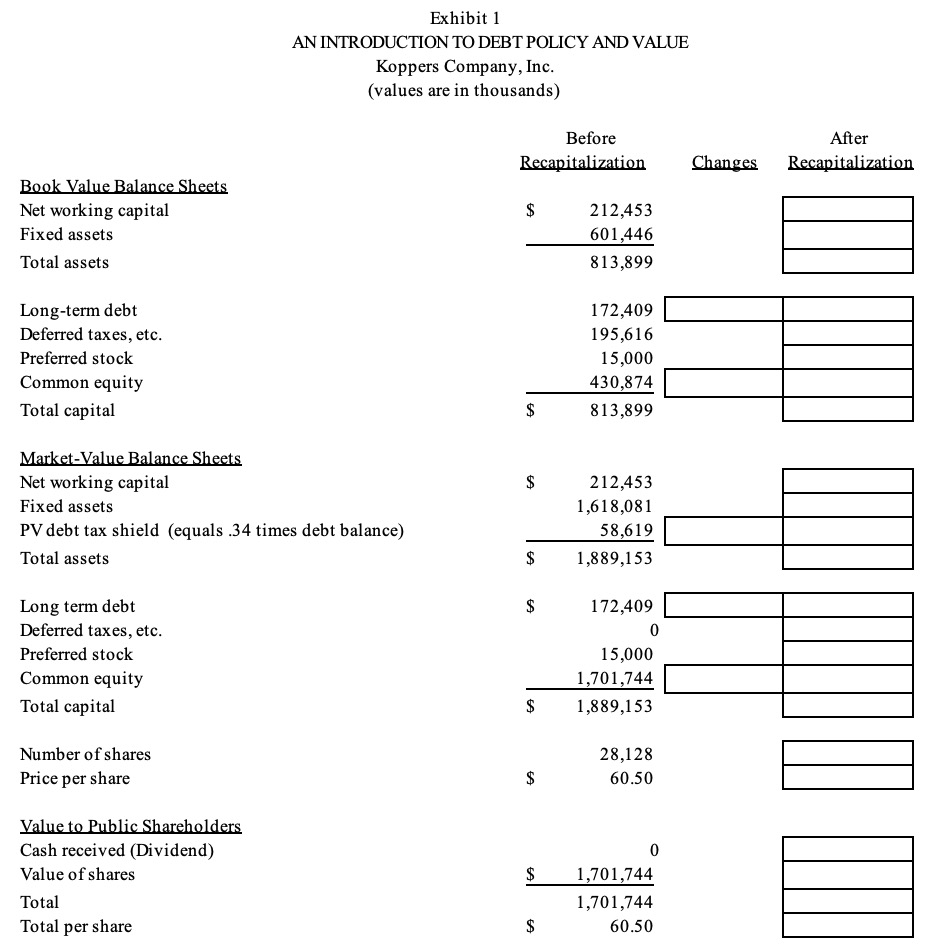
7. As a way of illustrating the usefulness of the M&M theory and consolidating your grasp of the mechanics, consider the following case and complete the work sheet. On March 3, 1988, Beazer Plc, a British construction company, and Shearson Lehman Hutton, Inc. (an investment banking firm), commenced a hostile tender offer to purchase all the outstanding stock of Koppers Company, Inc., a producer of construction materials, chemicals, and building products. Originally the raiders offered $45 per share; subsequently the offer was raised to $56, and then finally $61 per share. The Koppers board generally asserted that the offers were inadequate and its management was reviewing the possibility of a major recapitalization. To test the valuation effects of the recapitalization alternative, assume that Koppers could borrow a a maximum of $1,738,095,000 at a pretax cost of debt of 10.5 percent and that the aggregate amount of debt will remain constant in perpetuity. Thus, Koppers will take on additional debt of $1,565,686,000 (I.e., $1,738,095,000 - $172,409,000). Also assume that the proceeds of the loan would be paid as an extraordinary dividend to shareholders. Exhibit 1 presents Koppers' book- and market value balance sheets assuming the capital structure before recapitalization. Please complete the work sheet for the recapitalization alternative. Exhibit 1 AN INTRODUCTION TO DEBT POLICY AND VALUE Koppers Company, Inc. (values are in thousands) Before Recapitalization After Recapitalization Changes Book Value Balance Sheets Net working capital Fixed assets Total assets 212,453 601,446 813,899 Long-term debt Deferred taxes, etc. Preferred stock Common equity Total capital 172,409 195,616 15,000 430,874 813,899 Market Value Balance Sheets Net working capital Fixed assets PV debt tax shield (equals .34 times debt balance) Total assets 212,453 1,618,081 58,619 1,889,153 Long term debt Deferred taxes, etc. Preferred stock Common equity Total capital 172,409 0 15,000 1,701,744 1,889,153 $ Number of shares Price per share 28,128 60.50 Value to Public Shareholders Cash received (Dividend) Value of shares Total Total per share 1,701,744 1,701,744 60.50 7. As a way of illustrating the usefulness of the M&M theory and consolidating your grasp of the mechanics, consider the following case and complete the work sheet. On March 3, 1988, Beazer Plc, a British construction company, and Shearson Lehman Hutton, Inc. (an investment banking firm), commenced a hostile tender offer to purchase all the outstanding stock of Koppers Company, Inc., a producer of construction materials, chemicals, and building products. Originally the raiders offered $45 per share; subsequently the offer was raised to $56, and then finally $61 per share. The Koppers board generally asserted that the offers were inadequate and its management was reviewing the possibility of a major recapitalization. To test the valuation effects of the recapitalization alternative, assume that Koppers could borrow a a maximum of $1,738,095,000 at a pretax cost of debt of 10.5 percent and that the aggregate amount of debt will remain constant in perpetuity. Thus, Koppers will take on additional debt of $1,565,686,000 (I.e., $1,738,095,000 - $172,409,000). Also assume that the proceeds of the loan would be paid as an extraordinary dividend to shareholders. Exhibit 1 presents Koppers' book- and market value balance sheets assuming the capital structure before recapitalization. Please complete the work sheet for the recapitalization alternative. Exhibit 1 AN INTRODUCTION TO DEBT POLICY AND VALUE Koppers Company, Inc. (values are in thousands) Before Recapitalization After Recapitalization Changes Book Value Balance Sheets Net working capital Fixed assets Total assets 212,453 601,446 813,899 Long-term debt Deferred taxes, etc. Preferred stock Common equity Total capital 172,409 195,616 15,000 430,874 813,899 Market Value Balance Sheets Net working capital Fixed assets PV debt tax shield (equals .34 times debt balance) Total assets 212,453 1,618,081 58,619 1,889,153 Long term debt Deferred taxes, etc. Preferred stock Common equity Total capital 172,409 0 15,000 1,701,744 1,889,153 $ Number of shares Price per share 28,128 60.50 Value to Public Shareholders Cash received (Dividend) Value of shares Total Total per share 1,701,744 1,701,744 60.50








